Iowa’s skies and woodlands are adorned with a stunning array of avian wonders. Among them, the orange-feathered birds stand out, adding a splash of vibrant color to the landscape. From the melodious calls of the Baltimore Oriole to the striking presence of the Red-headed Woodpecker, these orange-hued beauties are a testament to the state’s rich biodiversity.
In this post, we’ll delve into the world of 9 iconic orange birds that grace the skies of Iowa. Whether you’re an avid birder or just starting your ornithological journey, these birds promise a visual treat!
Orange Birds Found In Iowa
Iowa’s diverse landscape of prairies, forests, and wetlands serves as a birdwatcher’s paradise, drawing a colorful spectrum of avian species.
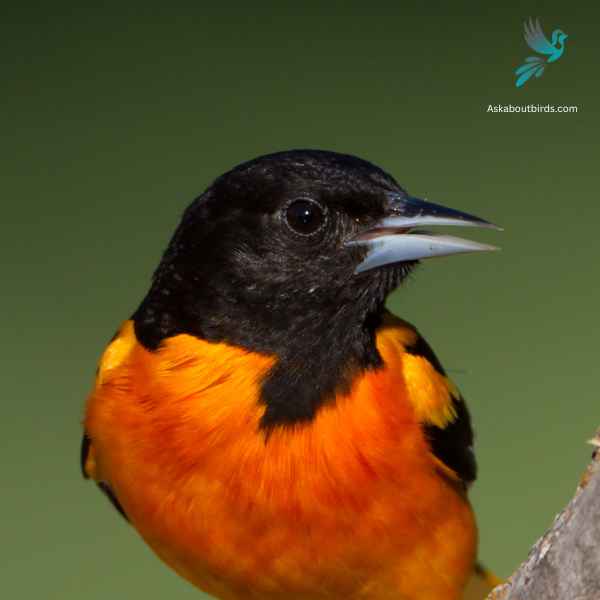
Baltimore Oriole


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus galbula |
| Length | 6.7–8.7 in |
| Wingspan | 9.1–12.6 in |
| Weight | 22.3-42 g |
The Baltimore Oriole is a stunning bird, best known for its vibrant coloration and its rich, whistling song.
Appearance: The male Baltimore Oriole is notable for his bright orange and black plumage and black and white wing bars, a stark contrast to the more muted yellow-brown coloration of the female. Both sexes, however, have long pointed bills and white bars on their wings.
Diet: Baltimore Orioles have a diverse diet that includes insects, fruits, and nectar. Their preference for sweet juices and fruit pulp often brings them to backyard feeders offering oranges and jelly.
Reproduction: The female Baltimore Oriole is responsible for building the distinctive hanging nest, often woven together from fine materials like hair and grass. These nests are usually high in trees to avoid predators. The female lays 3-7 eggs, which are incubated for about two weeks.
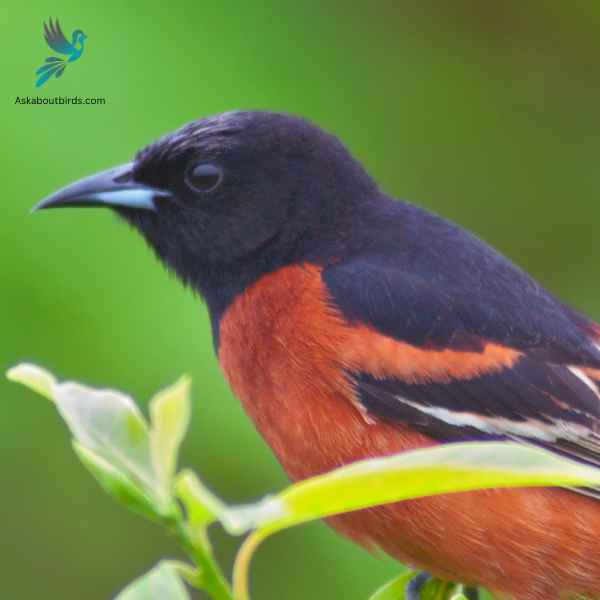
Orchard Oriole
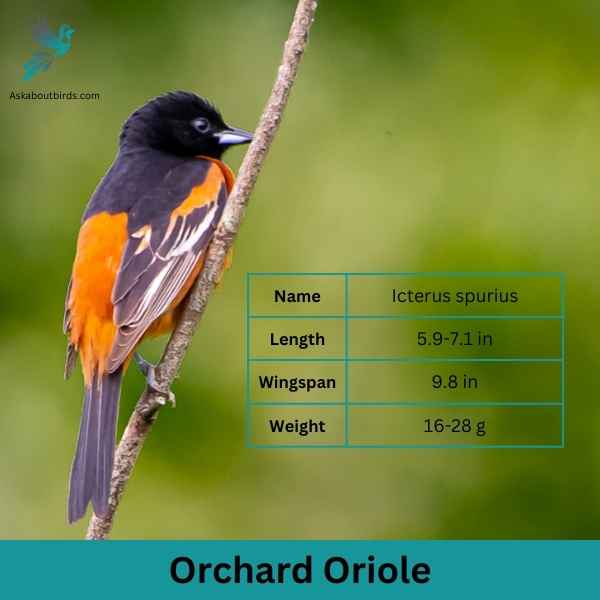

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus spurius |
| Length | 5.9-7.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 in |
| Weight | 16-28 g |
The Orchard Oriole is a small songbird noted for its distinctive coloration and melodic song.
Appearance: Male Orchard Orioles are a striking sight with their dark chestnut body and black head and black and white wings, while females and immature males are olive-green and feature a yellowish underpart. The species is often recognized by its slender body and pointed bill.
Diet: The diet of the Orchard Oriole consists primarily of insects, fruits, and nectar. They are adept at catching insects mid-air and are also known to sip nectar from flowers, aiding in pollination. When fruits are in season, they make up a substantial portion of the bird’s diet.
Reproduction: Orchard Orioles often nest in open woodlands and orchards, hence their name. The female is responsible for building the nest, typically choosing a location in a tree or shrub. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates for about two weeks.
Scarlet Tanager

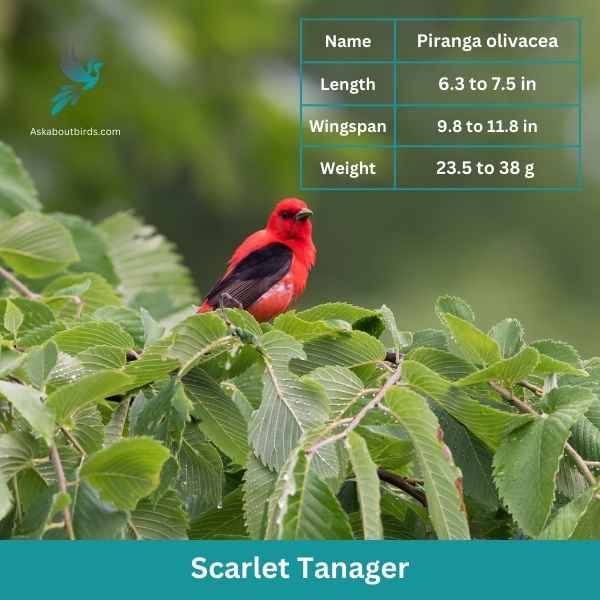
| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga olivacea |
| Length | 6.3 to 7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 to 11.8 in |
| Weight | 23.5 to 38 g |
The Scarlet Tanager is a strikingly colorful bird known for its brilliant plumage and distinctive song.
Appearance: Male Scarlet Tanagers are notable for their vibrant scarlet bodies contrasted with black wings and tail, making them one of the most intensely colored birds. Females and juveniles, on the other hand, have a subdued olive-yellow body color with darker wings and tail.
Diet: The diet of the Scarlet Tanager is largely made up of insects, including beetles, cicadas, aphids, and others. They are adept flycatchers, seizing insects in mid-air or picking them off foliage. They also consume fruits and berries, especially during migration and in their winter habitats.
Reproduction: The female Scarlet Tanager builds a cup-shaped nest using twigs, rootlets, and grass, typically well-hidden in the dense foliage of trees. She lays 3 to 5 eggs and incubates them for about two weeks.
Northern Flicker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Colaptes auratus |
| Length | 11–12 in |
| Wingspan | 17–20 in |
| Weight | 3.9–5.6 oz |
The Northern Flicker is a medium-sized woodpecker, recognized by its unique patterns and coloring, often found drumming on trees or foraging on the ground across North America.
Appearance: The Northern Flicker stands out with its grayish brown body, black-scalloped plumage, and a black bib. Males sport a distinctive black or red mustache stripe. Depending on the subspecies, the underwing and undertail feathers can be bright yellow or red, flashing vividly during flight.
Diet: While most woodpeckers are tree-bark foragers, the Northern Flicker prefers hunting on the ground. Its primary diet consists of ants and beetles, supplemented occasionally by fruits, berries, seeds, and other small insects.
Reproduction: Northern Flickers are cavity nesters, preferring to excavate their nesting hole in dead or diseased tree trunks. The interior of the nest is lined with wood chips.
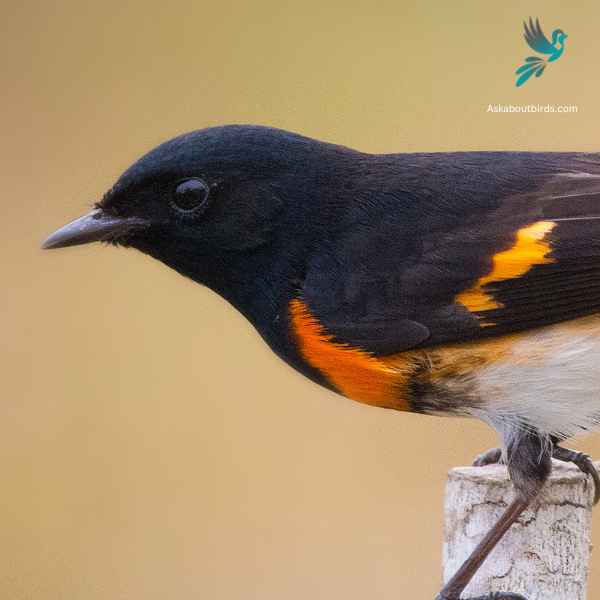
American Redstart
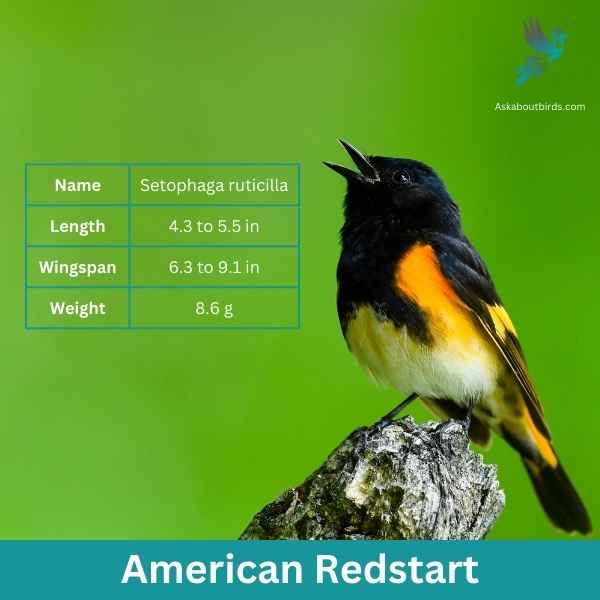

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
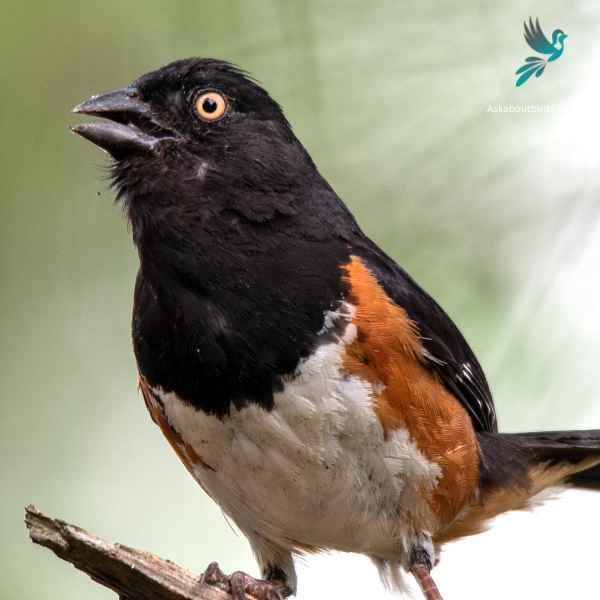
Eastern Towhee
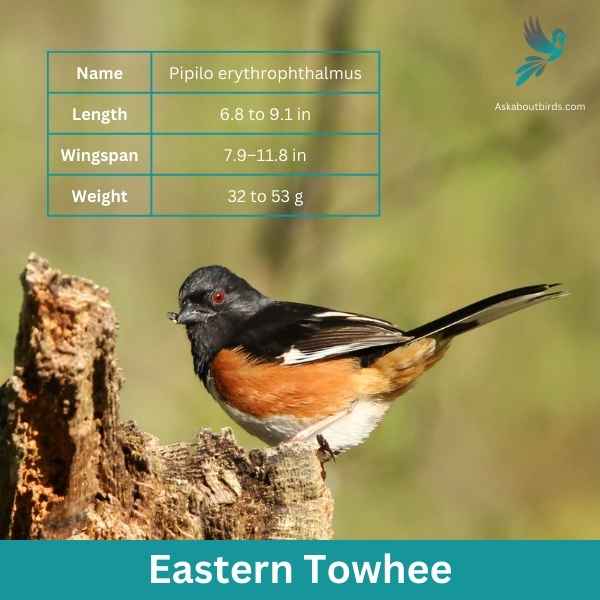

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo erythrophthalmus |
| Length | 6.8 to 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9–11.8 in |
| Weight | 32 to 53 g |
The Eastern Towhee is a distinctive songbird known for its unique calls and eye-catching coloration.
Appearance: Male Eastern Towhees are characterized by a striking combination of a black head, back and tail, contrasting with a white belly and rufous flanks. Females sport similar patterns but instead of black, they have a rich brown color. Both genders have red eyes, lending a special charm to their overall appearance.
Diet: Eastern Towhees primarily feed on a variety of insects, seeds, and berries. Their diet is quite diverse, taking advantage of seasonal offerings, which includes beetles, caterpillars, spiders, acorns, grass seeds, and various fruits and berries.
Reproduction: Eastern Towhees build their nests on or near the ground, often in a shrub or a small tree. The female lays around 3-5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubating them over about 12-13 days.
Red-headed Woodpecker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Melanerpes erythrocephalus |
| Length | 7.5–9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 16.5 in |
| Weight | 2.0–3.2 oz |
The Red-headed Woodpecker is a striking forest bird with a bold tri-colored pattern.
Appearance: This woodpecker features a completely red head and neck, contrasting starkly with its white underparts and black wings. Its wings also have large white patches which are conspicuous in flight.
Diet: Red-headed Woodpeckers have a varied diet including insects, seeds, fruits, berries, and occasionally even the eggs of other birds. They’re also known to store food by wedging it into crevices in bark.
Reproduction: These woodpeckers nest in cavities which they excavate in dead wood or dead parts of live trees. These cavities can be found anywhere from 2 to 80 feet off the ground.
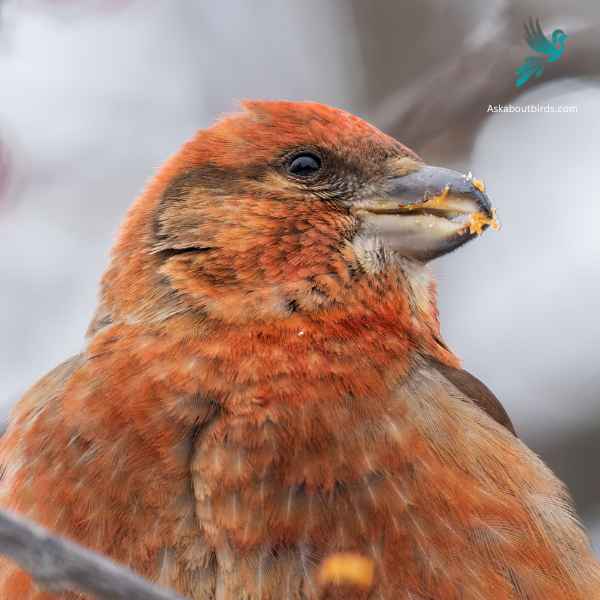
Red Crossbill


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Loxia curvirostra |
| Length | 5.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8–10.6 in |
| Weight | 0.9–1.4 oz |
The Red Crossbill is a distinctive finch known for its unusual bill, which has evolved to extract seeds from conifer cones.
Appearance: Males are typically bright red or orange, while females are greenish-yellow or olive. Both genders have the characteristic crossed bill, which they use to expertly extract seeds from tightly closed conifer cones.
Diet: Red Crossbills primarily feed on the seeds of coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir. Their specialized bills allow them to efficiently pry apart conifer cone scales to access the seeds.
Reproduction: Red Crossbills are somewhat nomadic and don’t adhere to a strict breeding schedule. Instead, they breed whenever and wherever food is abundant. Their nests are usually built on horizontal branches of conifer trees.
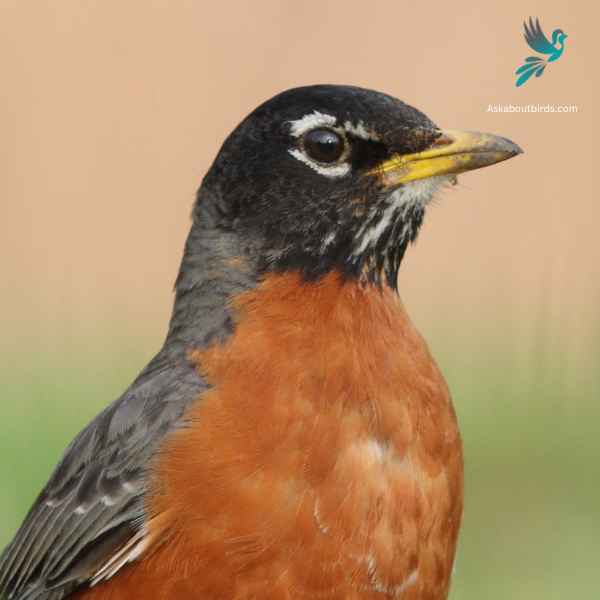
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
Where to Spot Iowa’s Orange Birds
Iowa, with its varied terrains, is a birdwatching haven, and over the years, I’ve discovered some hidden gems teeming with avian life. Here are some of the top locations that every bird enthusiast should consider:
- Neal Smith National Wildlife Refuge: A sprawling prairie landscape dedicated to native ecosystem restoration. It’s an excellent spot for sighting grassland birds and, of course, our orange-feathered friends.
- Mississippi River Flyway: Stretching along Iowa’s eastern border, this migratory route is a hotspot during migration seasons, with numerous waterfowl and songbirds passing through.
- Loess Hills State Forest: Nestled in western Iowa, its unique loess soil formations support a mix of forest and prairie habitats, drawing a wide variety of bird species.
- Rathbun Lake: This large reservoir in southern Iowa attracts a vast number of waterfowl and shorebirds, making it a must-visit for bird enthusiasts.
- Big Hollow Recreation Area: A peaceful retreat in southeast Iowa, its mix of woodlands, prairie, and a sizable lake draws a diverse group of birds year-round.
| State’s Orange Birds | Best Spots for Orange Birds |
|---|---|
| Minnesota’s Orange Birds | Agassiz National Wildlife Refuge, Tamarac National Wildlife Refuge, Sax-Zim Bog |
| Wisconsin’s Orange Birds | Horicon Marsh, Apostle Islands National Lakeshore, Crex Meadows Wildlife Area |
| Illinois’s Orange Birds | Montrose Point Bird Sanctuary, Starved Rock State Park, Illinois Beach State Park |
| Missouri’s Orange Birds | Squaw Creek National Wildlife Refuge, Mingo National Wildlife Refuge, Shaw Nature Reserve |
| Nebraska’s Orange Birds | Sandhills Journey Scenic Byway, Fort Niobrara National Wildlife Refuge, Rowes Sanctuary |
| South Dakota’s Orange Birds | Bear Butte State Park, Badlands National Park, Custer State Park |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in Iowa
Which birds with bright orange plumage are native to Iowa?
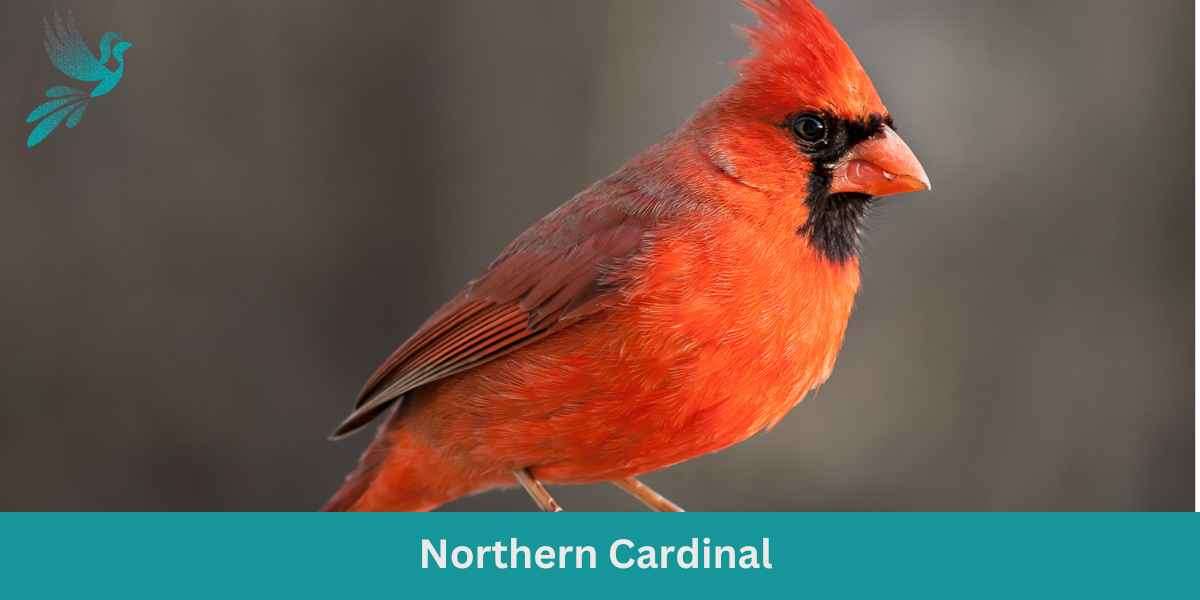
Iowa is home to several birds with bright orange plumage. Notable among them are the Hooded Oriole and the Northern Cardinal. The male Hooded Oriole is recognized for its orange body contrasted by a black mask and hood. Meanwhile, the male Northern Cardinal boasts a vibrant red-orange hue throughout its body. These birds can often be spotted in deciduous trees and at the edges of mixed forests.
How can I attract orange birds to my backyard in Iowa?
To bring these common backyard birds into your Iowa backyard, consider setting up a bird feeder filled with sunflower seeds, which are favored by many bird species. For the Hooded Oriole, you can also provide oriole feeders filled with grape jelly or orange slices to visit bird feeders. Hummingbird feeders with sugar water may attract some birds with tints of red or orange in their plumage. Creating a bird-friendly environment with deciduous trees and native plants further supports these species and offers them nesting and feeding grounds. During the breeding season in Iowa, many birds display bright orange patches and distinct white wing bars, making them a vibrant spectacle for birdwatchers.
When is the best time to spot these orange birds in Iowa?
Many of these bright-feathered birds, such as the Northern Cardinal, are year-round residents of Iowa and can be observed throughout the year. However, migratory birds like the Hooded Oriole and Yellow Warbler (a yellow bird with a bright yellow throat) are more prominent during the spring and summer months. Bird watchers can have a rewarding experience during these times, especially at forest edges and in areas with deciduous trees.




