Welcome to the delightful journey of exploring the world of avians in our guide, “10 Orange Birds in Delaware.” In this vibrant corner of the world, between its coastal beauty and rich forests, Delaware is a haven for a variety of bird species.
This guide is dedicated to introducing you to the top 10 orange birds that grace the skies of Delaware. These fiery feathered inhabitants are a sight to behold and are sure to add a splash of color to your birdwatching experience.
Get ready to dive in and discover the unique characteristics, behaviors, and habitats of these magnificent creatures.
Orange Birds Found In Delaware
Straddling the Atlantic coastline and encompassing lush forests, verdant wetlands, and sprawling farmlands, Delaware offers a rich mosaic of habitats, attracting an impressive variety of birds, including an array of vibrant orange species.
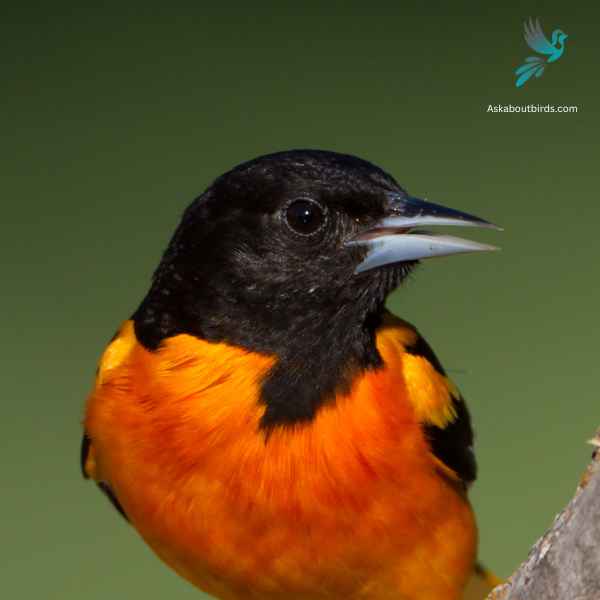
Baltimore Oriole


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus galbula |
| Length | 6.7–8.7 in |
| Wingspan | 9.1–12.6 in |
| Weight | 22.3-42 g |
The Baltimore Oriole is a stunning bird, best known for its vibrant coloration and its rich, whistling song.
Appearance: The male Baltimore Oriole is notable for his bright orange and black plumage and black and white wing bars, a stark contrast to the more muted yellow-brown coloration of the female. Both sexes, however, have long pointed bills and white bars on their wings.
Diet: Baltimore Orioles have a diverse diet that includes insects, fruits, and nectar. Their preference for sweet juices and fruit pulp often brings them to backyard feeders offering oranges and jelly.
Reproduction: The female Baltimore Oriole is responsible for building the distinctive hanging nest, often woven together from fine materials like hair and grass. These nests are usually high in trees to avoid predators. The female lays 3-7 eggs, which are incubated for about two weeks.
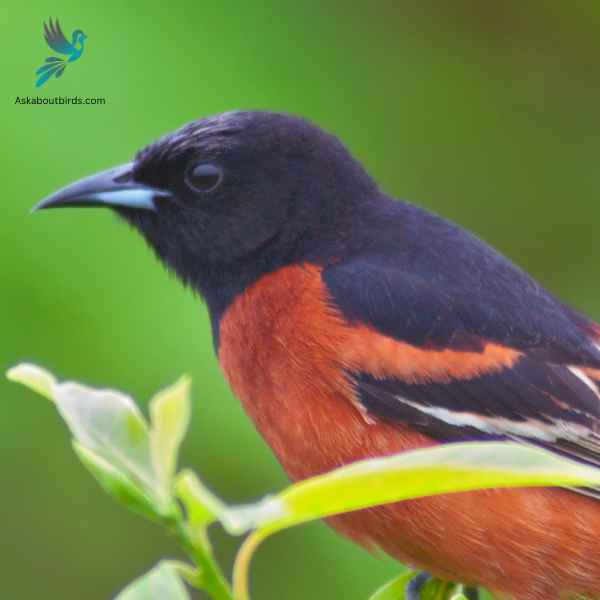
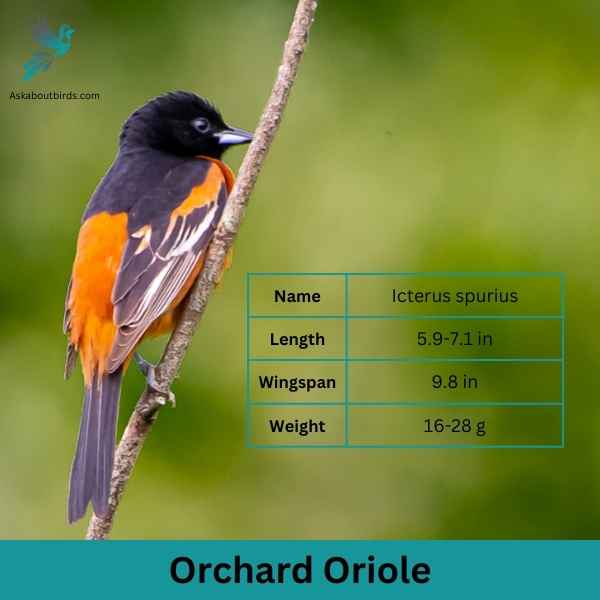
Orchard Oriole

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus spurius |
| Length | 5.9-7.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 in |
| Weight | 16-28 g |
The Orchard Oriole is a small songbird noted for its distinctive coloration and melodic song.
Appearance: Male Orchard Orioles are a striking sight with their dark chestnut body and black head and black and white wings, while females and immature males are olive-green and feature a yellowish underpart. The species is often recognized by its slender body and pointed bill.
Diet: The diet of the Orchard Oriole consists primarily of insects, fruits, and nectar. They are adept at catching insects mid-air and are also known to sip nectar from flowers, aiding in pollination. When fruits are in season, they make up a substantial portion of the bird’s diet.
Reproduction: Orchard Orioles often nest in open woodlands and orchards, hence their name. The female is responsible for building the nest, typically choosing a location in a tree or shrub. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates for about two weeks.
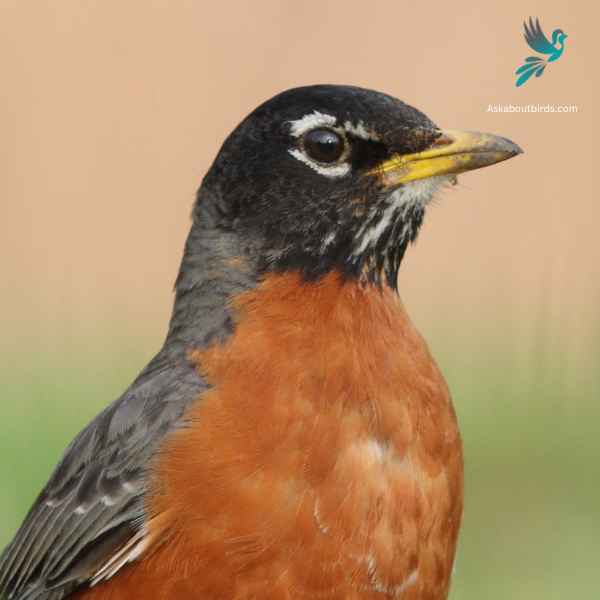
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
House Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous mexicanus |
| Length | 5–6 in |
| Wingspan | 8–10 in |
| Weight | 0.6–0.9 oz |
The House Finch is a small songbird widely distributed across North America and is commonly found in urban and suburban areas.
Appearance: Males of this species are brightly colored with crimson faces and throats, which can extend to the chest and back, while their flanks have streaks. The female is streaked brown and lacks the red coloring. Both have a square-tipped tail and a distinctively long, flat-topped bill.
Diet: House Finches primarily eat seeds, grains, and berries. They have a particular fondness for sunflower seeds and can be commonly seen at bird feeders. Occasionally, they will also consume insects, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: House Finches are cavity-nesters and might choose ledges, vents, ledges, and other urban settings. They might also utilize trees or shrubs. Their nests can be made of a wide array of materials, from feathers to twigs.
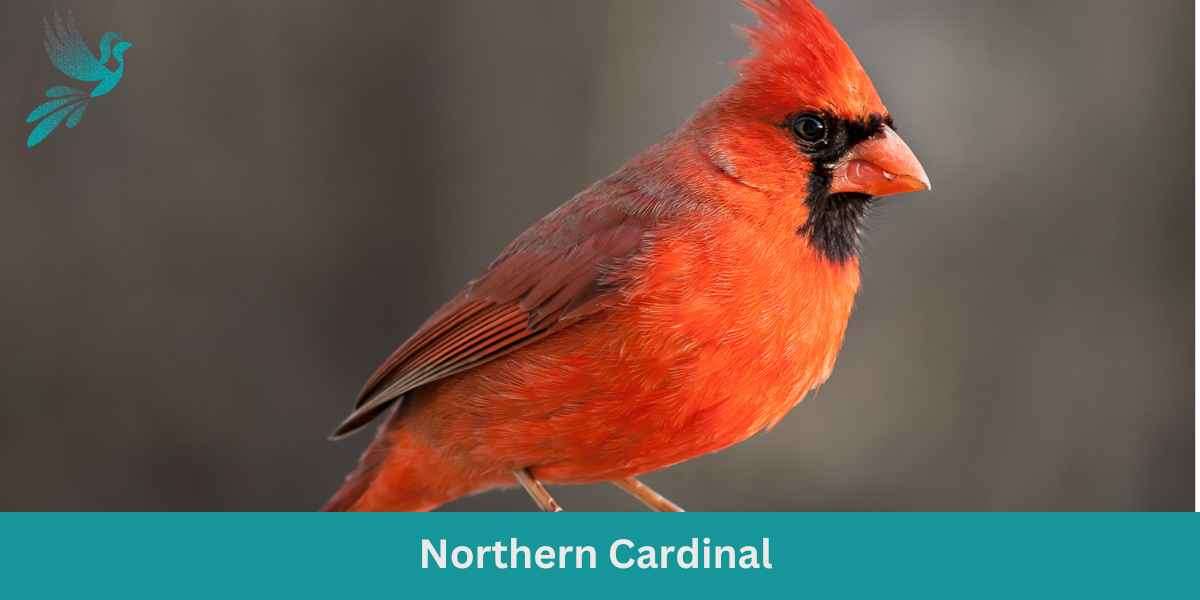
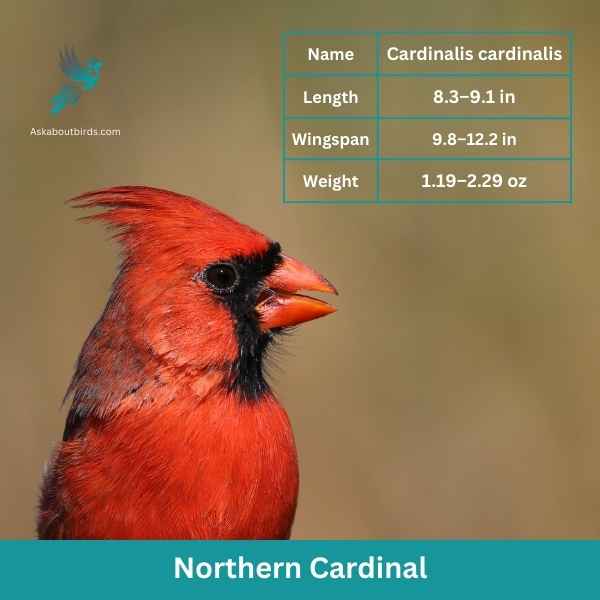
Northern Cardinal

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cardinalis cardinalis |
| Length | 8.3 – 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 – 12.2 in |
| Weight | 1.19 – 2.29 oz |
The Northern Cardinal is an iconic North American bird, easily recognized by its vibrant color and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Northern Cardinals are a brilliant scarlet red, while females display a more subdued reddish olive. Both sexes have a distinctive black ‘mask’ on their face around the bill and a pointed crest on their head. The bird’s beak is robust, cone-shaped, and bright orange in color.
Diet: Northern Cardinals are primarily granivorous, with a diet largely consisting of seeds and grains. They also eat fruits and insects. These birds typically feed off the ground and are frequent visitors to bird feeders.
Reproduction: Northern Cardinals are monogamous, and a pair will breed together for life. The female typically builds a well-hidden nest in a dense thicket or shrub. She lays 2-5 eggs per clutch, which she incubates for around two weeks.
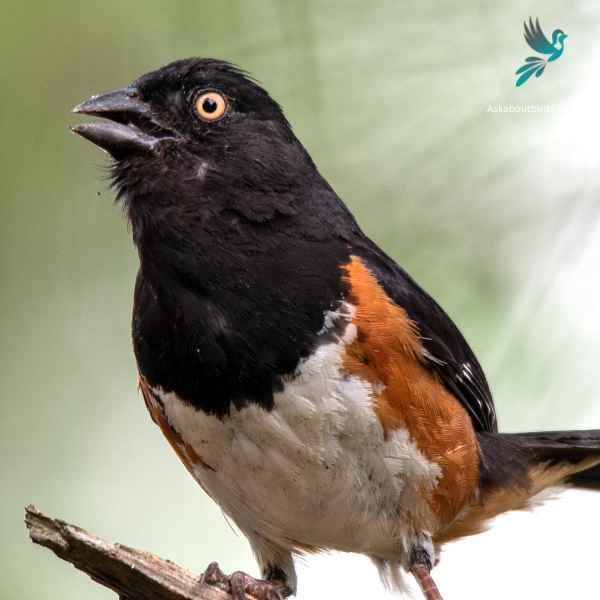
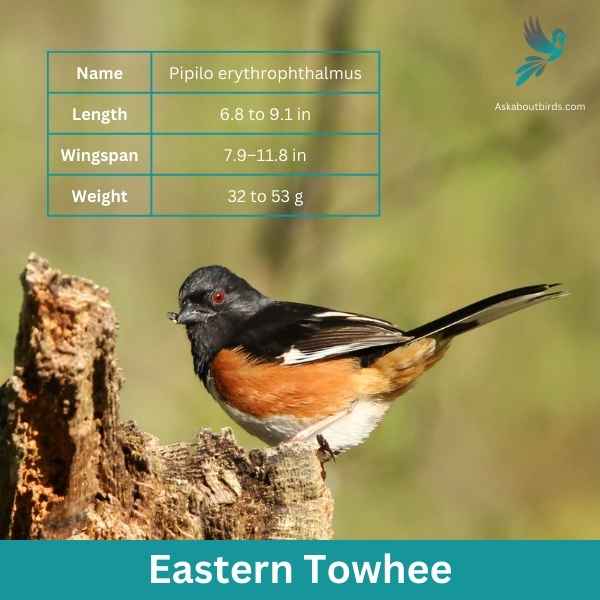
Eastern Towhee

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo erythrophthalmus |
| Length | 6.8 to 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9–11.8 in |
| Weight | 32 to 53 g |
The Eastern Towhee is a distinctive songbird known for its unique calls and eye-catching coloration.
Appearance: Male Eastern Towhees are characterized by a striking combination of a black head, back and tail, contrasting with a white belly and rufous flanks. Females sport similar patterns but instead of black, they have a rich brown color. Both genders have red eyes, lending a special charm to their overall appearance.
Diet: Eastern Towhees primarily feed on a variety of insects, seeds, and berries. Their diet is quite diverse, taking advantage of seasonal offerings, which includes beetles, caterpillars, spiders, acorns, grass seeds, and various fruits and berries.
Reproduction: Eastern Towhees build their nests on or near the ground, often in a shrub or a small tree. The female lays around 3-5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubating them over about 12-13 days.
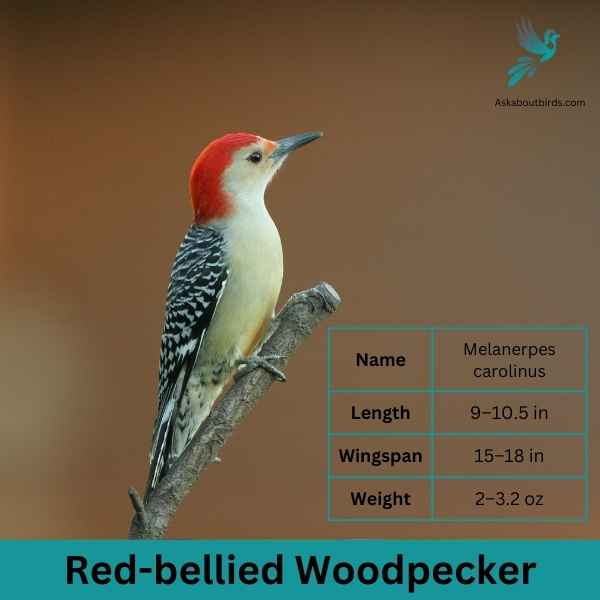
Red-bellied Woodpecker

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Thryothorus ludovicianus |
| Length | 4.7–5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 11 in |
| Weight | 0.63–0.81 oz |
The Red-bellied Woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker commonly found in woodlands, forests, and backyards across the eastern and central U.S.
Appearance: The Red-bellied Woodpecker sports a pale gray face, throat, and belly, contrasted by a zebra-striped back. Its name derives from the subtle reddish tinge on its belly, but it’s more commonly recognized by the vivid red cap on the head of males and the partial red cap on females.
Diet: This woodpecker has a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, nuts, and seeds. They frequently forage on tree trunks and branches, using their sticky, barbed-tipped tongue to extract ants, beetles, and other insects from crevices.
Reproduction: Red-bellied Woodpeckers are cavity nesters, excavating holes in tree trunks for their nests. The inside of the nest is typically unlined or sparingly lined with wood chips.
Northern Flicker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Colaptes auratus |
| Length | 11–12 in |
| Wingspan | 17–20 in |
| Weight | 3.9–5.6 oz |
The Northern Flicker is a medium-sized woodpecker, recognized by its unique patterns and coloring, often found drumming on trees or foraging on the ground across North America.
Appearance: The Northern Flicker stands out with its grayish brown body, black-scalloped plumage, and a black bib. Males sport a distinctive black or red mustache stripe. Depending on the subspecies, the underwing and undertail feathers can be bright yellow or red, flashing vividly during flight.
Diet: While most woodpeckers are tree-bark foragers, the Northern Flicker prefers hunting on the ground. Its primary diet consists of ants and beetles, supplemented occasionally by fruits, berries, seeds, and other small insects.
Reproduction: Northern Flickers are cavity nesters, preferring to excavate their nesting hole in dead or diseased tree trunks. The interior of the nest is lined with wood chips.
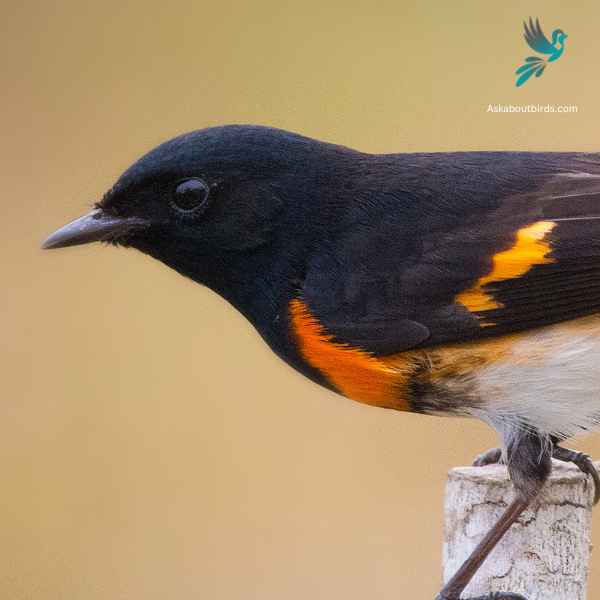
American Redstart
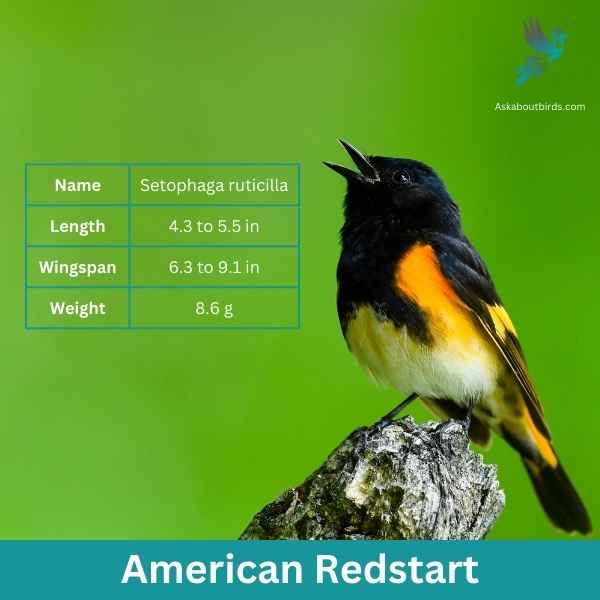

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
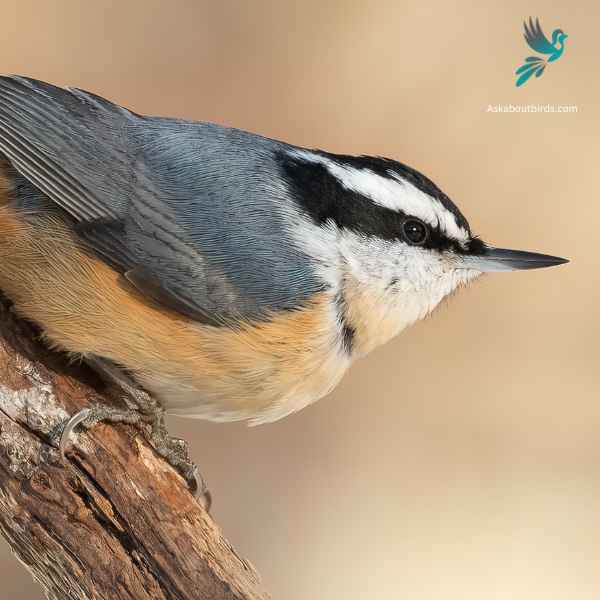
Red-breasted Nuthatch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sitta canadensis |
| Length | 4.3–4.7 in |
| Wingspan | 8.3 in |
| Weight | 0.3–0.5 oz |
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, agile songbird, known for its ability to move headfirst down tree trunks while searching for food.
Appearance: This bird boasts a slate-blue back and a pale rust-red underside. A prominent black stripe runs through the eye and is bordered above by a white eyebrow. Their sharp, pointed bill is characteristic of the species.
Diet: Red-breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds, especially those from coniferous trees. They have a fondness for large seeds, which they wedge into bark crevices to hack open with their bills.
Reproduction: These birds construct nests in natural tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker holes, often lining the entrance with resin. This is thought to deter predators or competitors from entering. The female typically lays a clutch of 5 to 6 eggs, and both parents partake in feeding the chicks once they hatch.
Where to Spot Delaware’s Orange Birds
Delaware, with its diverse habitats spanning from coastal beaches to inland forests, provides numerous locations for bird enthusiasts to spot a wide array of species, especially the vibrant orange birds. Here are some of the top birding hotspots in the state that every birder should have on their list:
- Bombay Hook National Wildlife Refuge: Located on the coast of Delaware Bay, this refuge is a magnet for migrating birds and birdwatchers alike. Its extensive wetlands and tidal salt marshes attract a variety of orange bird species, especially during migration seasons.
- Prime Hook National Wildlife Refuge: Another fantastic birding location on Delaware’s coast. It hosts a wide variety of habitats, including salt marshes, freshwater marshes, ponds, and forests, making it a paradise for diverse bird species, including our highlighted orange birds.
- Brandywine Creek State Park: Nestled in the rolling hills of northern Delaware, the park offers 933 acres of fields, mature hardwood forests, and freshwater streams. These diverse habitats attract a plethora of bird species, providing excellent opportunities for spotting orange avians throughout the year.
- Cape Henlopen State Park: Known for its coastal habitats and woodland areas, this state park is another fantastic birding spot. During the migratory season, birders can spot an array of bird species, including the vivid orange ones.
- Delaware Seashore State Park: Spanning over six miles of ocean and bay shoreline, this park is a premier location for waterfowl and shorebird viewing. Its diversity of habitats ensures a rewarding birdwatching experience, including the chance to see some stunning orange birds.
| State’s Orange Birds | Best spots to see a wide range of orange birds |
|---|---|
| Pennsylvania’s Orange Birds | John Heinz National Wildlife Refuge at Tinicum, Hawk Mountain Sanctuary, Presque Isle State Park |
| New Jersey’s Orange Birds | Cape May Point State Park, Great Swamp National Wildlife Refuge, Island Beach State Park |
| Maryland’s Orange Birds | Assateague Island National Seashore, Catoctin Mountain Park, Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in Delaware
What kind is the orange bird?
The term “orange bird” often refers to various bird species that display bright orange patches on their plumage. Many of these birds, such as the Yellow warbler, though primarily yellow, can exhibit bright yellow throats that might appear orange under certain lighting conditions, especially when observed in deciduous forests.
What bird is brown with orange underbelly?
Birds that have a brown appearance with an “orange” or bright yellow underbelly are often warblers. The Yellow-throated warbler, for instance, features a blend of brown or black wings with white wing bars and distinctive bright yellow throats or underbelly, commonly seen in deciduous forests.Identifying yellow birds, such as these yellow birds or yellow warblers, can be fascinating, especially when noting species like the yellow-rumped warblers and the pine warbler with its yellow-green hue, which are winter birds commonly found in Central and South America.




