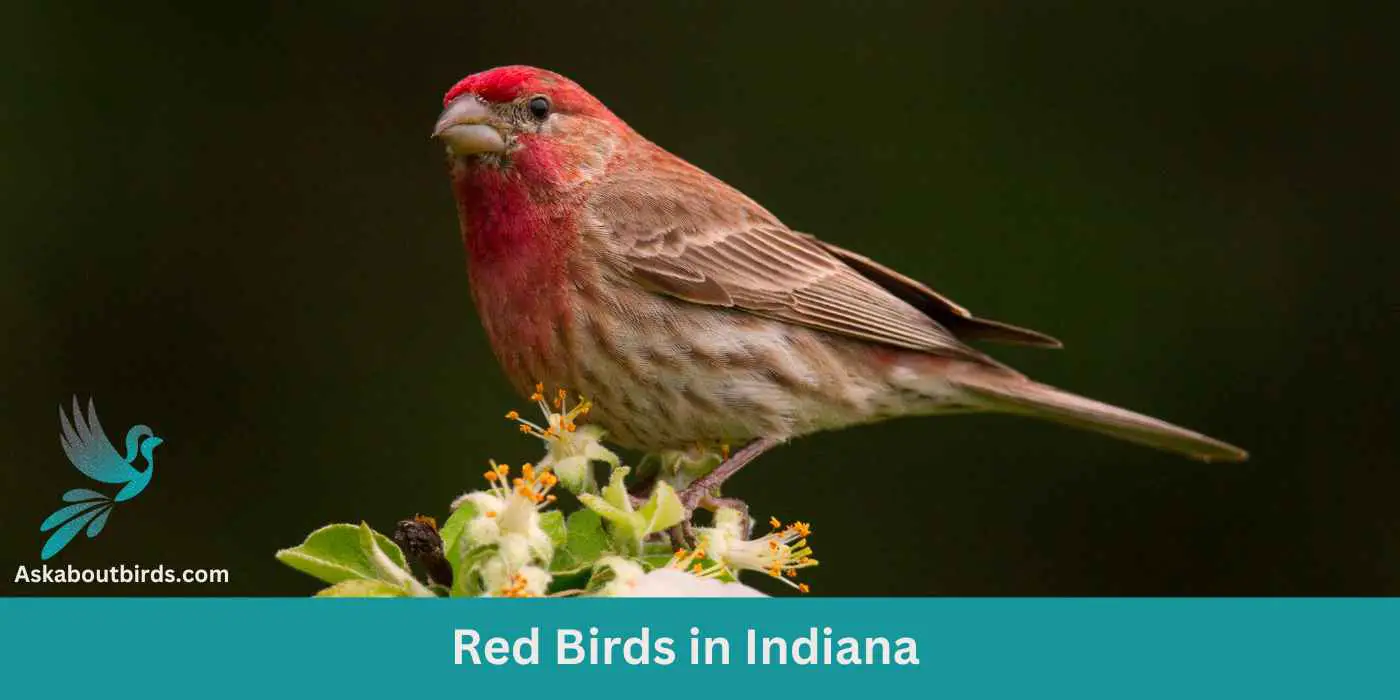
Indiana, with its lush forests, serene wetlands, and picturesque meadows, is not just a haven for nature enthusiasts, but also a paradise for birdwatchers. The Hoosier State boasts a plethora of avian species, but there’s something uniquely captivating about its radiant red birds.
Dive into this comprehensive guide, where we’ll introduce you to 10 of Indiana’s most vibrant red feathered residents.
Red Birds Found In Indiana
Bird enthusiasts find Indiana to be a treasure trove due to its diverse habitats. From the shores of Lake Michigan to the dense woodlands of Hoosier National Forest, these varied ecosystems provide nesting grounds, migratory stopovers, and ample food sources.
The state’s position in the migratory flyway further enhances its avian diversity, drawing both resident and migratory species to its bounteous landscapes.
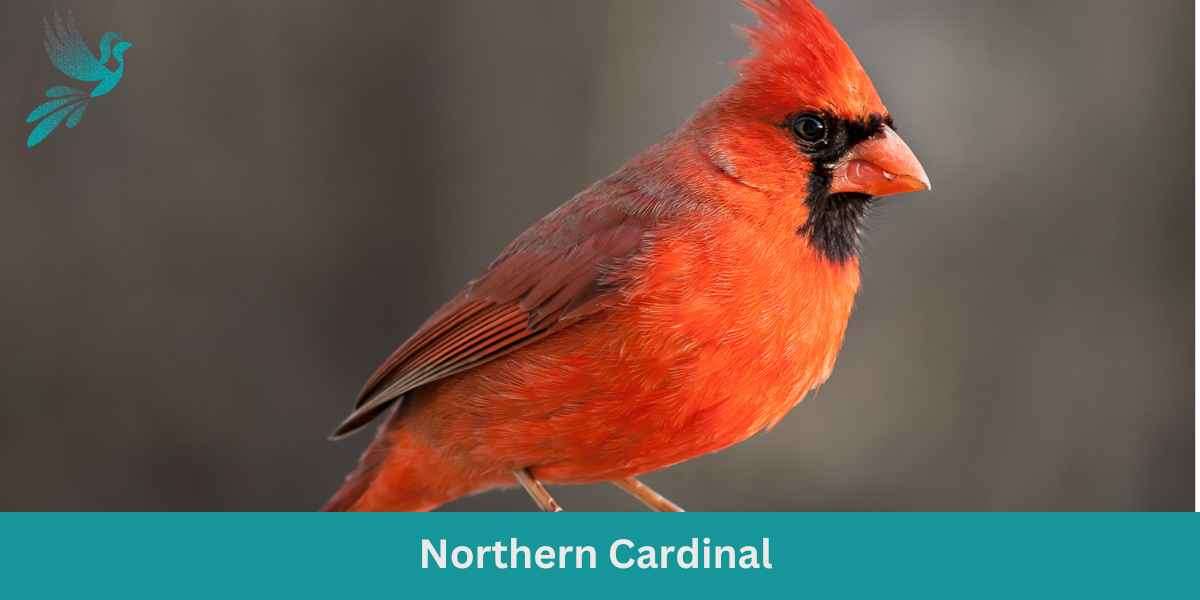
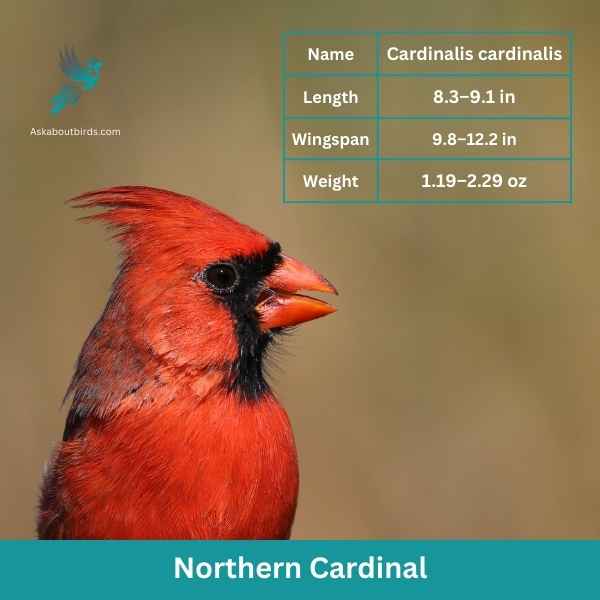
Northern Cardinal

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cardinalis cardinalis |
| Length | 8.3 – 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 – 12.2 in |
| Weight | 1.19 – 2.29 oz |
The Northern Cardinal is an iconic North American bird, easily recognized by its vibrant color and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Northern Cardinals are a brilliant scarlet red, while females display a more subdued reddish olive. Both sexes have a distinctive black ‘mask’ on their face around the bill and a pointed crest on their head. The bird’s beak is robust, cone-shaped, and bright orange in color.
Diet: Northern Cardinals are primarily granivorous, with a diet largely consisting of seeds and grains. They also eat fruits and insects. These birds typically feed off the ground and are frequent visitors to bird feeders.
Reproduction: Northern Cardinals are monogamous, and a pair will breed together for life. The female typically builds a well-hidden nest in a dense thicket or shrub. She lays 2-5 eggs per clutch, which she incubates for around two weeks.
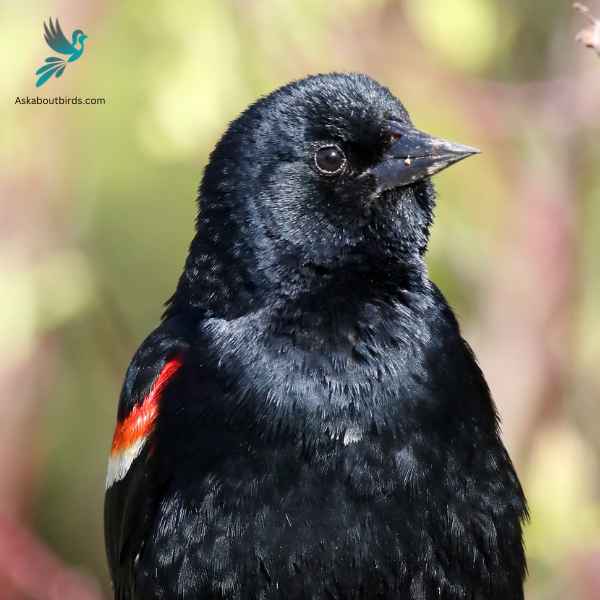
Red-Winged Blackbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Agelaius phoeniceus |
| Length | 6.7-9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 12.2-15.7 in |
| Weight | 41.5-65 g |
The Red-Winged Blackbird is a familiar sight across North America, especially in wetlands and open areas. Known for its striking coloration and distinct call, it is often seen perched on cattails or utility lines.
Appearance: Male Red-Winged Blackbirds are glossy black with bright red-and-yellow shoulder patches, while females are streaky brown, resembling a large sparrow. The males’ red patches become more prominent when they’re displaying or agitated.
Diet: Red-Winged Blackbirds primarily feed on seeds and insects. Their diet includes grains, sunflower seeds, and corn, but they also eat beetles, caterpillars, and other small invertebrates, especially in the breeding season.
Reproduction: Red-Winged Blackbirds nest in marshes, along watercourses, and in wet fields. The female constructs a cup-shaped nest using grass and sedge, attaching it to plants above water. She typically lays a clutch of 3 to 4 blue-green eggs, which she incubates for about 11-12 days. Males, being polygynous, often have multiple mates during a single breeding season.
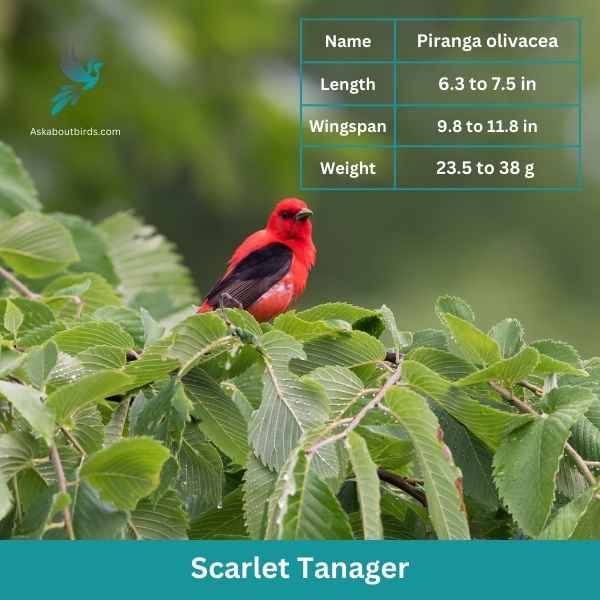
Scarlet Tanager

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga olivacea |
| Length | 6.3 to 7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 to 11.8 in |
| Weight | 23.5 to 38 g |
The Scarlet Tanager is a strikingly colorful bird known for its brilliant plumage and distinctive song.
Appearance: Male Scarlet Tanagers are notable for their vibrant scarlet bodies contrasted with black wings and tail, making them one of the most intensely colored birds. Females and juveniles, on the other hand, have a subdued olive-yellow body color with darker wings and tail.
Diet: The diet of the Scarlet Tanager is largely made up of insects, including beetles, cicadas, aphids, and others. They are adept flycatchers, seizing insects in mid-air or picking them off foliage. They also consume fruits and berries, especially during migration and in their winter habitats.
Reproduction: The female Scarlet Tanager builds a cup-shaped nest using twigs, rootlets, and grass, typically well-hidden in the dense foliage of trees. She lays 3 to 5 eggs and incubates them for about two weeks.
Summer Tanager


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga rubra |
| Length | 6.7 in |
| Wingspan | 28 to 30 cm |
| Weight | 29 g |
The Summer Tanager is a medium-sized songbird admired for its radiant plumage and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Summer Tanagers are an impressive bright red, while females and juveniles present a softer, yellow-orange color. Both genders have a large, slightly hooked bill and relatively short tail.
Diet: Summer Tanagers primarily feed on insects, including bees and wasps, which they catch in flight or pick off vegetation. They are also known to eat fruits and berries, making them helpful in controlling pest populations and seed dispersal.
Reproduction: The female Summer Tanager builds a loose, shallow cup-shaped nest out of twigs and grass, usually hidden in the foliage of trees. The female typically lays 3-5 eggs, which she will incubate for about two weeks.
House Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous mexicanus |
| Length | 5–6 in |
| Wingspan | 8–10 in |
| Weight | 0.6–0.9 oz |
The House Finch is a small songbird widely distributed across North America and is commonly found in urban and suburban areas.
Appearance: Males of this species are brightly colored with crimson faces and throats, which can extend to the chest and back, while their flanks have streaks. The female is streaked brown and lacks the red coloring. Both have a square-tipped tail and a distinctively long, flat-topped bill.
Diet: House Finches primarily eat seeds, grains, and berries. They have a particular fondness for sunflower seeds and can be commonly seen at bird feeders. Occasionally, they will also consume insects, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: House Finches are cavity-nesters and might choose ledges, vents, ledges, and other urban settings. They might also utilize trees or shrubs. Their nests can be made of a wide array of materials, from feathers to twigs.
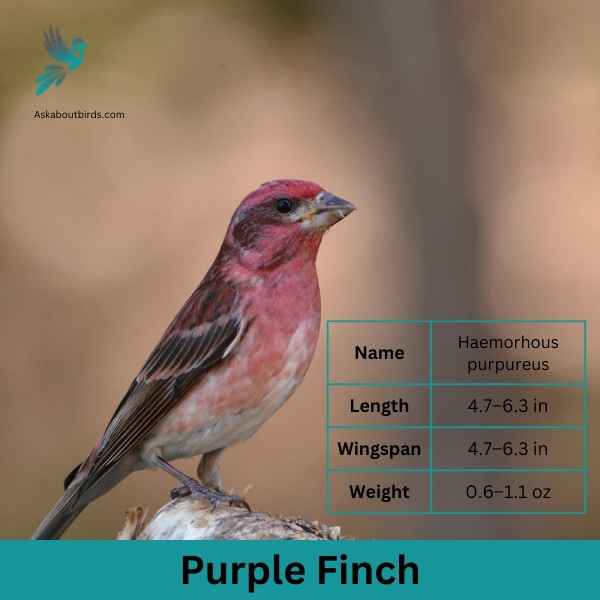
Purple Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous purpureus |
| Length | 4.7–6.3 in |
| Wingspan | 4.7–6.3 in |
| Weight | 0.6–1.1 oz |
The Purple Finch is a vibrant songbird often mistaken for its close relative, the House Finch, but it exhibits a different hue and patterns.
Appearance: Males are raspberry red on the head, throat, and breast, with streaky brown backs and wings. The intensity of the red can vary among individuals. Females are brown and streaked all over but might show a slight blush on the face. They lack the strong facial patterns seen in female House Finches.
Diet: Purple Finches primarily consume seeds, with a preference for sunflower seeds, dandelion seeds, and buds. They also eat insects and berries, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: These finches often nest in conifers or mixed woodlands. The nest, typically located on a horizontal branch, is made from twigs and grass, then lined with feathers.
Red-headed Woodpecker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Melanerpes erythrocephalus |
| Length | 7.5–9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 16.5 in |
| Weight | 2.0–3.2 oz |
The Red-headed Woodpecker is a striking forest bird with a bold tri-colored pattern.
Appearance: This woodpecker features a completely red head and neck, contrasting starkly with its white underparts and black wings. Its wings also have large white patches which are conspicuous in flight.
Diet: Red-headed Woodpeckers have a varied diet including insects, seeds, fruits, berries, and occasionally even the eggs of other birds. They’re also known to store food by wedging it into crevices in bark.
Reproduction: These woodpeckers nest in cavities which they excavate in dead wood or dead parts of live trees. These cavities can be found anywhere from 2 to 80 feet off the ground.
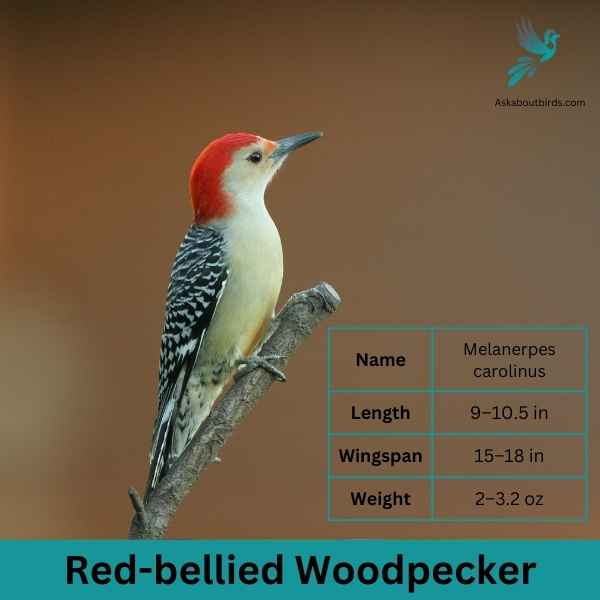
Red-bellied Woodpecker

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Thryothorus ludovicianus |
| Length | 4.7–5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 11 in |
| Weight | 0.63–0.81 oz |
The Red-bellied Woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker commonly found in woodlands, forests, and backyards across the eastern and central U.S.
Appearance: The Red-bellied Woodpecker sports a pale gray face, throat, and belly, contrasted by a zebra-striped back. Its name derives from the subtle reddish tinge on its belly, but it’s more commonly recognized by the vivid red cap on the head of males and the partial red cap on females.
Diet: This woodpecker has a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, nuts, and seeds. They frequently forage on tree trunks and branches, using their sticky, barbed-tipped tongue to extract ants, beetles, and other insects from crevices.
Reproduction: Red-bellied Woodpeckers are cavity nesters, excavating holes in tree trunks for their nests. The inside of the nest is typically unlined or sparingly lined with wood chips.
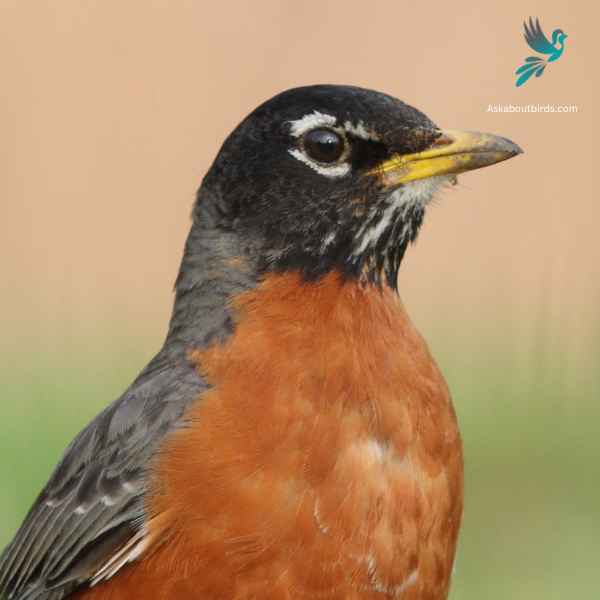
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
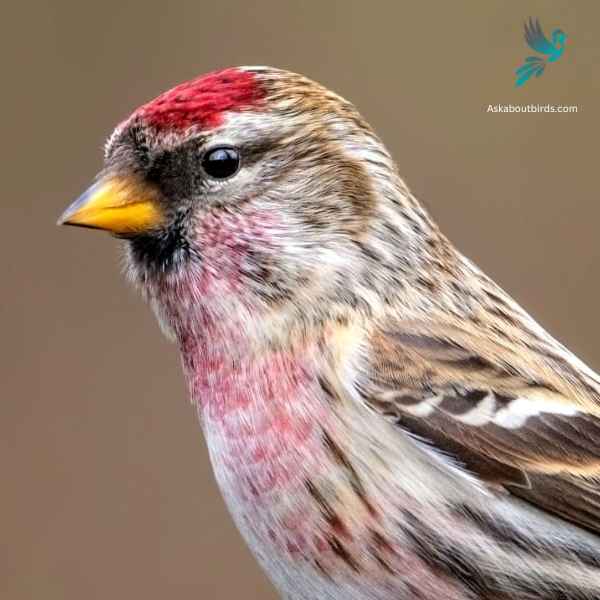
Common Redpoll


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Acanthis flammea |
| Length | 5.0-5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 7.5-8.5 in |
| Weight | 0.4-0.9 oz |
The Common Redpoll is a small songbird that is easily identifiable by its rosy-red forehead, black chin, and often fluttering flight pattern.
Appearance: Common Redpolls exhibit a distinctive rosy-red forehead patch and black chin. The males typically have a more extensive pink wash on their chest and face than females. The rest of their body is primarily streaked brown and white, with two white wing bars and a notched tail.
Diet: The diet of the Common Redpoll predominantly consists of seeds, particularly from birches and alders. They have a specialized throat pouch where they can temporarily store seeds, allowing them to consume them later in a more sheltered location.
Reproduction: Common Redpolls nest in shrubs or on the ground, using grasses, twigs, and feathers for construction. The female is responsible for the majority of the incubation and typically lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs. After the eggs hatch, both parents take part in feeding the young.
Where to Spot Indiana’s Red Birds
Indiana, with its diverse landscapes, is a haven for birdwatchers, offering several prime locations to spot a myriad of avian species, especially the vibrant red ones. Here are some of the top spots:
- Indiana Dunes State Park: Located on the southern tip of Lake Michigan, this park offers over 350 bird species throughout the year, making it a hotspot for birdwatching. Its dunes, swamps, and woodlands create varied habitats that attract a multitude of birds.
- Eagle Creek Park: One of the largest city parks in the U.S., Eagle Creek is home to both resident and migratory birds. Its reservoir and woodlands provide ample opportunities to spot waterfowl, songbirds, and raptors.
- Goose Pond Fish and Wildlife Area: A restored wetland, Goose Pond draws in thousands of waterfowl and shorebirds, especially during migration seasons. Its 9,000+ acres serve as a crucial habitat in the Midwest.
- Hoosier National Forest: Spanning over 200,000 acres, this forest boasts an array of habitats, from hardwoods to wetlands. It’s an excellent place to spot woodland birds, including various red species.
- Muscatatuck National Wildlife Refuge: With its mix of wetlands, forests, and grasslands, Muscatatuck is a haven for over 280 bird species. The refuge is especially known for its waterfowl and songbirds.
| State’s Red Birds | Top Spots for Red Birds |
|---|---|
| Illinois’s Red birds | 1. Starved Rock State Park 2. Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie 3. Cache River Wetlands |
| Kentucky’s Red birds | 1. Mammoth Cave National Park 2. Red River Gorge 3. Land Between the Lakes National Recreation Area |
| Ohio’s Red birds | 1. Magee Marsh Wildlife Area 2. Cuyahoga Valley National Park 3. Shawnee State Forest |
| Michigan’s Red birds | 1. Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore 2. Tahquamenon Falls State Park 3. Seney National Wildlife Refuge |
FAQs on Red Bird Species Found in Indiana
What red birds can be found in the pine oak woodlands and coniferous forests of Indiana?
In the pine oak woodlands and coniferous forests of Indiana, bird enthusiasts can spot several species with red or bright red plumage. Among them are the White Winged Crossbills and the Red Breasted Nuthatch. While White Winged Crossbills are known to feast on conifer seeds, the Red Breasted Nuthatch is often seen extracting tree sap and searching for small insects in dense vegetation.
Which birds with vibrant red plumage visit backyard feeders in Indiana during winter months?
During the winter months in Indiana, Rose Breasted Grosbeaks and Summer Tanager males are frequent visitors to backyard feeders. Their vibrant red plumage stands out against the snowy backdrop. To attract these birds, residents often set up feeders filled with black oil sunflower seeds and offer wild fruit from berry plants. Both of these birds migrate from the northern and western states to the southern and eastern states during winter.
Are there any red birds in Indiana with bright blue heads and a yellow throat?
The Ruby Throated Hummingbird, a medium-sized bird, is notable for its bright blue heads and striking yellow throat. These agile birds are often seen hovering around flower nectars and feeding stations in Indiana during their migration. They primarily feed on tree sap, small insects, and nectar.
Which red birds with white stripes are common in Indiana’s shade trees and forest edges?
The Rose Breasted Grosbeak, easily identifiable by its bright red plumage combined with distinctive white stripes and a pale bill, is frequently spotted among the shade trees and forest edges in Indiana. These birds are attracted to fruit trees and backyard feeders filled with black oil sunflower seeds.





