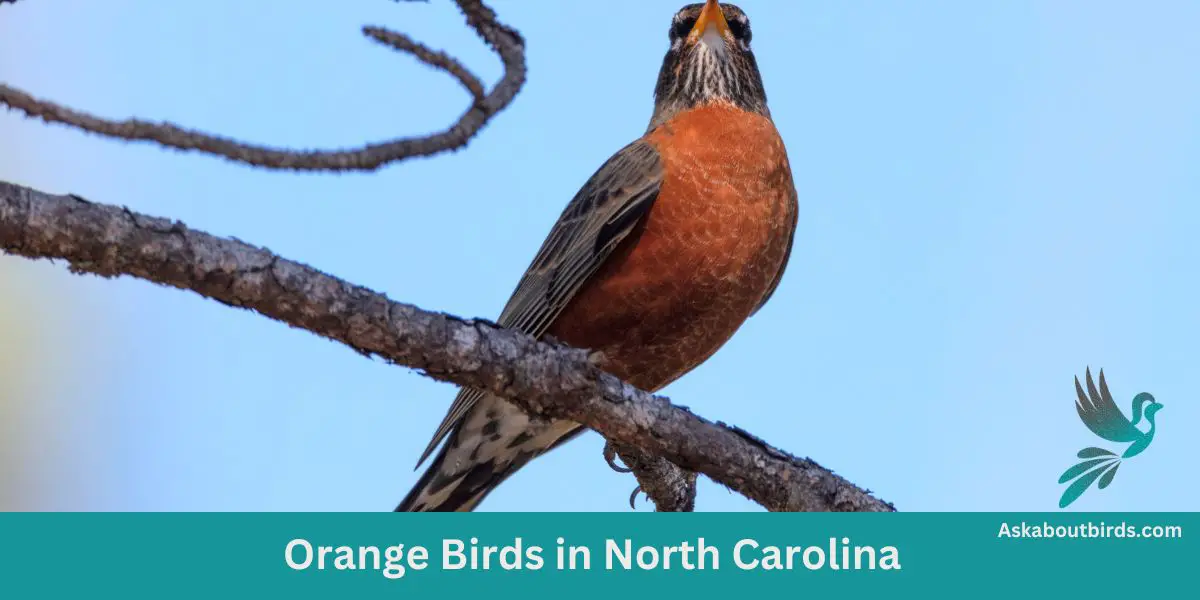
From the majestic peaks of the Appalachians to the serene shores of the Atlantic, North Carolina’s diverse landscapes offer a haven for bird enthusiasts. Among the state’s feathery residents, a group of vibrant orange birds captures the imagination with their striking hues and melodic calls.
Orange Birds Found In North Carolina
North Carolina’s rich tapestry of habitats, from its towering mountain peaks to its expansive coastal marshes, offers birds an array of nesting and foraging opportunities. Coastal areas provide refuge for shorebirds, while the dense forests of the interior are home to numerous woodland species.
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
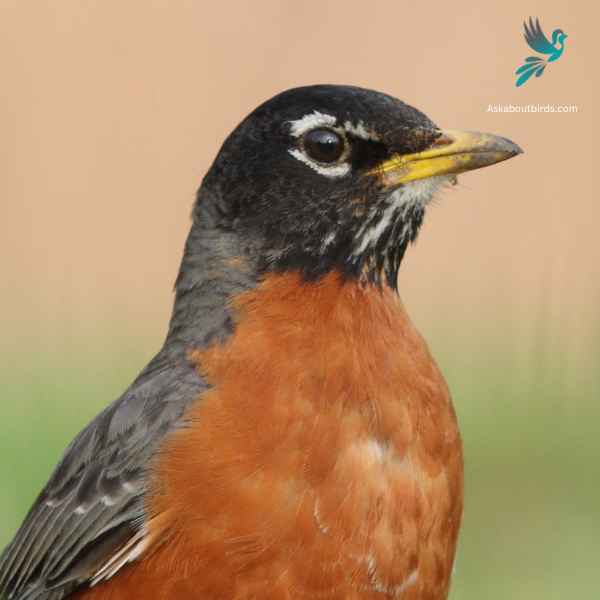
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
Baltimore Oriole


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus galbula |
| Length | 6.7–8.7 in |
| Wingspan | 9.1–12.6 in |
| Weight | 22.3-42 g |
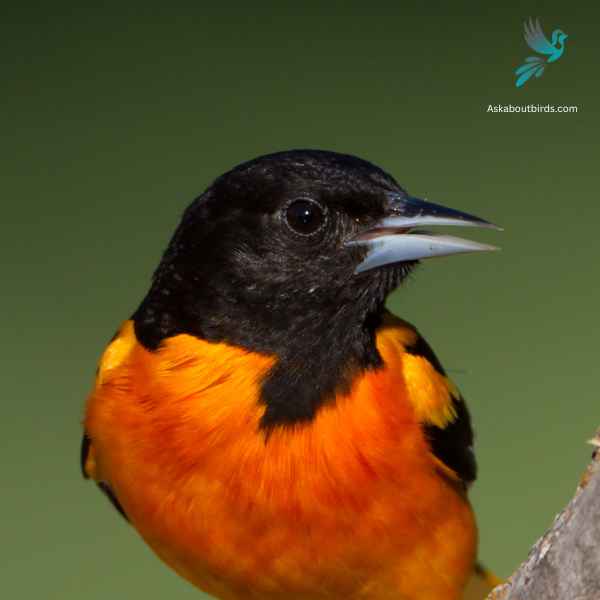
The Baltimore Oriole is a stunning bird, best known for its vibrant coloration and its rich, whistling song.
Appearance: The male Baltimore Oriole is notable for his bright orange and black plumage and black and white wing bars, a stark contrast to the more muted yellow-brown coloration of the female. Both sexes, however, have long pointed bills and white bars on their wings.
Diet: Baltimore Orioles have a diverse diet that includes insects, fruits, and nectar. Their preference for sweet juices and fruit pulp often brings them to backyard feeders offering oranges and jelly.
Reproduction: The female Baltimore Oriole is responsible for building the distinctive hanging nest, often woven together from fine materials like hair and grass. These nests are usually high in trees to avoid predators. The female lays 3-7 eggs, which are incubated for about two weeks.
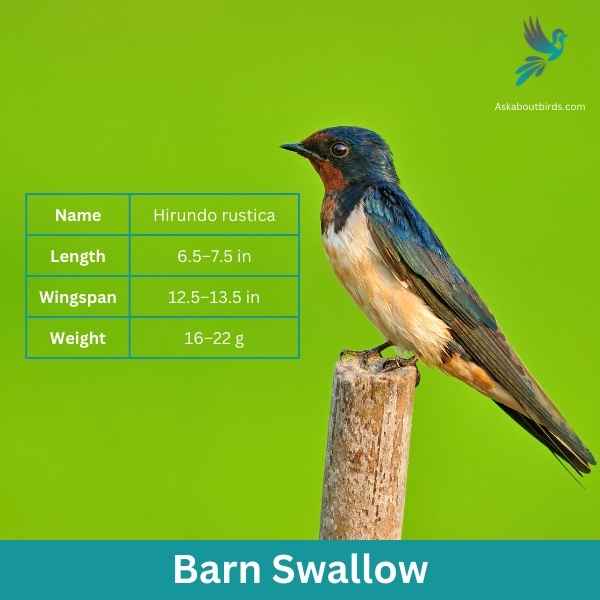
Barn Swallow

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hirundo rustica |
| Length | 6.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.5–13.5 in |
| Weight | 16–22 g |
The Barn Swallow is a sleek, agile bird renowned for its graceful flight patterns and iconic forked tail, often seen darting over fields and water bodies in search of flying insects.
Appearance: Barn Swallows have deep blue, almost iridescent, upperparts and a rufous to tawny underbelly. Their distinctively forked tail and long wings give them a streamlined look. Both males and females have a similar appearance, though males often exhibit slightly brighter colors and a deeper fork in the tail.
Diet: Barn Swallows feed primarily on flying insects, which they catch in mid-air during their agile and acrobatic flights. Their diet includes flies, beetles, moths, and other small flying insects.
Reproduction: Barn Swallows are known for building their mud nests on man-made structures, particularly barns, bridges, and eaves. The nest is cup-shaped and made from mud pellets, often lined with feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs.
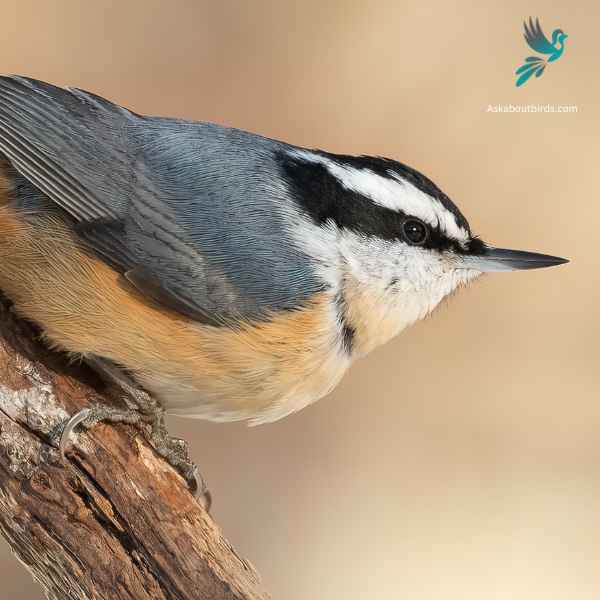
Red-breasted Nuthatch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sitta canadensis |
| Length | 4.3–4.7 in |
| Wingspan | 8.3 in |
| Weight | 0.3–0.5 oz |
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, agile songbird, known for its ability to move headfirst down tree trunks while searching for food.
Appearance: This bird boasts a slate-blue back and a pale rust-red underside. A prominent black stripe runs through the eye and is bordered above by a white eyebrow. Their sharp, pointed bill is characteristic of the species.
Diet: Red-breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds, especially those from coniferous trees. They have a fondness for large seeds, which they wedge into bark crevices to hack open with their bills.
Reproduction: These birds construct nests in natural tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker holes, often lining the entrance with resin. This is thought to deter predators or competitors from entering. The female typically lays a clutch of 5 to 6 eggs, and both parents partake in feeding the chicks once they hatch.
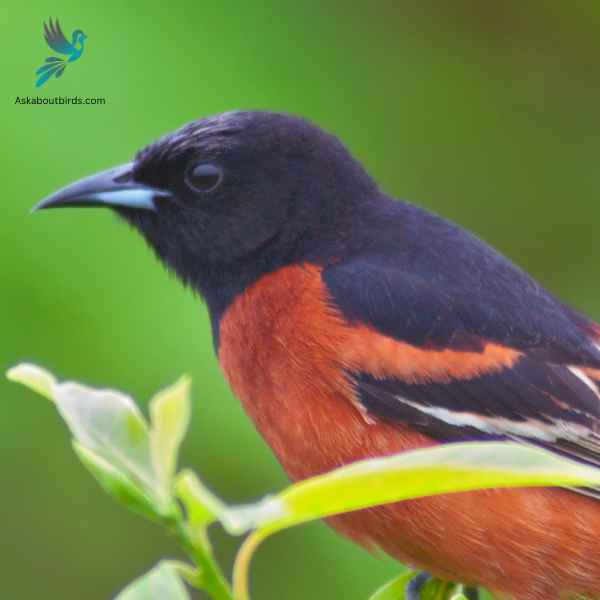
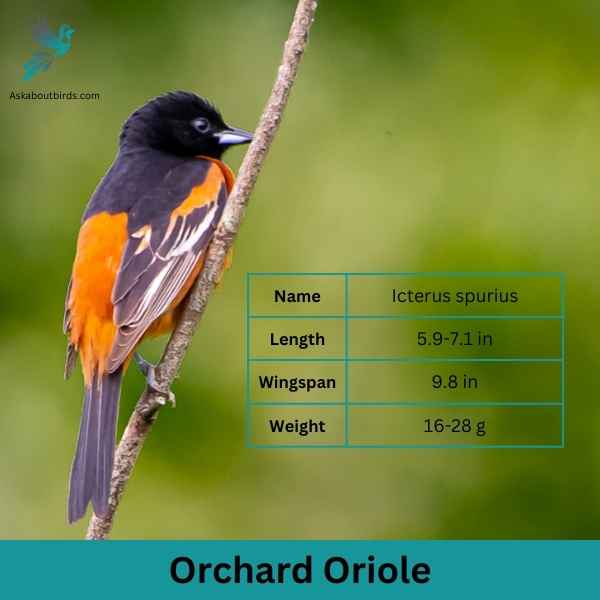
Orchard Oriole

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus spurius |
| Length | 5.9-7.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 in |
| Weight | 16-28 g |
The Orchard Oriole is a small songbird noted for its distinctive coloration and melodic song.
Appearance: Male Orchard Orioles are a striking sight with their dark chestnut body and black head and black and white wings, while females and immature males are olive-green and feature a yellowish underpart. The species is often recognized by its slender body and pointed bill.
Diet: The diet of the Orchard Oriole consists primarily of insects, fruits, and nectar. They are adept at catching insects mid-air and are also known to sip nectar from flowers, aiding in pollination. When fruits are in season, they make up a substantial portion of the bird’s diet.
Reproduction: Orchard Orioles often nest in open woodlands and orchards, hence their name. The female is responsible for building the nest, typically choosing a location in a tree or shrub. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates for about two weeks.
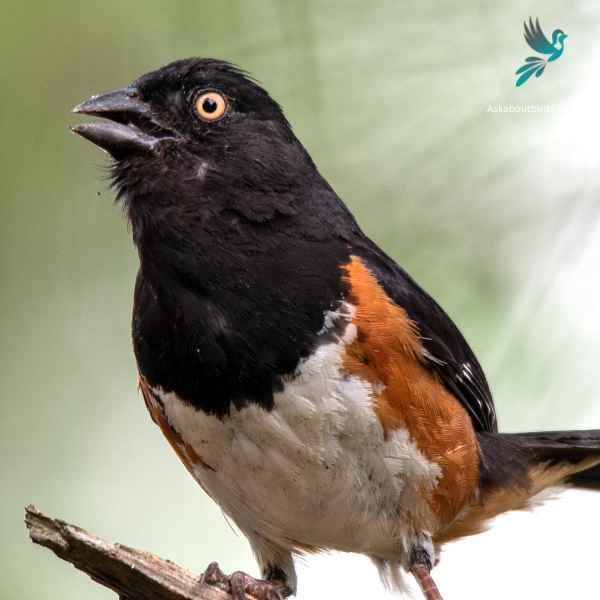
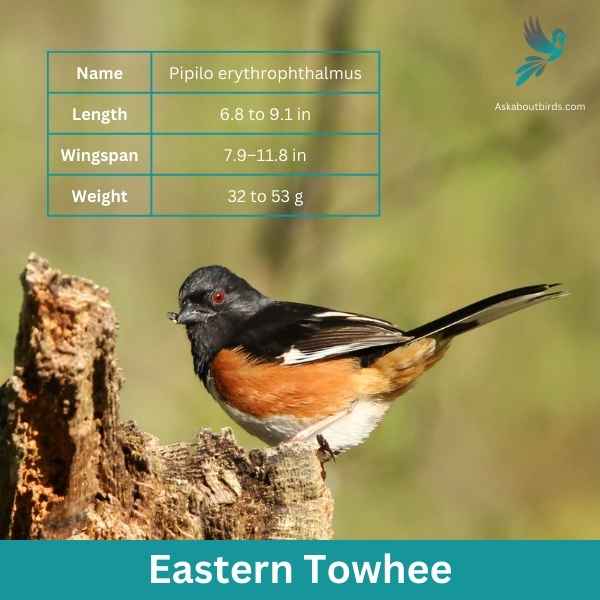
Eastern Towhee

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo erythrophthalmus |
| Length | 6.8 to 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9–11.8 in |
| Weight | 32 to 53 g |
The Eastern Towhee is a distinctive songbird known for its unique calls and eye-catching coloration.
Appearance: Male Eastern Towhees are characterized by a striking combination of a black head, back and tail, contrasting with a white belly and rufous flanks. Females sport similar patterns but instead of black, they have a rich brown color. Both genders have red eyes, lending a special charm to their overall appearance.
Diet: Eastern Towhees primarily feed on a variety of insects, seeds, and berries. Their diet is quite diverse, taking advantage of seasonal offerings, which includes beetles, caterpillars, spiders, acorns, grass seeds, and various fruits and berries.
Reproduction: Eastern Towhees build their nests on or near the ground, often in a shrub or a small tree. The female lays around 3-5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubating them over about 12-13 days.
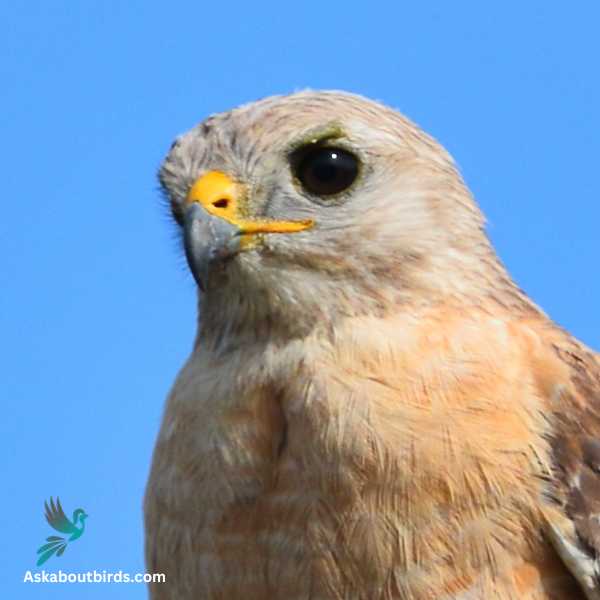
Red-Shouldered Hawk


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Buteo lineatus |
| Length | 15 to 23 in |
| Wingspan | 35 to 50 in |
| Weight | 1.21 lb- 1.5 lb |
The Red-Shouldered Hawk is a medium-sized bird of prey, belonging to the Buteo genus, prevalent in North America. It is characterized by its reddish-brown shoulder patches, from which it derives its name. Other distinctive features include its banded tail and translucent crescents near the wingtips that are visible during flight.
Red-Shouldered Hawks typically inhabit mixed woodlands, often near rivers and swamps, where they hunt for a variety of prey, including small mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and occasionally other birds. Unlike some other hawk species, they are quite vocal, emitting a distinctive, repetitive whistle that often gives away their presence. These hawks build nests high in deciduous trees where they usually lay 2 to 4 eggs. The pairs are monogamous, often maintaining their bond for many years and defending their territories fiercely.
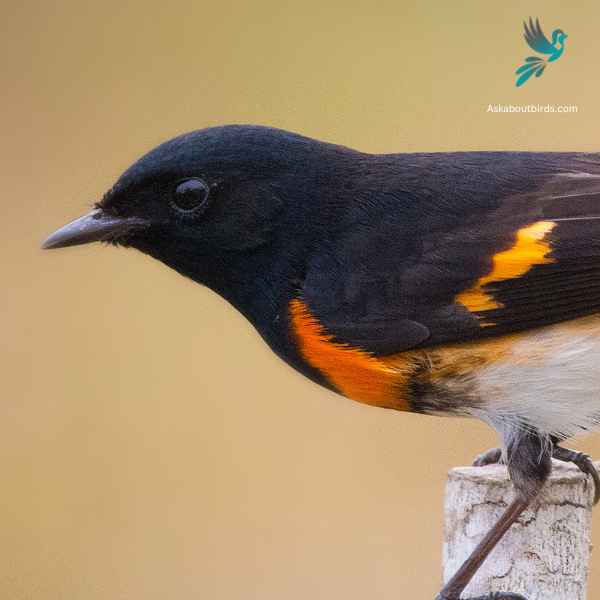
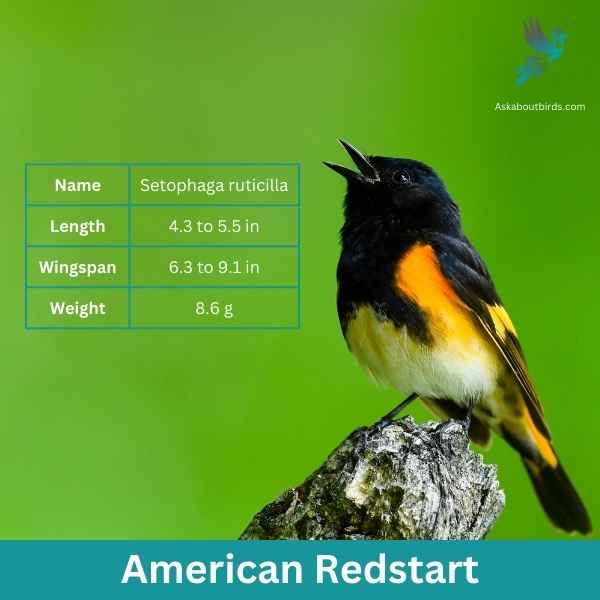
American Redstart

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
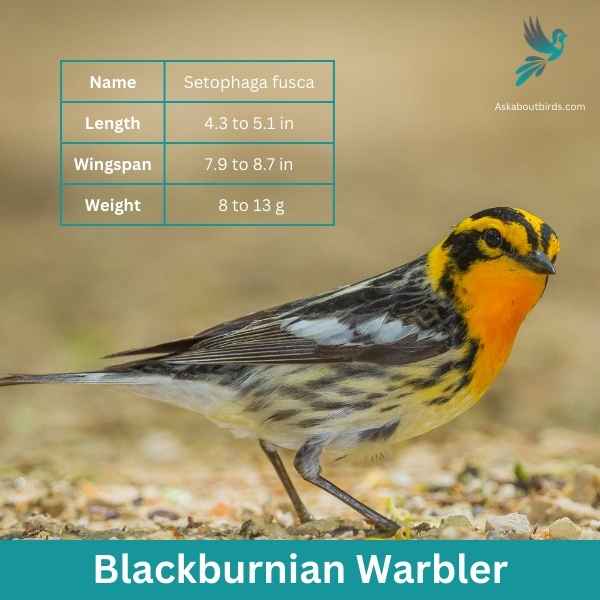
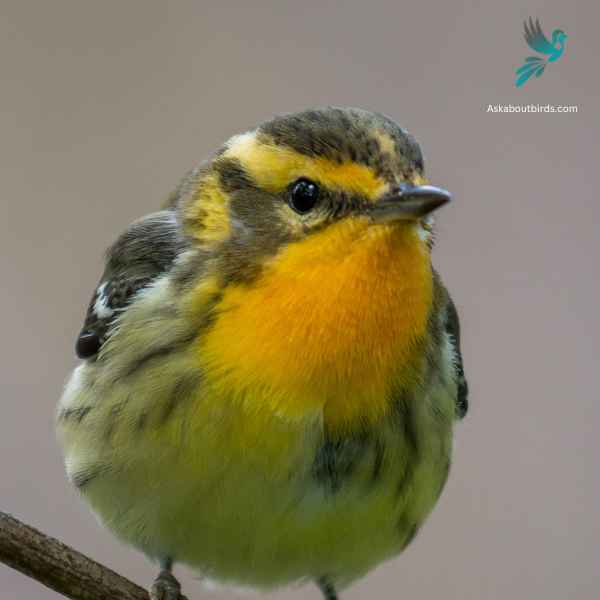
Blackburnian Warbler


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga fusca |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9 to 8.7 in |
| Weight | 8 to 13 g |
The Blackburnian Warbler is a strikingly colored songbird that captivates observers with its vivid plumage, especially during the breeding season. Often found flitting high in the treetops of North American forests, its melodious song is as enchanting as its appearance.
Appearance: Male Blackburnian Warblers are distinguished by their fiery-orange throats, contrasting sharply with a black face, crown, and streaked back. They also have white underparts with black streaks on the sides. Females have a more muted coloration, with a yellowish or pale orange throat and less pronounced streaking.
Diet: Blackburnian Warblers primarily feed on insects and spiders. They are adept at foraging in the canopy, where they glean insects from the surface of leaves and branches or catch them mid-air in quick, agile flights.
Reproduction: Blackburnian Warblers build their nests high up in coniferous trees, often on horizontal branches. The nest is a neat cup made of twigs, grass, and moss, lined with softer materials like hair or feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 5 eggs and takes the lead in incubation.
Rufous Hummingbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Selasphorus rufus |
| Length | 3.1–3.9 in |
| Wingspan | 4.3 in |
| Weight | 0.1–0.2 oz |
The Rufous Hummingbird is a small, brilliantly colored bird known for its impressive migratory journeys and feisty behavior.
Appearance: The male Rufous Hummingbird boasts a gleaming orange-red body with a white chest and an iridescent red throat, called a gorget. The female has green upperparts with rufous-washed flanks and tail. Her throat may have some iridescent patches, but it’s generally whitish.
Diet: Like other hummingbirds, the Rufous Hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar from a variety of flowering plants. They also eat insects and spiders for protein, catching them in flight or plucking them from vegetation.
Reproduction: Rufous Hummingbirds nest in trees, shrubs, or even ferns. The female alone selects the site, builds the nest, and cares for the offspring.
Where to Spot North Carolina’s Orange Birds
North Carolina, with its blend of coastal, piedmont, and mountainous terrains, is a haven for birdwatchers. Here are the top locations, especially for spotting the mesmerizing orange birds:
- Cape Hatteras National Seashore: A pristine stretch along the Outer Banks, this area is ideal for spotting coastal and migratory birds. Its varied habitats from dunes to marshes are a magnet for a range of species.
- Pee Dee National Wildlife Refuge: Nestled in the piedmont region, this refuge offers a blend of wetlands, forests, and grasslands. It serves as an important wintering site for waterfowl and other migratory birds.
- Pisgah National Forest: Located in the Appalachian Mountains, this expansive forest is teeming with high-elevation bird species. Its varied ecosystems, from dense forests to rushing streams, are perfect for spotting woodland birds.
- Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge: Home to a vast expanse of wetland habitats, this refuge in eastern North Carolina is renowned for its rich bird diversity, including many wading and water birds.
- Mattamuskeet National Wildlife Refuge: A freshwater lake surrounded by marshes and forests, this refuge is a hotspot for wintering waterfowl and other bird species, making it a must-visit for avid birdwatchers.
| State’s Orange Birds | Top Spots for Orange Birds |
|---|---|
| Virginia’s Orange Birds | 1. Great Dismal Swamp National Wildlife Refuge 2. Shenandoah National Park 3. Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge |
| South Carolina’s Orange Birds | 1. Congaree National Park 2. Ace Basin National Wildlife Refuge 3. Santee Coastal Reserve |
| Georgia’s Orange Birds | 1. Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge 2. Chattahoochee National Forest 3. Sapelo Island National Estuarine Research Reserve |
| Tennessee’s Orange Birds | 1. Great Smoky Mountains National Park 2. Hiwassee Refuge 3. Radnor Lake State Natural Area |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in North Carolina
What kind of bird has an orange head in North Carolina?
In North Carolina, the Rufous Hummingbird can be identified by its distinctive orange or rufous-colored head, particularly in males. Although more common in the western U.S., these birds occasionally make their way to the east, including North Carolina, especially during migration periods.
What bird is black with orange in NC?
The Baltimore Oriole is a bird that is primarily black with vibrant orange underparts. They are found in North Carolina, particularly during the spring and summer months. Male Baltimore Orioles exhibit a bright orange chest and belly, contrasted by a black head, back, and wings, making them easily distinguishable among other birds in the region.
Which of the most common backyard birds in North Carolina can I expect to see visiting bird feeders?
In North Carolina, some of the most common backyard birds that frequent bird feeders include the House Finch, Northern Cardinal, and Carolina Chickadee or the hooded oriole (known for its bright orange plumage) or the Hooded Orioles (know for being bright yellow). Offering a variety of seeds such as sunflower seeds or black oil sunflower seeds will see more visit bird feeders. Many are not year round residents and will migrate to South America and Central America in the winter months.
I’ve noticed birds with black wings feeding in my yard. What might these be?
Several birds in North Carolina sport black wings. The Red-winged Blackbirds, known for their starkly contrasted bright red shoulders, and Starlings with their iridescent sheen, are just a couple of examples.





