From the lush rainforests of the Olympic Peninsula to the arid landscapes of eastern Washington, the state boasts a diverse array of habitats. It’s no surprise then that Washington is home to a spectacular variety of avian species.
Orange Birds Found In Washington
The state’s unique geographical setting contributes to its bird diversity. With habitats ranging from coastal wetlands to alpine regions, rainforests of the Olympic Peninsula, and the arid areas of Eastern Washington, there’s a wide variety of environments that attract different bird species.
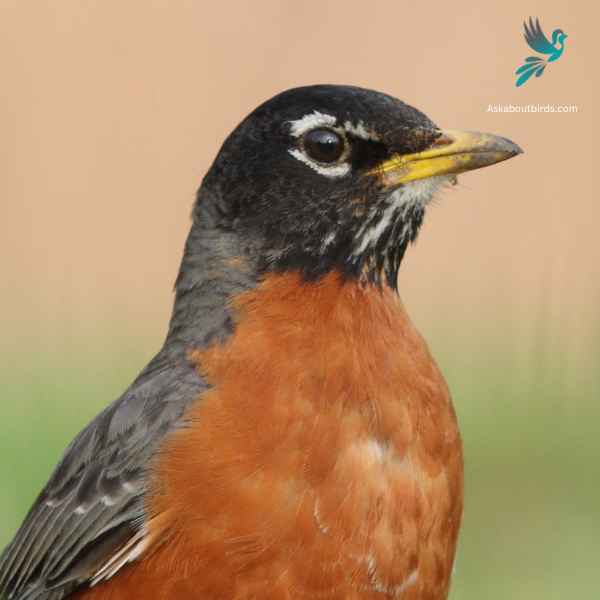
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
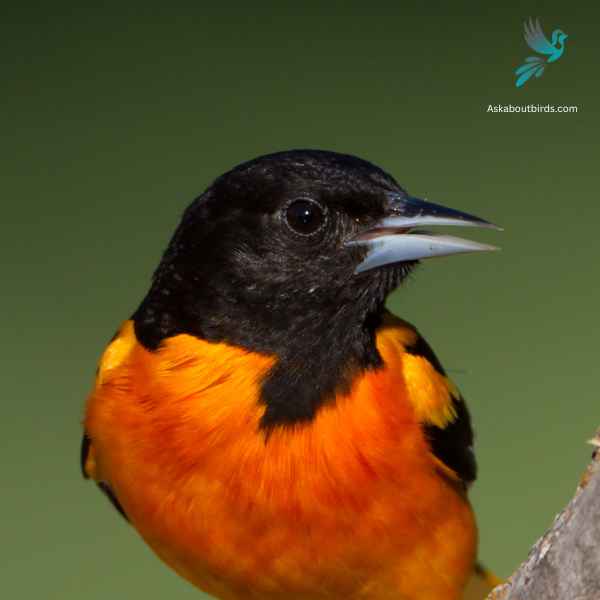
Baltimore Oriole


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus galbula |
| Length | 6.7–8.7 in |
| Wingspan | 9.1–12.6 in |
| Weight | 22.3-42 g |
The Baltimore Oriole is a stunning bird, best known for its vibrant coloration and its rich, whistling song.
Appearance: The male Baltimore Oriole is notable for his bright orange and black plumage and black and white wing bars, a stark contrast to the more muted yellow-brown coloration of the female. Both sexes, however, have long pointed bills and white bars on their wings.
Diet: Baltimore Orioles have a diverse diet that includes insects, fruits, and nectar. Their preference for sweet juices and fruit pulp often brings them to backyard feeders offering oranges and jelly.
Reproduction: The female Baltimore Oriole is responsible for building the distinctive hanging nest, often woven together from fine materials like hair and grass. These nests are usually high in trees to avoid predators. The female lays 3-7 eggs, which are incubated for about two weeks.
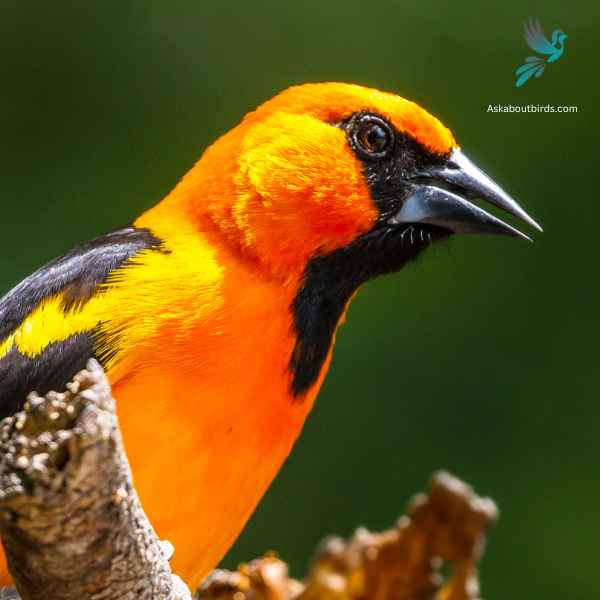
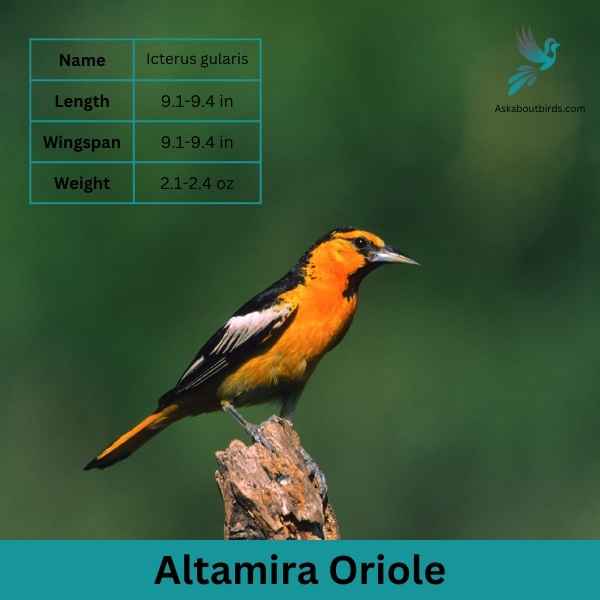
Bullock’s Oriole

| Feature | Measurement (Imperial) |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus bullockii |
| Length | 7.5-8.5 inches |
| Wingspan | 11.8-12.6 inches |
| Weight | 0.9-1.2 oz |
The Bullock’s Oriole is a bright and lively songbird, known for its stunning contrasting colors and vibrant melodies, predominantly found across the western regions of North America.
Appearance: The male Bullock’s Oriole boasts a brilliant orange chest, belly, and face with a black crown, eye line, throat, and back. Its wings are black with a prominent white patch and white-edged coverts. Females are more muted in coloration, displaying a yellowish-orange hue with grayish-brown wings that still retain the white patches.
Diet: These orioles primarily feed on insects, especially caterpillars, beetles, and grasshoppers. Apart from insects, their diet also includes fruits, berries, and nectar. They’re adept foragers, often hanging upside-down on branches to find hidden prey.
Reproduction: Bullock’s Orioles are noted for their skill in crafting hanging, woven nests, often positioned on the tips of slender branches, ensuring they are difficult for predators to access. Both parents partake in feeding the young, who then fledge about two weeks after hatching.
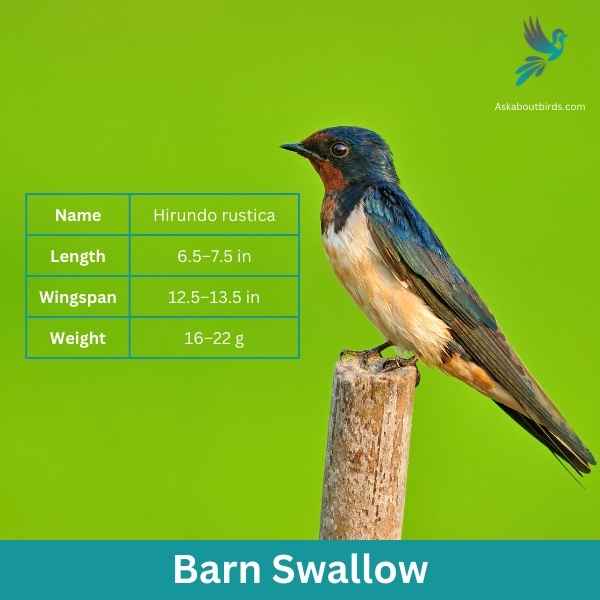
Barn Swallow

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hirundo rustica |
| Length | 6.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.5–13.5 in |
| Weight | 16–22 g |
The Barn Swallow is a sleek, agile bird renowned for its graceful flight patterns and iconic forked tail, often seen darting over fields and water bodies in search of flying insects.
Appearance: Barn Swallows have deep blue, almost iridescent, upperparts and a rufous to tawny underbelly. Their distinctively forked tail and long wings give them a streamlined look. Both males and females have a similar appearance, though males often exhibit slightly brighter colors and a deeper fork in the tail.
Diet: Barn Swallows feed primarily on flying insects, which they catch in mid-air during their agile and acrobatic flights. Their diet includes flies, beetles, moths, and other small flying insects.
Reproduction: Barn Swallows are known for building their mud nests on man-made structures, particularly barns, bridges, and eaves. The nest is cup-shaped and made from mud pellets, often lined with feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs.
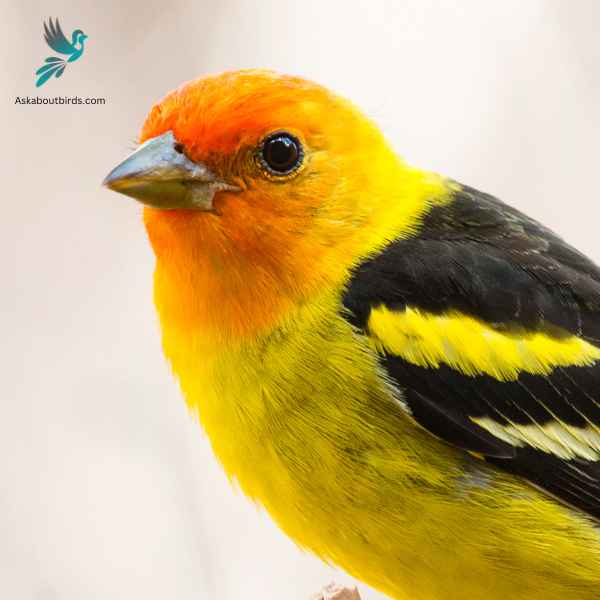
Western Tanager


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga ludoviciana |
| Length | 6.3-7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 11.5 in |
| Weight | 24-36 g |
The Western Tanager is a vibrant songbird that graces the forests and woodlands of the western regions of North America, enchanting observers with its colorful plumage and melodious song.
Appearance: The male Western Tanager is renowned for its bright yellow body contrasted with a striking red head and black wings and tail. The females are more subdued in hue, primarily being yellow with grayish wings and back, and lacking the brilliant red head of the males.
Diet: Western Tanagers primarily feed on insects, especially when breeding, but they also incorporate a significant amount of fruits and berries into their diet, especially during migration and winter.
Reproduction: Western Tanagers build their nests high in coniferous trees, often well concealed from potential predators. The female usually lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubation, while both parents are involved in feeding the chicks after they hatch.
Rufous Hummingbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Selasphorus rufus |
| Length | 3.1–3.9 in |
| Wingspan | 4.3 in |
| Weight | 0.1–0.2 oz |
The Rufous Hummingbird is a small, brilliantly colored bird known for its impressive migratory journeys and feisty behavior.
Appearance: The male Rufous Hummingbird boasts a gleaming orange-red body with a white chest and an iridescent red throat, called a gorget. The female has green upperparts with rufous-washed flanks and tail. Her throat may have some iridescent patches, but it’s generally whitish.
Diet: Like other hummingbirds, the Rufous Hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar from a variety of flowering plants. They also eat insects and spiders for protein, catching them in flight or plucking them from vegetation.
Reproduction: Rufous Hummingbirds nest in trees, shrubs, or even ferns. The female alone selects the site, builds the nest, and cares for the offspring.
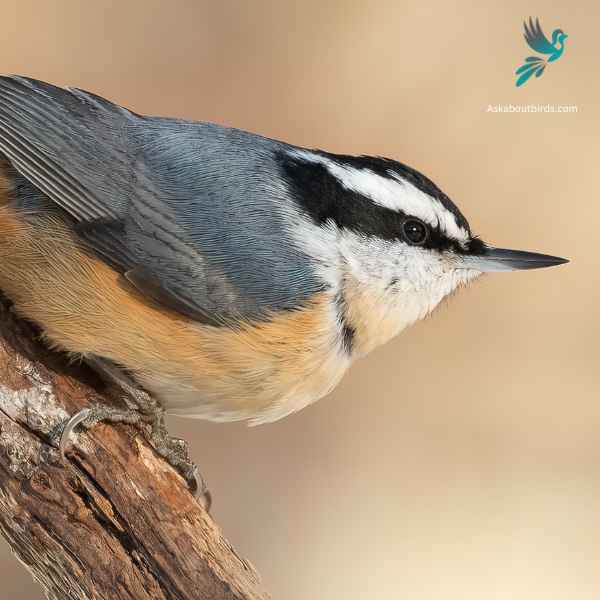
Red-breasted Nuthatch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sitta canadensis |
| Length | 4.3–4.7 in |
| Wingspan | 8.3 in |
| Weight | 0.3–0.5 oz |
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, agile songbird, known for its ability to move headfirst down tree trunks while searching for food.
Appearance: This bird boasts a slate-blue back and a pale rust-red underside. A prominent black stripe runs through the eye and is bordered above by a white eyebrow. Their sharp, pointed bill is characteristic of the species.
Diet: Red-breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds, especially those from coniferous trees. They have a fondness for large seeds, which they wedge into bark crevices to hack open with their bills.
Reproduction: These birds construct nests in natural tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker holes, often lining the entrance with resin. This is thought to deter predators or competitors from entering. The female typically lays a clutch of 5 to 6 eggs, and both parents partake in feeding the chicks once they hatch.
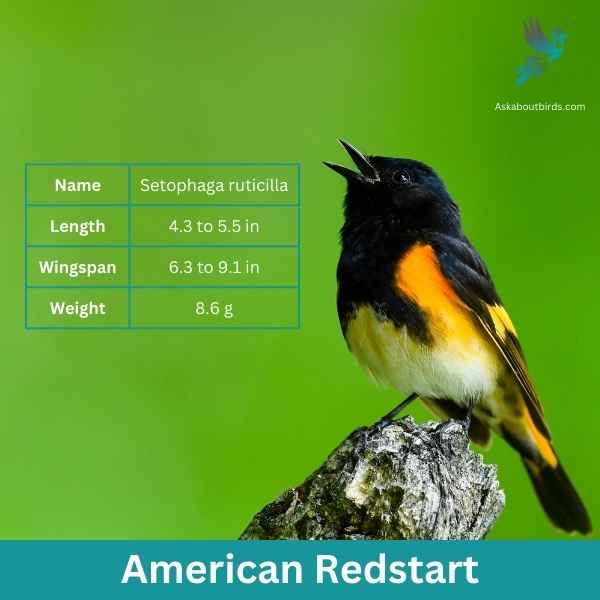
American Redstart

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
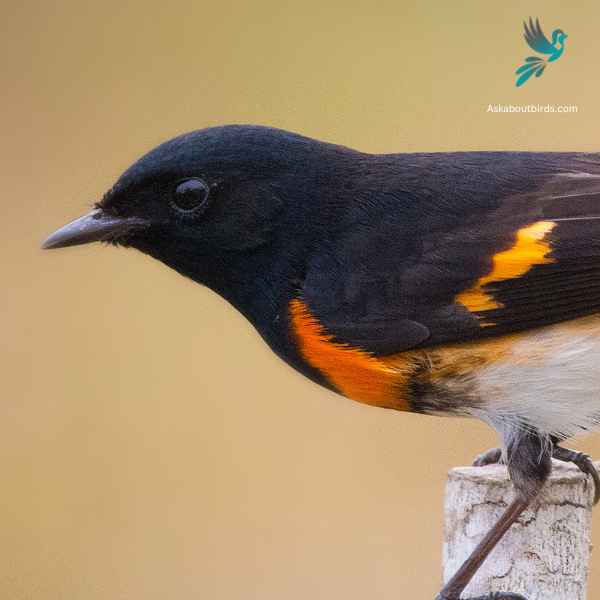
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
Northern Flicker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Colaptes auratus |
| Length | 11–12 in |
| Wingspan | 17–20 in |
| Weight | 3.9–5.6 oz |
The Northern Flicker is a medium-sized woodpecker, recognized by its unique patterns and coloring, often found drumming on trees or foraging on the ground across North America.
Appearance: The Northern Flicker stands out with its grayish brown body, black-scalloped plumage, and a black bib. Males sport a distinctive black or red mustache stripe. Depending on the subspecies, the underwing and undertail feathers can be bright yellow or red, flashing vividly during flight.
Diet: While most woodpeckers are tree-bark foragers, the Northern Flicker prefers hunting on the ground. Its primary diet consists of ants and beetles, supplemented occasionally by fruits, berries, seeds, and other small insects.
Reproduction: Northern Flickers are cavity nesters, preferring to excavate their nesting hole in dead or diseased tree trunks. The interior of the nest is lined with wood chips.
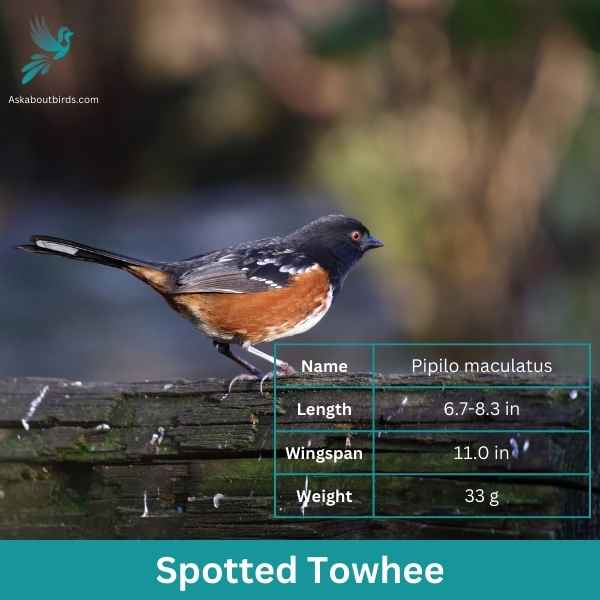
Spotted Towhee

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo maculatus |
| Length | 6.7-8.3 in |
| Wingspan | 11.0 in |
| Weight | 33 g |
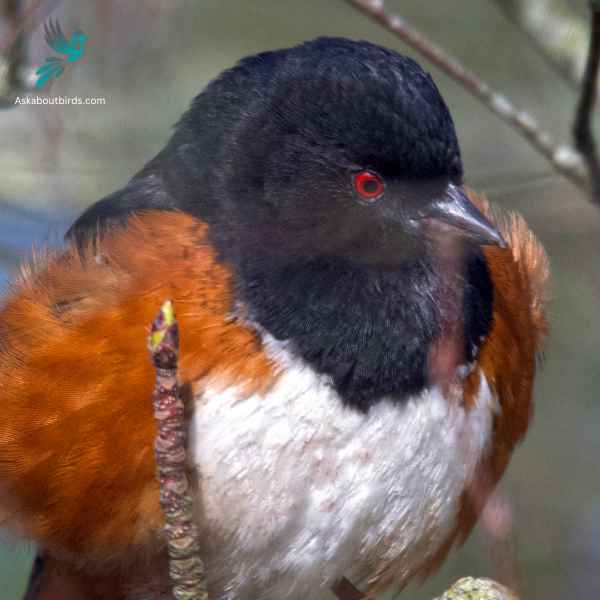
The Spotted Towhee is a distinctive songbird commonly found in the shrubby undergrowth and thickets of the western parts of North America. Its song, a series of melodious chirps, often punctuates the early morning air.
Appearance: Male Spotted Towhees showcase a coal-black head, throat, and upper body contrasted with rufous sides and a white belly. Their wings and back are dark but adorned with white spots, hence their name. Females have a similar pattern but are more brownish than black.
Diet: Spotted Towhees primarily feed on a mixture of insects and seeds. They often forage on the ground, scratching through leaf litter to uncover beetles, ants, and other insects, as well as various seeds and berries.
Reproduction: Spotted Towhees usually nest on the ground, concealed by dense vegetation or sometimes in low shrubs. The female builds the nest and lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. She incubates the eggs, while the male stands guard and both parents partake in feeding the fledglings after hatching.
Varied Thrush


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ixoreus naevius |
| Length | 7.9 to 10.2 in |
| Wingspan | 13 to 17 in |
| Weight | 65 to 100 g |
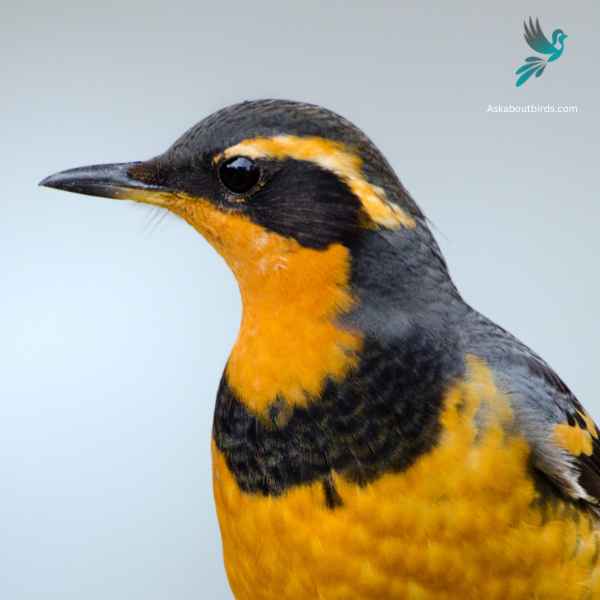
The Varied Thrush is a songbird known for its striking appearance and melodious, haunting song that echoes through the dense forests of the Pacific Northwest.
Appearance: The Varied Thrush has a bold pattern. Males display a blue-gray upper body, contrasted with an orange throat and breast, and a black band that extends from the eyes to the neck. The wings have two orange bands and the belly is usually lighter. Females have a similar pattern but are generally more muted in color.
Diet: Varied Thrushes primarily consume insects, berries, and seeds. Their diet can shift seasonally, with insects being more prevalent in the warmer months and berries and seeds making up the bulk of their diet in colder months.
Reproduction: Varied Thrushes nest in trees, often close to the trunk and concealed by dense branches or foliage. The female typically lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates.
Black-headed Grosbeak
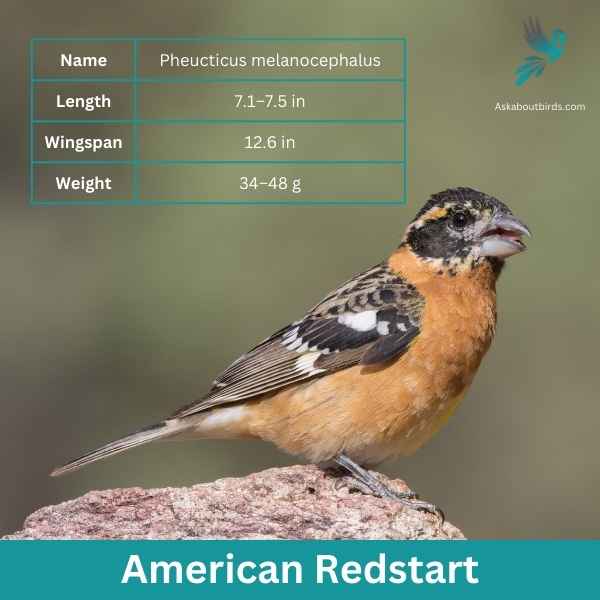

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pheucticus melanocephalus |
| Length | 7.1–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.6 in |
| Weight | 34–48 g |
The Black-headed Grosbeak is a vibrant songbird known for its melodious song, often confused with that of the American Robin but more rich and varied.
Appearance: Males are recognizable by their orange chest, black head, and black and white wings. Females, on the other hand, have a streaked brown appearance, resembling large sparrows but with hints of orange on their sides and flanks.
Diet: Black-headed Grosbeaks primarily feed on insects, seeds, and fruits. They are especially fond of beetles and caterpillars, and they’re one of the few birds that can eat monarch butterflies without suffering from the toxins.
Reproduction: They often nest in deciduous trees or shrubs. The nest is a loose, cup-like structure made from twigs and grasses. The female usually lays 3 to 4 eggs, which she incubates. Both parents share the responsibility of feeding the chicks.
Where to Spot Washington’s Orange Birds
Washington’s varied ecosystems beckon birdwatchers from near and far, offering a stunning array of avian spectacles. For those with a penchant for orange-feathered wonders, here are some top spots:
- Olympic National Park: Home to rainforests, mountains, and coastline, this park attracts a plethora of bird species, including the stunning Western Tanager.
- Nisqually National Wildlife Refuge: A haven for migratory birds, this tidal estuary provides excellent opportunities to spot various waterfowl and songbirds.
- Spokane River: This Eastern Washington river and its associated wetlands are a hotspot for diverse bird species, with its unique interplay of water and arid landscapes.
- Mt. Rainier National Park: Elevated regions not only offer breathtaking views but also house high-altitude bird species, including the vibrant American Robin.
- San Juan Islands: Nestled between the U.S. and Canada, these islands provide diverse habitats attracting a variety of sea birds and passerines.
| State’s Orange Birds | Top Spots for Orange Birds |
|---|---|
| Oregon’s Orange Birds | 1. Malheur National Wildlife Refuge 2. Mount Hood National Forest 3. Siletz Bay National Wildlife Refuge |
| Idaho’s Orange Birds | 1. Coeur d’Alene Lake 2. Sawtooth National Recreation Area 3. Camas National Wildlife Refuge |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in Washington
Which black and orange birds are frequently seen in Washington?
In Washington, the Black-headed Grosbeak is a prominent bird displaying both black and orange colors. These medium-sized birds, with their distinctive black head and bright orange plumage, are particularly noticeable during the spring and summer months. They are fond of sunflower seeds and often visit bird feeders in open woods and forest edges. Their song is melodious, making them a delight for bird enthusiasts.
Are there any orange-bellied birds that frequent Washington’s bird feeders?
Yes, American Robins, with their orange bellies and dark gray wings, are common visitors to bird feeders in Washington, especially those stocked with seeds and fruit. Another bird to watch for is the House Finch, which can have yellow-orange to bright orange bellies, differentiated by their streaked appearance and a distinct black line behind the eye.
What types of birds in Washington have orange wings and white wing patches?
The Barn Swallow is a bird native to Washington with orange to mottled brown underparts and deep blue upperparts. They have a deeply forked tail and exhibit a bright orange hue on their wings, especially noticeable when in flight. Their large white wing patches, combined with their agile flying maneuvers, make them easily distinguishable among other birds.
Do any birds with bright orange throats reside in the western half of Washington?
Certainly! Western Washington, with its dense forests and open woodlands, is a haven for the Red-breasted Nuthatch. This small bird showcases a striking bright orange throat and underparts. They are often seen scaling tree trunks, especially in areas populated by western red cedar trees, in search of insects and seeds. Their distinct “yank-yank” call can be heard echoing through the woods.





