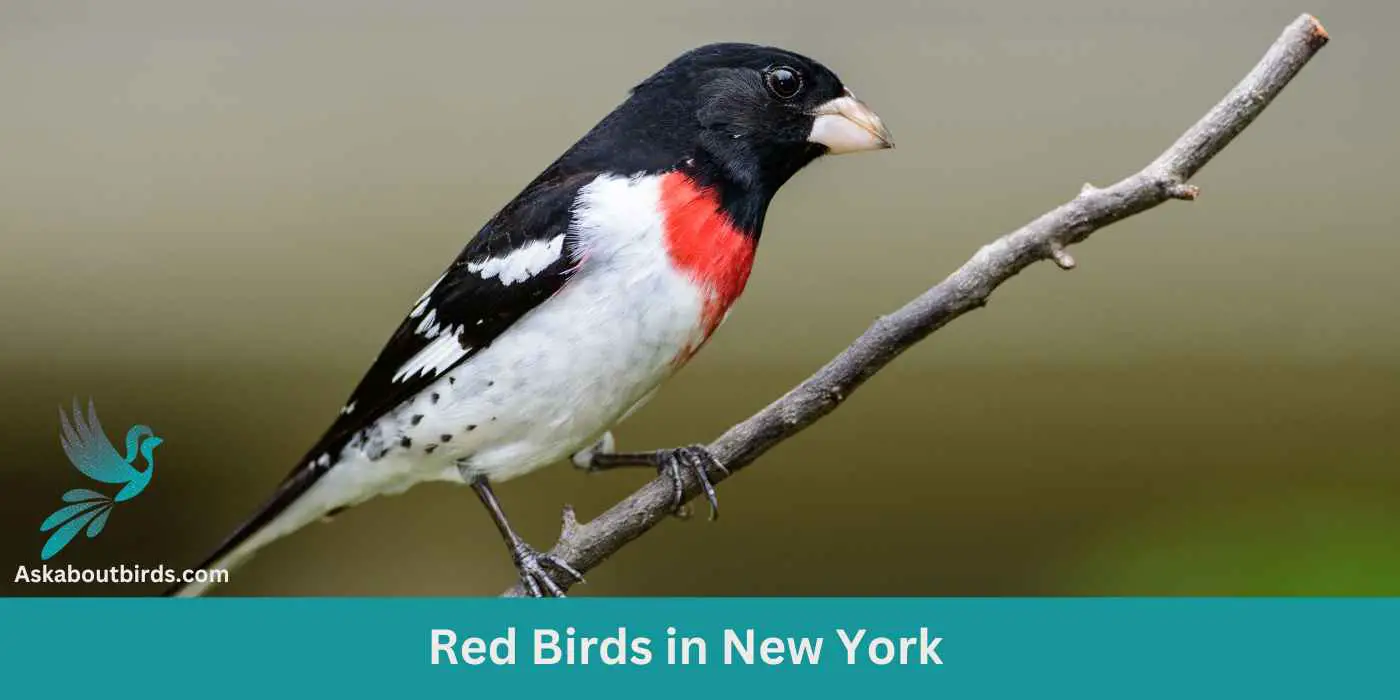
New York, renowned for its iconic skyline and bustling streets, is also a treasure trove for nature enthusiasts, hiding vibrant hues in its green spaces and forests. Beyond the city that never sleeps lies a world teeming with avian wonders.
Our comprehensive photo guide invites you to explore and appreciate the 11 resplendent red birds that call the Empire State home. Dive in and let New York’s natural charm captivate you!
Red Birds Found In New York
The vast geographical tapestry of New York provides a habitat kaleidoscope, inviting a rich avian diversity. The state boasts the rugged Adirondack Mountains, fertile Hudson Valley, expansive freshwater lakes, and dense urban parks like Central Park.
This mix of altitude variances, freshwater sources, and green refuges in metropolitan areas offers year-round habitats and migratory stops.
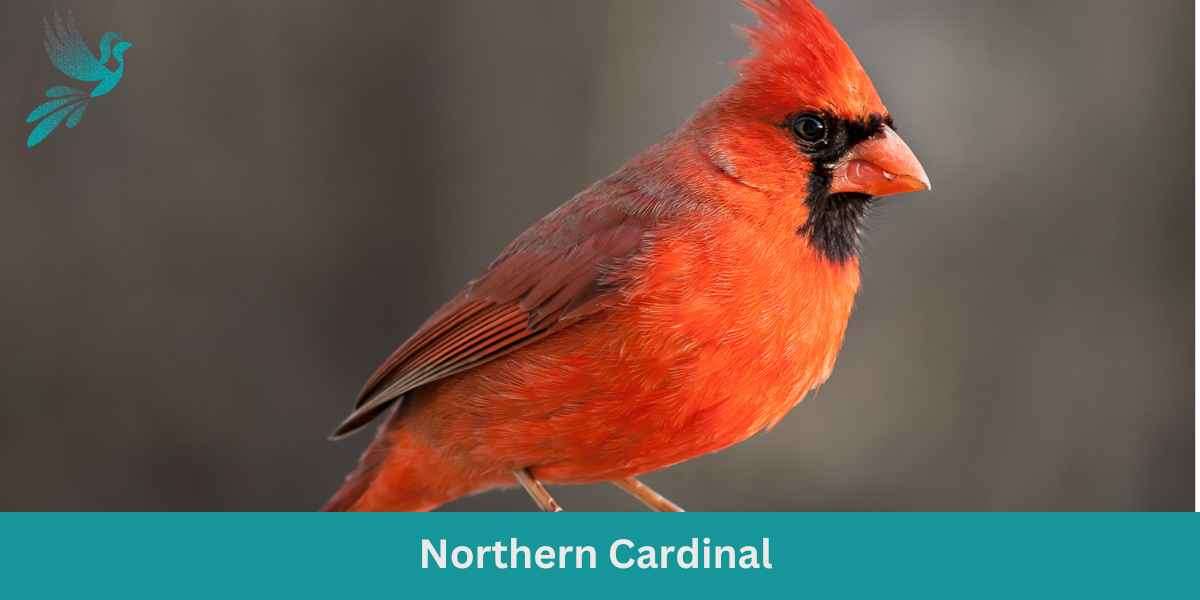
Northern Cardinal

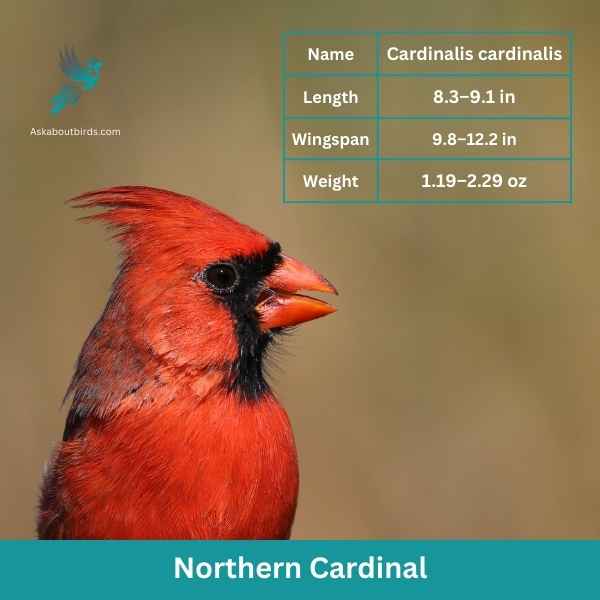
| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cardinalis cardinalis |
| Length | 8.3 – 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 – 12.2 in |
| Weight | 1.19 – 2.29 oz |
The Northern Cardinal is an iconic North American bird, easily recognized by its vibrant color and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Northern Cardinals are a brilliant scarlet red, while females display a more subdued reddish olive. Both sexes have a distinctive black ‘mask’ on their face around the bill and a pointed crest on their head. The bird’s beak is robust, cone-shaped, and bright orange in color.
Diet: Northern Cardinals are primarily granivorous, with a diet largely consisting of seeds and grains. They also eat fruits and insects. These birds typically feed off the ground and are frequent visitors to bird feeders.
Reproduction: Northern Cardinals are monogamous, and a pair will breed together for life. The female typically builds a well-hidden nest in a dense thicket or shrub. She lays 2-5 eggs per clutch, which she incubates for around two weeks.
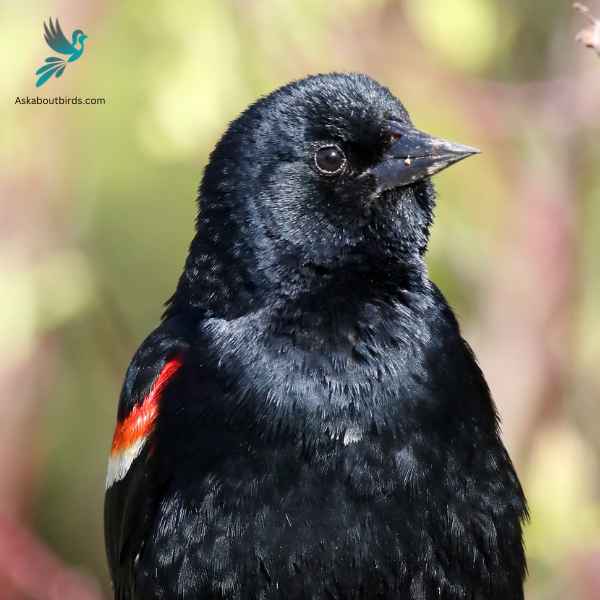
Red-Winged Blackbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Agelaius phoeniceus |
| Length | 6.7-9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 12.2-15.7 in |
| Weight | 41.5-65 g |
The Red-Winged Blackbird is a familiar sight across North America, especially in wetlands and open areas. Known for its striking coloration and distinct call, it is often seen perched on cattails or utility lines.
Appearance: Male Red-Winged Blackbirds are glossy black with bright red-and-yellow shoulder patches, while females are streaky brown, resembling a large sparrow. The males’ red patches become more prominent when they’re displaying or agitated.
Diet: Red-Winged Blackbirds primarily feed on seeds and insects. Their diet includes grains, sunflower seeds, and corn, but they also eat beetles, caterpillars, and other small invertebrates, especially in the breeding season.
Reproduction: Red-Winged Blackbirds nest in marshes, along watercourses, and in wet fields. The female constructs a cup-shaped nest using grass and sedge, attaching it to plants above water. She typically lays a clutch of 3 to 4 blue-green eggs, which she incubates for about 11-12 days. Males, being polygynous, often have multiple mates during a single breeding season.
Scarlet Tanager

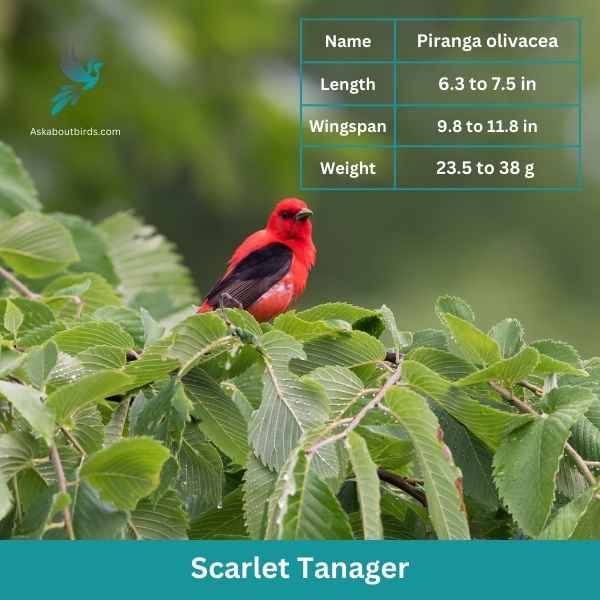
| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga olivacea |
| Length | 6.3 to 7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 to 11.8 in |
| Weight | 23.5 to 38 g |
The Scarlet Tanager is a strikingly colorful bird known for its brilliant plumage and distinctive song.
Appearance: Male Scarlet Tanagers are notable for their vibrant scarlet bodies contrasted with black wings and tail, making them one of the most intensely colored birds. Females and juveniles, on the other hand, have a subdued olive-yellow body color with darker wings and tail.
Diet: The diet of the Scarlet Tanager is largely made up of insects, including beetles, cicadas, aphids, and others. They are adept flycatchers, seizing insects in mid-air or picking them off foliage. They also consume fruits and berries, especially during migration and in their winter habitats.
Reproduction: The female Scarlet Tanager builds a cup-shaped nest using twigs, rootlets, and grass, typically well-hidden in the dense foliage of trees. She lays 3 to 5 eggs and incubates them for about two weeks.
House Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous mexicanus |
| Length | 5–6 in |
| Wingspan | 8–10 in |
| Weight | 0.6–0.9 oz |
The House Finch is a small songbird widely distributed across North America and is commonly found in urban and suburban areas.
Appearance: Males of this species are brightly colored with crimson faces and throats, which can extend to the chest and back, while their flanks have streaks. The female is streaked brown and lacks the red coloring. Both have a square-tipped tail and a distinctively long, flat-topped bill.
Diet: House Finches primarily eat seeds, grains, and berries. They have a particular fondness for sunflower seeds and can be commonly seen at bird feeders. Occasionally, they will also consume insects, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: House Finches are cavity-nesters and might choose ledges, vents, ledges, and other urban settings. They might also utilize trees or shrubs. Their nests can be made of a wide array of materials, from feathers to twigs.
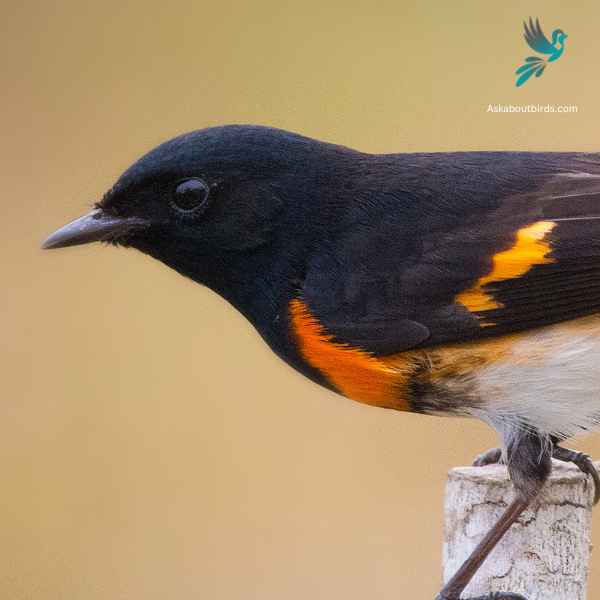
American Redstart
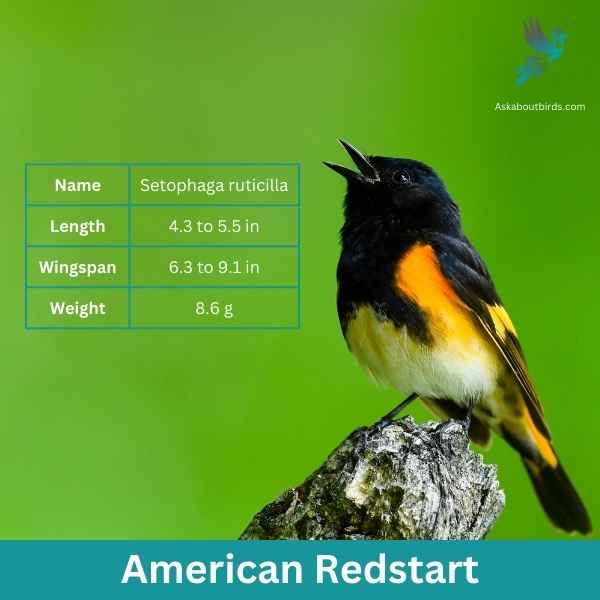

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
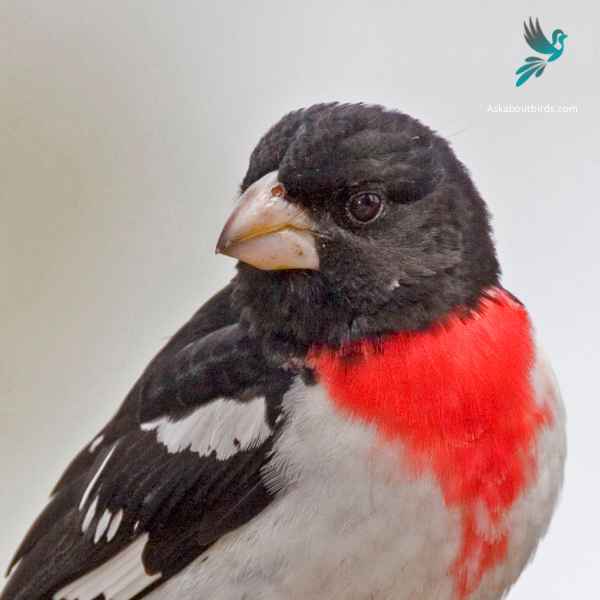
Rose-breasted Grosbeak


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pheucticus ludovicianus |
| Length | 7.5-8.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.5-13 in |
| Weight | 1.2-1.7 oz |
The Rose-breasted Grosbeak is a songbird of medium size, widely recognized for its vibrant coloration and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Rose-breasted Grosbeaks boast a striking contrast with black and white plumage accompanied by a radiant rose-colored patch on the chest and under the wings. In contrast, females exhibit streaked brown and white plumage, resembling large sparrows but with a thick bill.
Diet: The diet of the Rose-breasted Grosbeak consists of a mixture of seeds, insects, and fruits. During summer, they primarily feed on insects, while seeds and fruits become more prevalent in their diet during the colder months.
Reproduction: These birds build cup-shaped nests typically situated in trees or large shrubs. Both the male and female partake in incubation duties, ensuring the eggs’ safety and warmth. After hatching, the chicks are primarily fed insects.
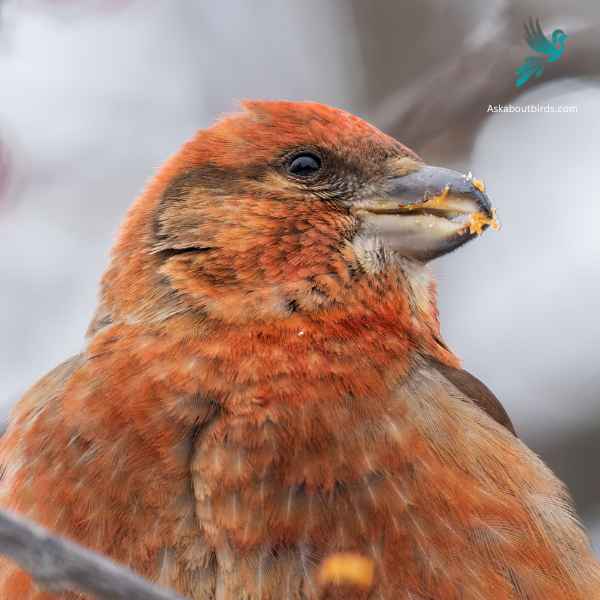
Red Crossbill


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Loxia curvirostra |
| Length | 5.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8–10.6 in |
| Weight | 0.9–1.4 oz |
The Red Crossbill is a distinctive finch known for its unusual bill, which has evolved to extract seeds from conifer cones.
Appearance: Males are typically bright red or orange, while females are greenish-yellow or olive. Both genders have the characteristic crossed bill, which they use to expertly extract seeds from tightly closed conifer cones.
Diet: Red Crossbills primarily feed on the seeds of coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir. Their specialized bills allow them to efficiently pry apart conifer cone scales to access the seeds.
Reproduction: Red Crossbills are somewhat nomadic and don’t adhere to a strict breeding schedule. Instead, they breed whenever and wherever food is abundant. Their nests are usually built on horizontal branches of conifer trees.
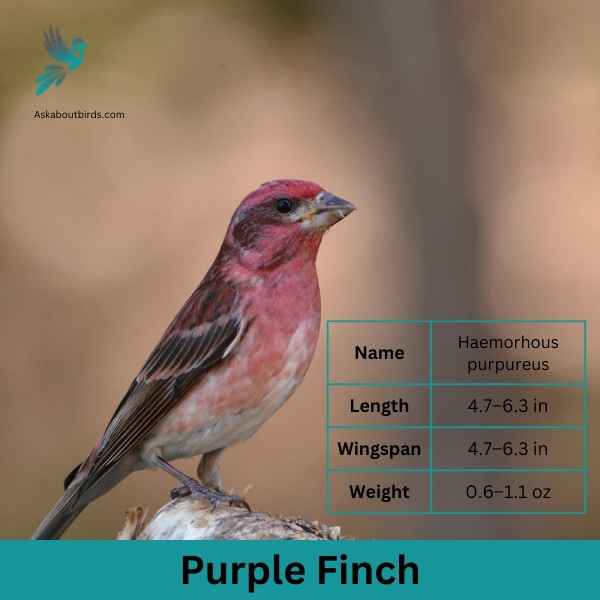
Purple Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous purpureus |
| Length | 4.7–6.3 in |
| Wingspan | 4.7–6.3 in |
| Weight | 0.6–1.1 oz |
The Purple Finch is a vibrant songbird often mistaken for its close relative, the House Finch, but it exhibits a different hue and patterns.
Appearance: Males are raspberry red on the head, throat, and breast, with streaky brown backs and wings. The intensity of the red can vary among individuals. Females are brown and streaked all over but might show a slight blush on the face. They lack the strong facial patterns seen in female House Finches.
Diet: Purple Finches primarily consume seeds, with a preference for sunflower seeds, dandelion seeds, and buds. They also eat insects and berries, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: These finches often nest in conifers or mixed woodlands. The nest, typically located on a horizontal branch, is made from twigs and grass, then lined with feathers.
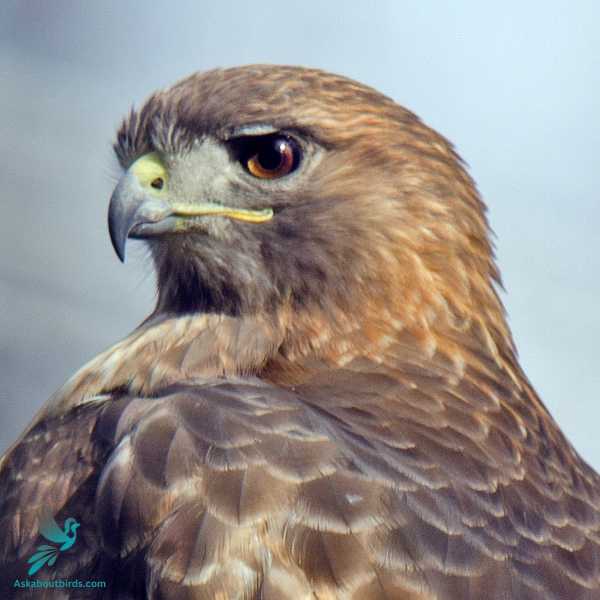
Red-Tailed Hawk


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Buteo jamaicensis |
| Length | 45–65 cm (18–26 in) |
| Wingspan | 110–141 cm (3 ft 7 in – 4 ft 8 in) |
| Weight | 690 to 1,600 g (1.5 to 3.5 lb) |
The Red-Tailed Hawk is a bird of prey that is commonly found across North America. This adaptable raptor is known for its brick-red tail, which is most noticeable in adults from above or underneath. The diet of the Red-Tailed Hawk is very diverse, including small mammals like mice and squirrels, as well as birds and reptiles.
This hawk is often seen perched on poles or soaring in wide circles high above fields, forests, and highways. Its habitat is extremely varied, ranging from desert and scrublands to forests and tropical rainforests. Its call, a raspy, screaming kee-eeeee-arr, is often used in movies to represent any bird of prey.
Red-bellied Woodpecker
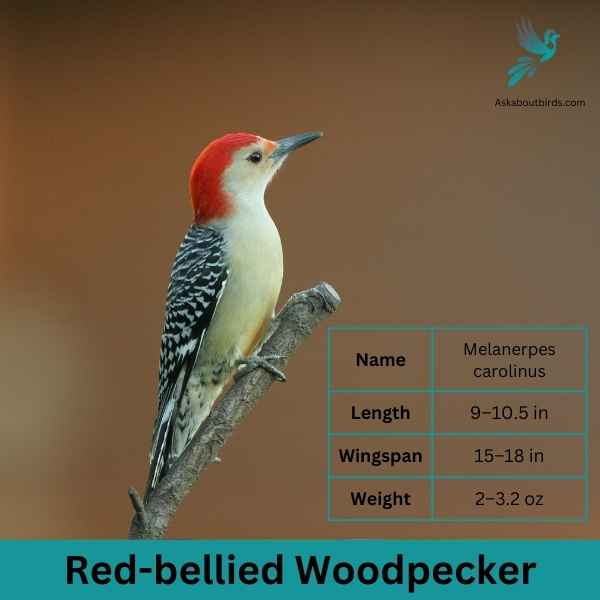

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Thryothorus ludovicianus |
| Length | 4.7–5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 11 in |
| Weight | 0.63–0.81 oz |
The Red-bellied Woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker commonly found in woodlands, forests, and backyards across the eastern and central U.S.
Appearance: The Red-bellied Woodpecker sports a pale gray face, throat, and belly, contrasted by a zebra-striped back. Its name derives from the subtle reddish tinge on its belly, but it’s more commonly recognized by the vivid red cap on the head of males and the partial red cap on females.
Diet: This woodpecker has a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, nuts, and seeds. They frequently forage on tree trunks and branches, using their sticky, barbed-tipped tongue to extract ants, beetles, and other insects from crevices.
Reproduction: Red-bellied Woodpeckers are cavity nesters, excavating holes in tree trunks for their nests. The inside of the nest is typically unlined or sparingly lined with wood chips.
Red-headed Woodpecker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Melanerpes erythrocephalus |
| Length | 7.5–9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 16.5 in |
| Weight | 2.0–3.2 oz |
The Red-headed Woodpecker is a striking forest bird with a bold tri-colored pattern.
Appearance: This woodpecker features a completely red head and neck, contrasting starkly with its white underparts and black wings. Its wings also have large white patches which are conspicuous in flight.
Diet: Red-headed Woodpeckers have a varied diet including insects, seeds, fruits, berries, and occasionally even the eggs of other birds. They’re also known to store food by wedging it into crevices in bark.
Reproduction: These woodpeckers nest in cavities which they excavate in dead wood or dead parts of live trees. These cavities can be found anywhere from 2 to 80 feet off the ground.
Where to Spot New York’s Red Birds
New York’s diverse landscapes serve as a backdrop for some of the most rewarding birdwatching locales in the nation. Here are the top destinations to witness its vibrant red avian residents and more:
- Central Park, New York City: An urban oasis, this iconic park is a hotspot for migratory birds, especially during the spring and fall. Its varied habitats attract a wide array of species, from warblers to tanagers.
- Montezuma National Wildlife Refuge: Nestled at the northern tip of Cayuga Lake, this refuge boasts marshes and wetlands that draw waterfowl, shorebirds, and songbirds, making it a birdwatcher’s dream year-round.
- Shawangunk Grasslands National Wildlife Refuge: Formerly an airfield, this refuge in the Hudson Valley is a prime location for grassland birds. Its open fields are perfect for spotting red-tailed hawks and northern harriers.
- Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge: Located in Queens, this coastal habitat is a haven for both migratory and resident birds. The salt marshes and mudflats are particularly attractive to wading birds and shorebirds.
- Adirondack Park: As the largest publicly protected area in the contiguous U.S., the Adirondacks offer diverse habitats from alpine meadows to dense forests. Here, bird enthusiasts can spot the American three-toed woodpecker, boreal chickadee, and other unique species.
| State’s Red Birds | Best Spots for Red Birds |
|---|---|
| New Jersey’s Red birds | 1. Great Swamp National Wildlife Refuge 2. Cape May Point State Park 3. Island Beach State Park |
| Pennsylvania’s Red birds | 1. Hawk Mountain Sanctuary 2. Presque Isle State Park 3. John Heinz National Wildlife Refuge at Tinicum |
| Vermont’s Red birds | 1. Dead Creek Wildlife Area 2. Green Mountain National Forest 3. Missisquoi National Wildlife Refuge |
| Connecticut’s Red birds | 1. Hammonasset Beach State Park 2. White Memorial Conservation Center 3. Shepaug Dam Bald Eagle Observation Area |
| Massachusetts’ Red birds | 1. Parker River National Wildlife Refuge 2. Plum Island 3. Quabbin Reservoir |
FAQs on Red Bird Species Found in New York
Why are black oil sunflower seeds popular in backyard bird feeders?
Black oil sunflower seeds have become a staple in backyard bird feeders across both northern and western states as well as southern and eastern states. The seeds, rich in nutrients, are favored by a plethora of birds, from the striking red birds with bright red plumage to the very common red birds. The painted bunting, a tiny bird native to Central and South America, is especially attracted to these seeds, showcasing its bright red feathers and dark gray wings with two white wing bars when visiting backyard feeders.
What distinct features can help in bird identification of the painted bunting?
The painted bunting, frequently spotted in Central and South America, stands out among bright red birds due to its distinctive features. Adult males exhibit bright red plumage contrasted with dark gray wings adorned with two white wing bars. These tiny birds, when compared to the more common house finch with its brown streaked coloring or the American robin’s rosy red coloring, easily grab attention, making bird identification an engaging task for enthusiasts.
How does the painted bunting’s habitat differ from other red birds?
The painted bunting primarily inhabits open woodlands and forest canopy regions in Central and South America. While American robins or the more common house finch might be found in various habitats across the northern and western states, the painted bunting’s preference leans towards forested regions, making them a unique sight in the southern and eastern states.
What distinguishes the painted bunting from other bright red birds found in the Americas?
The painted bunting, primarily found in Central and South America, holds a distinct allure among the bright red birds of the region. These tiny birds have bright red plumage, especially notable in adult males. This contrasts with the more common house finch, which displays brown streaked coloring, or the American robin with its rosy red coloring. The painted bunting’s dark gray wings with two white wing bars further set it apart. A remarkable feature is its association with backyard feeders; offering black oil sunflower seeds at a bird feeding station can attract this vibrant species, making bird identification an enchanting experience for enthusiasts.




