The Bluebird (Sialia genus) is a beloved bird known for its vibrant blue plumage and cheerful presence. While there are no birds that perfectly mimic the Bluebird’s appearance, there are several bird species that share similar features or colorations.
The Mountain Bluebird exhibits a stunning blue color similar to that of the Bluebird.
The Indigo Bunting shares a vibrant blue plumage, but differs in shape and size from the Bluebird.
The Eastern Bluebird and Western Bluebird closely resemble the Bluebird with their blue plumage and reddish-brown chests.
The male Eastern Bluebird may have a more intense blue coloration compared to the female.
List of Birds That Resemble Bluebirds
Blue Jay
Indigo Bunting
Blue Grosbeak
Tree Swallow
Lazuli Bunting
Steller’s Jay
California Scrub-Jay
Belted Kingfisher
Blue-gray Gnatcatcher
Black-throated Blue Warbler
Blue Jay
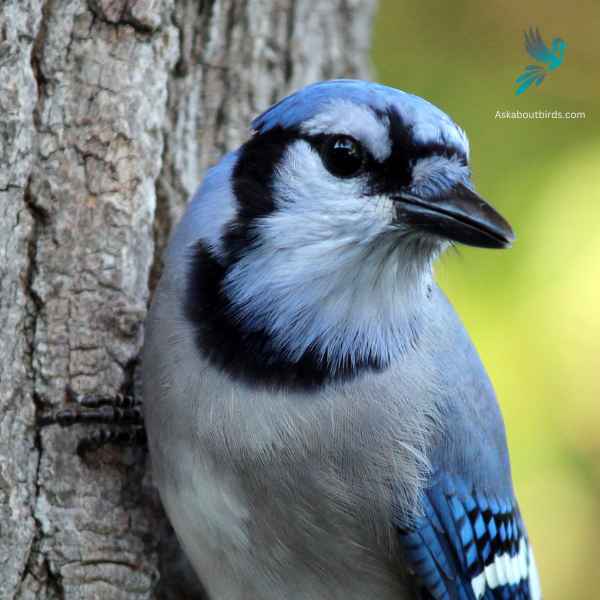


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cyanocitta cristata |
| Length | 9–12 in |
| Wingspan | 13–17 in |
| Weight | 70–100 g |
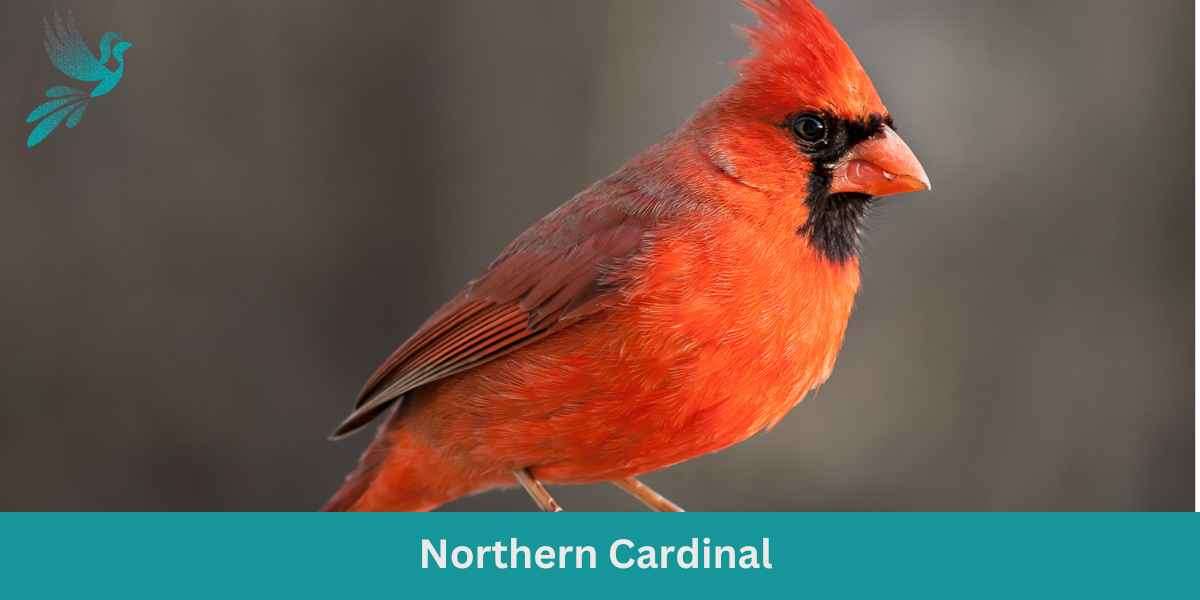
The Blue Jay is a vibrant and easily recognized bird, known for its intelligence, distinctive calls, and bold behavior, commonly found throughout the eastern and central United States.
Appearance: The Blue Jay sports a striking blue upper body with white and black markings. Its face has a pronounced white patch with a black necklace that runs across the throat and around the head. The bird also features a pronounced blue crest, which can be raised or lowered, and its wings and tail are brightly colored with black bars and white tips.
Diet: Blue Jays are omnivores. Their diet consists primarily of seeds, nuts, especially acorns, fruits, and small insects. They’ve also been known to eat eggs or nestlings of other birds occasionally. Blue Jays often store food items in caches to eat later.
Reproduction: Blue Jays are monogamous birds that form long-lasting pair bonds. They typically build their nests in trees or large shrubs, constructing them from twigs, grass, and sometimes using mud as a binder. The female lays a clutch of 3 to 6 eggs, which are pale blue or sometimes white with brown speckles.
Similarities
- Coloration: Both Blue Jays and Bluebirds have vibrant blue plumage.
- Feathers and Body Shape: They have sleek bodies with efficient flight feathers.
- Wing Patterns: Their wings display contrasting patterns.
Differences
- Size: Blue Jays are larger than Bluebirds.
- Crest: Blue Jays have a crest on their head, while Bluebirds do not.
- Coloration Variations: Blue Jays have deeper blue coloration with black and white markings, while Bluebirds exhibit varying shades of blue with rusty or orange tones.
Indigo Bunting


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Passerina cyanea |
| Length | 4.5–5.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.1–9.1 in |
| Weight | 11.2–21.4 g |
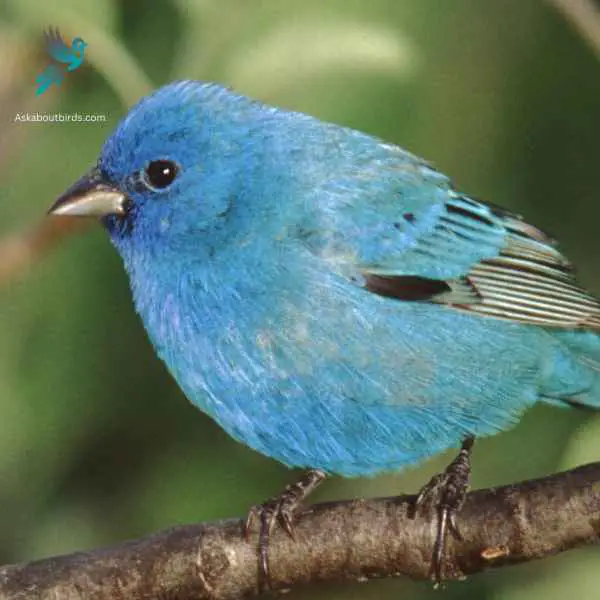
The Indigo Bunting is a strikingly vibrant songbird, often hailed for its brilliant blue plumage and melodic song that graces woodlands and meadows during the warmer months.
Appearance: Males are renowned for their bright indigo blue feathers, which can appear darker in certain lights. Females and juveniles, on the other hand, are brown with subtle hints of blue on their wings and tail. The species lacks the vibrant streaking or spotting commonly found in many other songbirds.
Diet: Indigo Buntings primarily subsist on seeds, especially during non-breeding seasons. During the breeding season, they also consume a variety of insects such as beetles, caterpillars, and spiders, providing essential protein for their growing chicks.
Reproduction: Indigo Buntings build their nests close to the ground in shrubs or low tree branches. These nests, crafted meticulously with grasses and other plant materials, cradle clutches of typically 3 to 4 eggs. After hatching, the young are fed by both parents until they’re ready to fledge.
Similarities
- Coloration: Both Indigo Buntings and Bluebirds have vivid blue plumage, although shades of blue may differ slightly.
- Small to Medium Size: Both species fall within the small to medium size range, with Indigo Buntings measuring around 5.5 to 5.9 inches (14 to 15 centimeters) and Bluebirds ranging from 5.5 to 8 inches (14 to 20 centimeters) in length.
- Attractive Appearance: Indigo Buntings and Bluebirds are visually appealing birds with their blue feathers adding splashes of vibrant color.
Differences
- Body Shape and Markings: Indigo Buntings have a slender body shape and darker wings, while Bluebirds have a more robust body shape and may display rusty or orange tones in their plumage.
- Habitat and Range: Indigo Buntings are commonly found in open woodlands, fields, and brushy areas, while Bluebirds prefer open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas.
- Song and Behavior: Indigo Buntings have a distinctive, melodic song, whereas Bluebirds have a softer, melodious warbling call. Their foraging behaviors and food preferences may also differ.
Blue Grosbeak


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Passerina caerulea |
| Length | 5.5 to 7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 10 to 11 in |
| Weight | 26 to 31.5 g |
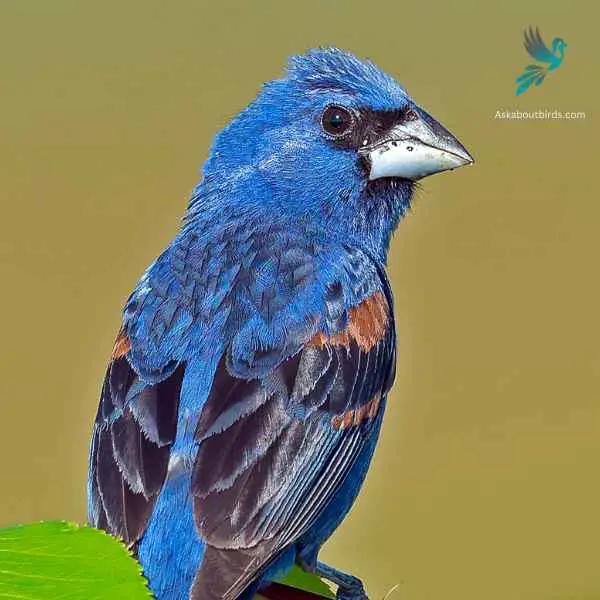
The Blue Grosbeak is a medium-sized songbird found in North and Central America. The male Blue Grosbeak displays stunning plumage with deep blue feathers on its body and head, while the female has more subdued brownish tones. Both sexes have a thick, conical bill, which gives them their name “grosbeak,” meaning large beak.
These birds prefer open habitats such as grasslands, brushy areas, and woodland edges. Blue Grosbeaks are known for their melodious songs, which consist of a series of rich and varied notes. They primarily feed on seeds and insects, using their strong beaks to crack open seeds and forage on the ground or in low vegetation.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both Blue Grosbeaks and Bluebirds have striking blue plumage.
- Size: They are similar in size, with Blue Grosbeaks measuring around 5.9 to 6.7 inches (15 to 17 centimeters) and Bluebirds ranging from 5.5 to 8 inches (14 to 20 centimeters) in length.
- Attractive Appearance: Both species possess visually appealing features, with their blue feathers adding vibrant color to their overall look.
Differences
- Body Shape and Markings: Blue Grosbeaks have a stockier body shape compared to Bluebirds, and they may exhibit additional brown or chestnut coloration on their wings, back, or breast.
- Habitat and Range: Blue Grosbeaks prefer brushy habitats, open woodlands, and grasslands, while Bluebirds are often found in open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas.
- Bill Shape: Blue Grosbeaks have a larger, thicker bill adapted for cracking seeds, while Bluebirds have a more slender bill designed for catching insects and berries.
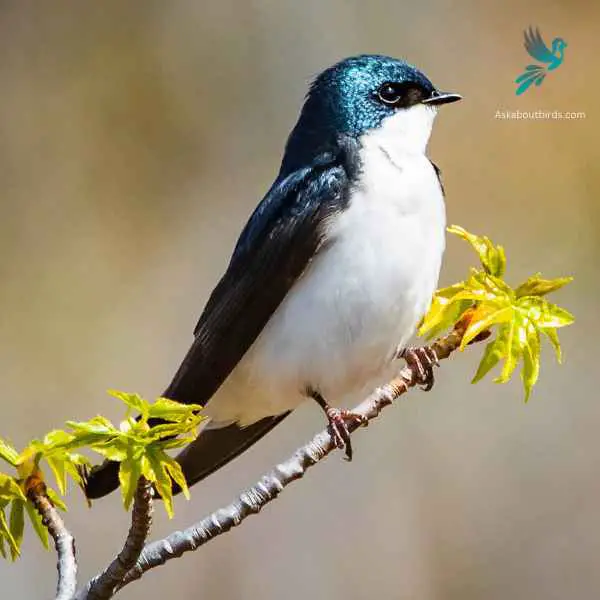
Tree Swallow


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Tachycineta bicolor |
| Length | 4.7 and 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12 to 14 in |
| Weight | 17 to 25.5 g |
The Tree Swallow is a graceful and agile bird, best recognized for its iridescent blue-green upperparts and sweeping flight patterns over open fields and water.
Appearance: The Tree Swallow is sleek with a streamlined body. The upperparts shine with a blue-green iridescence while the underparts are white. They possess long, pointed wings and a slightly forked tail, aiding in their agile flight.
Diet: Tree Swallows primarily feed on flying insects, skillfully catching them mid-air. During colder months when insects are scarce, they can switch to a diet of berries, particularly those of the bayberry, which other birds might find hard to digest.
Reproduction: Tree Swallows are cavity-nesters, typically choosing natural holes in trees or using bird boxes. They line their nests with feathers, creating a soft environment for the eggs. The female will lay a clutch of 4 to 7 white eggs.
Similarities
- Both Tree Swallows and Bluebirds have beautiful, vibrant plumage. Tree Swallows exhibit iridescent blue-green feathers on their upperparts, while Bluebirds showcase various shades of blue on their plumage.
- Size: Both species fall within the small to medium size range. Tree Swallows measure around 5.9 to 6.7 inches (15 to 17 centimeters) in length, similar to the size of Bluebirds.
- Eye-catching Appearance: Tree Swallows and Bluebirds are visually appealing with their eye-catching colors, adding a touch of beauty to their overall look
Differences
- Plumage Distribution: While Tree Swallows have blue-green feathers on their upperparts, their underparts are white. Bluebirds, on the other hand, display blue feathers on their upperparts and often have contrasting rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Bill Shape: Tree Swallows have a slender, slightly curved bill suited for catching insects in mid-air, whereas Bluebirds have a more straight and slender bill, ideal for capturing insects and eating berries.
- Habitat and Behavior: Tree Swallows are known for their aerial acrobatics and their preference for nesting in tree cavities or nest boxes near open water. Bluebirds tend to inhabit open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas, often perching on elevated spots to hunt for insects or worms.
Lazuli Bunting


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Passerina amoena |
| Length | 5.1-5.9 in |
| Wingspan | 8.7 in |
| Weight | 13-18 g |
The Lazuli Bunting is a vibrant songbird recognized for its brilliant colors and melodious song, frequently seen in brushy areas and woodlands during the summer months.
Appearance: The male boasts a dazzling bright blue head and back, offset by a white belly and rust-orange breast. Females and immature birds present a more muted brownish hue overall, with a hint of blue on the wings and tail.
Diet: Lazuli Buntings primarily feed on seeds, but during the breeding season, they’ll also consume insects. Their strong, conical beaks are perfectly adapted for seed-cracking.
Reproduction: The female Lazuli Bunting constructs a cup-shaped nest using grasses, twigs, and other fine materials, often placing it in a shrub or low tree. She typically lays a clutch of 3-4 pale blue or white eggs.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both Lazuli Buntings and Bluebirds possess vibrant blue feathers, contributing to their visual appeal.
- Size: Lazuli Buntings and Bluebirds share a similar size, with Lazuli Buntings measuring around 5.5 to 5.9 inches (14 to 15 centimeters) and Bluebirds ranging from 5.5 to 8 inches (14 to 20 centimeters) in length.
- Attractive Appearance: Both species exhibit an attractive appearance with their blue feathers, adding a touch of color to their overall look.
Differences
- Body Shape and Markings: Lazuli Buntings have a stocky yet streamlined body shape, often displaying a distinct blue color on their head and back. In contrast, Bluebirds have a more robust body shape and may exhibit additional rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Habitat and Range: Lazuli Buntings are commonly found in open woodlands, brushy areas, and forest edges, while Bluebirds prefer open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas as their habitat.
- Song and Behavior: Lazuli Buntings are known for their sweet and melodious song, typically heard during the breeding season. Bluebirds, however, have a softer, melodious warbling call. Additionally, their foraging behaviors and food preferences may differ.
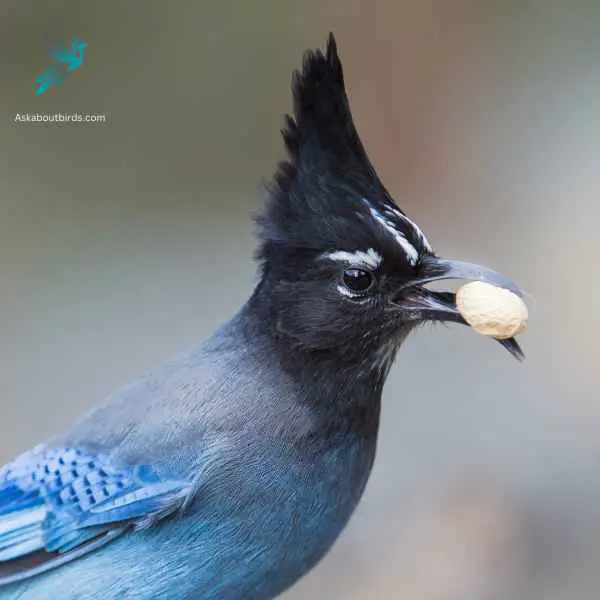
Steller’s Jay

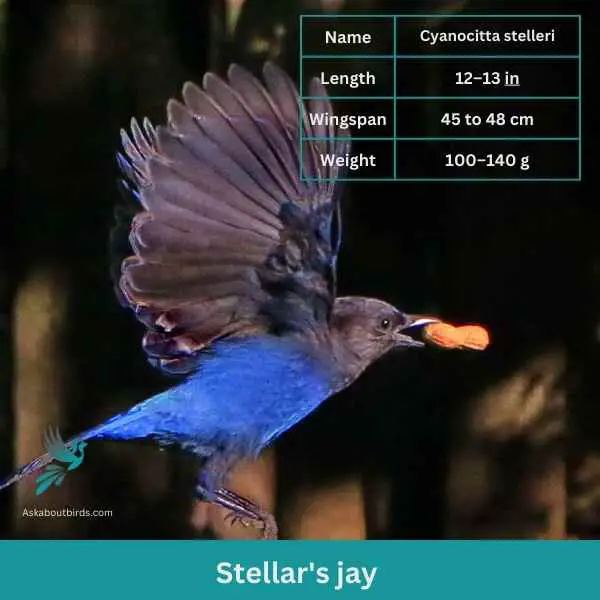
| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cyanocitta stelleri |
| Length | 12–13 in |
| Wingspan | 45 to 48 cm |
| Weight | 45 to 48 cm |
The Steller’s Jay is a charismatic and easily recognizable bird found mainly in the coniferous forests of the western North America, known for its bold behavior and loud, varied calls.
Appearance: The Steller’s Jay has a striking color contrast with a deep blue body and wings and a blackish head and upper body. One of its most distinguishing features is the tall, dark crest on its head, which can be raised or lowered depending on the bird’s mood. Its eyes are dark and its beak is strong and black.
Diet: The Steller’s Jay is omnivorous. It feeds on a wide range of items, from seeds, nuts, and berries to insects and small animals. It’s also known to raid campsites and picnics, often scavenging for human food.
Reproduction: Steller’s Jays form monogamous pairs that often remain together for several years. They typically build their nests in coniferous trees, made from twigs, moss, and other plant materials. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 6 eggs, which are usually pale green or blue with brown spots.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both Steller’s Jays and Bluebirds exhibit blue feathers, although the shades may differ.
- Size: Steller’s Jays and Bluebirds are similar in size, with Steller’s Jays measuring around 11 to 12 inches (28 to 30 centimeters) in length, similar to the size of Bluebirds.
- Eye-catching Appearance: Both species possess visually striking features, with their blue feathers adding vibrancy to their overall look.
Differences
- Coloration Patterns: Steller’s Jays have a deeper blue coloration with black heads and upperparts, while Bluebirds often display varying shades of blue with contrasting rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Habitat and Behavior: Steller’s Jays are often found in coniferous and mixed forests, while Bluebirds prefer open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas. Their behaviors and foraging techniques also differ.
- Crest and Facial Features: Steller’s Jays have a prominent crest on their head, which can be raised or lowered depending on their mood. Bluebirds lack a crest and have a more rounded head shape. Their facial features also differ, with Steller’s Jays having a longer, pointed bill compared to the slender bill of Bluebirds.
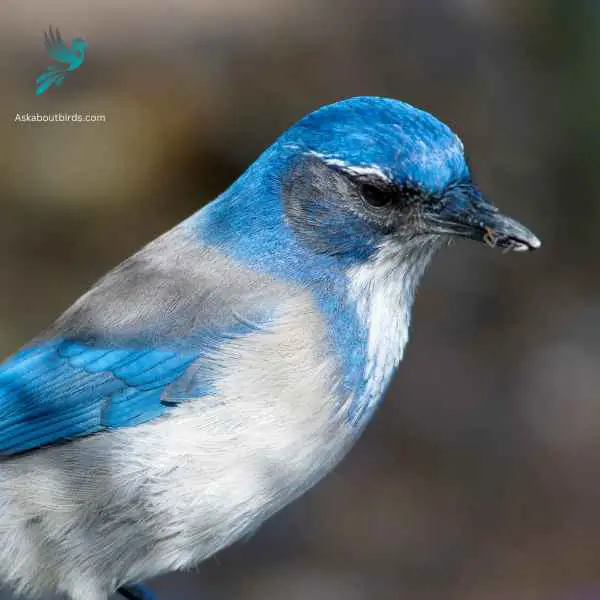
California Scrub-Jay


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Aphelocoma californica |
| Length | 11–12 in |
| Wingspan | 15 in |
| Weight | 80 g |
The California Scrub-Jay is a vivacious bird known for its intelligence and striking appearance, predominantly found in the chaparral, oak woodlands, and residential areas of California and parts of the Pacific Northwest.
Appearance: This jay boasts a vivid blue head, wings, and tail, complemented by a pronounced white eyebrow, a white underbelly, and a soft gray back. A distinguishing feature is the blue necklace or band across its throat and chest, which differentiates it from some other jay species.
Diet: California Scrub-Jays are omnivorous. Their diet consists of insects, fruits, seeds, and nuts, with acorns being a particular favorite. They, like their Floridian counterparts, will also cache acorns and other foods in the ground to consume later.
Reproduction: The California Scrub-Jay forms monogamous pairs. The nests, usually built between 1 to 3 meters off the ground in trees or shrubs, are constructed using twigs and lined with finer materials like hair or plant fibers. The female lays a clutch of 3 to 6 eggs that are greenish or bluish and speckled with brown.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both California Scrub-Jays and Bluebirds exhibit blue feathers, although the shades and patterns may differ.
- Size: California Scrub-Jays and Bluebirds share a similar size range, with California Scrub-Jays measuring around 11.8 to 12.6 inches (30 to 32 centimeters) in length, comparable to the size of Bluebirds.
Differences
- Coloration Patterns: California Scrub-Jays have vibrant blue feathers on their wings, back, and tail, often accompanied by a grayish-brown head and breast. Bluebirds typically display shades of blue on their upperparts and may have additional rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Crest and Head Shape: California Scrub-Jays have a prominent crest on their head, which can be raised or lowered based on their mood. Bluebirds lack a crest and have a more rounded head shape.
- Facial Features: California Scrub-Jays have a longer, pointed bill, while Bluebirds have a more slender bill.
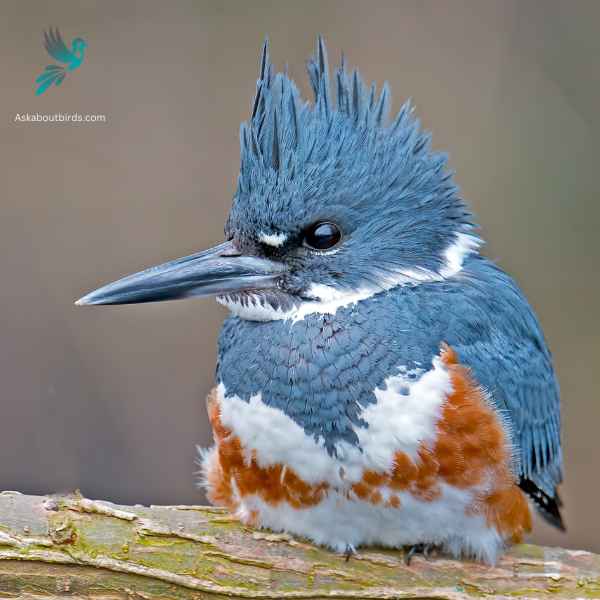
Belted Kingfisher


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Megaceryle alcyon |
| Length | 11–14 in |
| Wingspan | 19–23 in |
| Weight | 113 to 178 g |
The Belted Kingfisher is a distinctive and easily recognizable bird, frequently observed near water bodies, where it can be seen diving headfirst to catch prey.
Appearance: Sporting a prominent crest, the Belted Kingfisher has a slate blue-gray upper body and white underparts. Males possess a single blue band across their white chests, while females have an additional rufous band, making them one of the few bird species where females are more brightly colored than males. Their bill is long, sharp, and dagger-like.
Diet: As expert fishers, Belted Kingfishers mainly prey on small fish, but they’ll also consume crustaceans, insects, and amphibians. They’re known for their hunting tactic of hovering over water, spotting their prey, and then diving swiftly to snatch it.
Reproduction: Belted Kingfishers nest in burrows which they excavate in sandy or earthen banks, usually adjacent to water. The tunnel can be anywhere from 3 to 6 feet long, ending in a chamber. Within this chamber, the female lays a clutch of 5 to 8 white eggs.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both Belted Kingfishers and Bluebirds exhibit blue feathers, although the shades may differ slightly.
- Size: Belted Kingfishers and Bluebirds are similar in size, with Belted Kingfishers measuring around 11 to 14 inches (28 to 36 centimeters) in length, comparable to the size of Bluebirds.
Differences
- Coloration Patterns: Belted Kingfishers have a blue-gray upper body with a white belly and a distinct white collar or “belt,” while Bluebirds typically display shades of blue on their upperparts and may have additional rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Body Shape and Markings: Belted Kingfishers have a stocky build with a large head, a long, straight bill, and a shaggy crest on their head. Bluebirds have a more robust body shape and lack the prominent crest found in Belted Kingfishers.
- Habitat and Behavior: Belted Kingfishers are often found near bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, or coastlines, where they dive and catch fish. Bluebirds, on the other hand, prefer open woodlands, meadows, and suburban areas as their habitat, and they feed primarily on insects and berries.
Blue-gray Gnatcatcher


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Polioptila caerulea |
| Length | 3.9–5.1 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 in |
| Weight | 5–7 g |
The Blue-gray Gnatcatcher is a petite, active bird, frequently observed flitting about treetops, emitting its distinctive high-pitched calls as it moves agilely through the branches.
Appearance: This bird exhibits a predominantly blue-gray plumage with a subtle white eye ring and long, slender tail feathers. The tail has distinctive black and white edging, with the males sometimes showing a faint black line on their forehead during the breeding season.
Diet: Blue-gray Gnatcatchers primarily feed on small insects and spiders. They’re adept hunters, foraging actively among foliage and even catching insects in mid-air.
Reproduction: These birds weave compact, cup-shaped nests on tree branches using plant materials, spider webs, and lichen. The exterior of the nest often matches the tree bark, making it well camouflaged. Inside, the female lays a clutch of 3 to 5 blue or greenish eggs, which she incubates.
Similarities
- Blue Plumage: Both Blue-gray Gnatcatchers and Bluebirds exhibit shades of blue in their plumage, but Blue-gray Gnatcatchers have a lighter and more bluish-gray color compared to the Bluebirds’ deeper blue shades.
- Blue-gray Gnatcatchers and Bluebirds are similar in size, with Blue-gray Gnatcatchers measuring around 4.3 to 4.7 inches (11 to 12 centimeters) in length, comparable to the size of Bluebirds.
Differences
- Blue-gray Gnatcatchers have a predominantly bluish-gray plumage with a white eyering and a white undertail, while Bluebirds typically display shades of blue on their upperparts, along with rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Blue-gray Gnatcatchers have a slender body with a long tail that they actively flick and fan out. Bluebirds have a more robust body shape with a shorter tail.
Black-throated Blue Warbler


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga caerulescens |
| Length | 5.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.5-7.9 in |
| Weight | 8.4–12.4 g |
The Black-throated Blue Warbler is a small migratory bird that breeds in the eastern United States and parts of Canada. The male Black-throated Blue Warbler displays a striking appearance with deep blue plumage on its upperparts, contrasting sharply with a black throat and a white belly. Females, on the other hand, have more muted colors, featuring grayish-olive plumage with a lighter throat.
These warblers prefer deciduous and mixed woodlands, where they forage actively for insects and spiders. They have a slender bill, which they use to extract prey from foliage and tree bark. During the breeding season, males perform courtship displays, showcasing their vibrant plumage and singing a high-pitched song to attract mates.
Black-throated Blue Warblers are known for their long-distance migration. They spend their winters in the Caribbean and Central America, where they inhabit various forested habitats. They construct cup-shaped nests in trees or shrubs, often placing them close to the ground.
Similarities
- Both Black-throated Blue Warblers and Bluebirds display shades of blue in their plumage, although the specific shades may differ slightly.
- Black-throated Blue Warblers and Bluebirds are similar in size, with Black-throated Blue Warblers measuring around 5 to 5.5 inches (13 to 14 centimeters) in length, comparable to the size of Bluebirds.
Differences
- Black-throated Blue Warblers have a distinctive black throat, contrasting with their blue upperparts and white underparts. Bluebirds typically exhibit shades of blue on their upperparts, along with contrasting rusty or orange tones on their chest or flanks.
- Black-throated Blue Warblers have a slender and compact body shape, with males having a bold white patch on their wings. Bluebirds have a more robust body shape and lack the prominent wing patch seen in Black-throated Blue Warblers.
15 Fun Facts About Bluebirds
Bluebird Species: There are three species of true bluebirds found in the United States – Eastern Bluebird, Western Bluebird, and Mountain Bluebird. Each species has its unique characteristics and range.
Symbol of Happiness: Bluebirds are often seen as a symbol of happiness, joy, and good luck. Their vibrant blue plumage and melodious songs bring a sense of beauty and positivity to many people.
Cavity Nesters: Bluebirds are cavity nesters, meaning they seek out pre-existing holes in trees or nest boxes to build their nests. They do not excavate their own nesting cavities like woodpeckers.
Insect Eaters: Bluebirds are primarily insectivorous and feed on a variety of insects and spiders. They play a vital role in controlling insect populations, making them beneficial to gardens and ecosystems.
Nesting Pairs: Bluebirds are typically monogamous and form nesting pairs during the breeding season. They exhibit strong pair bonding and work together to build their nests and raise their young.
Colorful Eggs: Bluebird eggs are usually light blue or pale blue-green in color, which is where their name originates. The coloration helps camouflage the eggs and protect them from predators.
Brood Parasitism: Bluebirds occasionally fall victim to brood parasitism by Brown-headed Cowbirds. Cowbirds lay their eggs in bluebird nests, leaving the bluebirds to raise their young alongside their own.
Winter Migration: While some bluebirds are year-round residents, others undertake short-distance migratory movements to seek warmer climates during the winter months, particularly in northern regions.
Song Identification: Male bluebirds have distinctive songs that they use to defend their territories and attract mates. These songs are melodious and often include a series of whistling or warbling notes.
Nest Box Conservation: The decline of natural nesting sites has led to the establishment of bluebird nest box programs. These initiatives involve the placement of nest boxes to provide suitable nesting habitats for bluebirds and help increase their populations.
Double Brooding: Bluebirds may attempt to raise two broods in a single breeding season. After successfully raising the first brood, they quickly rebuild their nests and start a second nesting cycle.
Habitat Preferences: Bluebirds are commonly found in open habitats such as meadows, fields, and orchards with scattered trees. They require a mix of open space for foraging and perching sites for hunting insects.
Nestling Fledging: Bluebird nestlings fledge (leave the nest) at around 15 to 20 days of age. However, they remain dependent on their parents for food and protection for several weeks after leaving the nest.
Migratory Patterns: Eastern Bluebirds from northern regions often undertake short-distance migrations, moving southward during the colder months. Western and Mountain Bluebirds may exhibit altitudinal migrations, moving to lower elevations in winter.
Conservation Success: Bluebirds have faced population declines in the past due to habitat loss and competition for nesting sites. However, conservation efforts such as the establishment of nest box programs have helped increase their numbers in many areas.
What other birds are blue besides bluebirds?
Here is a list of birds that are blue (15 only)
Blue Jay
Blue-footed Booby
Blue Grosbeak
Blue-throated Macaw
Blue-faced Honeyeater
Blue-winged Teal
Blue-crowned Motmot
Blue-winged Pitta
Blue-faced Parrotfinch
Blue-throated Hummingbird
Blue Rock Thrush
Blue-capped Cordon-bleu
Blue-breasted Fairywren
Blue-headed Vireo
Blue-black Grassquit
Western blue birds
Western scrub jay
Blue canary
Purple martin
Florida scrub jay
Blue heron
Blue grosbeak
What bird looks similar to a bluebird?
Birds that look like bluebirds include the Blue Jay, the Mountain Bluebird, and the Indigo Bunting. Blue Jays are bigger, have a bright blue head, long tail, and distinctive white underparts. Mountain Bluebirds have a more uniform blue color and are found in western North America. Indigo Buntings possess a deep blue color, akin to the night sky. These bird species all share similar blue feathers but differ in size and specific markings.
What is a bird that looks like a blue bird but bigger?
A bird that resembles a blue bird but is larger is the Blue Jay. Blue Jays are one of the other birds often mistaken for bluebirds due to their vibrant blue wings and tail. However, they are significantly larger than most blue bird species, with a distinctive black tail and bright white underparts. Found across eastern North America, they are easily recognizable by their size and coloration.
What is the difference between blue birds and eastern bluebird?
The Eastern Bluebird is a species of bluebird, with its vibrant blue color being a distinctive trait. Eastern Bluebirds, native to eastern North America, have a bright blue head, wings, and tail, with a light orange color on their breast. In contrast, other bluebird species like the Western Bluebirds, found in Western North America, have a deep blue color with an orange-rust colored breast. Notably, male birds are more brightly colored than their female counterparts in these bluebird species.





