Oklahoma is a geographical crossroads, with its vast prairies merging into the foothills of the Ozarks in the east, and transitioning to arid plains and high mesas in the west. From the bustling suburbs to the tranquil plains, these feathered wonders add a splash of color to the local landscape.
Seasonal migrations further enrich the state’s birdlife, with Oklahoma acting as a critical stopover for many species journeying across the continent. Dive in and let our free photo guide be your compass to the radiant world of Oklahoma’s orange birds!
Orange Birds Found In Oklahoma
The abundance of rivers, lakes, and wetlands offers ample aquatic environments, while the forests and grasslands provide diverse nesting and feeding territories. This tapestry of habitats and strategic location ensures that bird enthusiasts can always find a plethora of species to admire throughout the year.
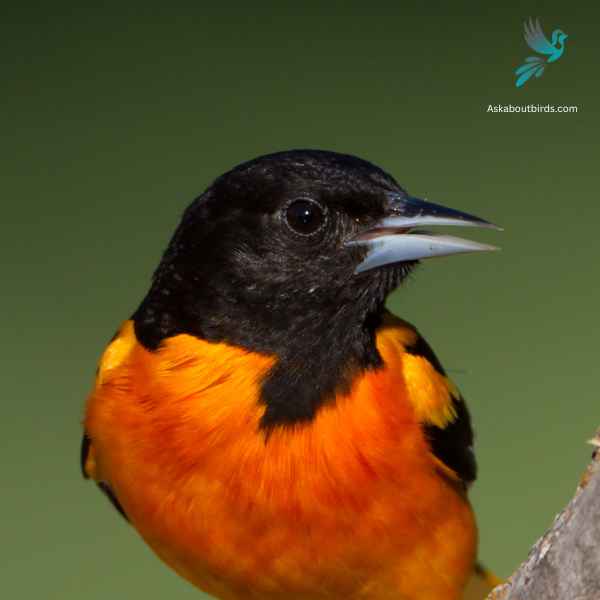
Baltimore Oriole


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus galbula |
| Length | 6.7–8.7 in |
| Wingspan | 9.1–12.6 in |
| Weight | 22.3-42 g |
The Baltimore Oriole is a stunning bird, best known for its vibrant coloration and its rich, whistling song.
Appearance: The male Baltimore Oriole is notable for his bright orange and black plumage and black and white wing bars, a stark contrast to the more muted yellow-brown coloration of the female. Both sexes, however, have long pointed bills and white bars on their wings.
Diet: Baltimore Orioles have a diverse diet that includes insects, fruits, and nectar. Their preference for sweet juices and fruit pulp often brings them to backyard feeders offering oranges and jelly.
Reproduction: The female Baltimore Oriole is responsible for building the distinctive hanging nest, often woven together from fine materials like hair and grass. These nests are usually high in trees to avoid predators. The female lays 3-7 eggs, which are incubated for about two weeks.
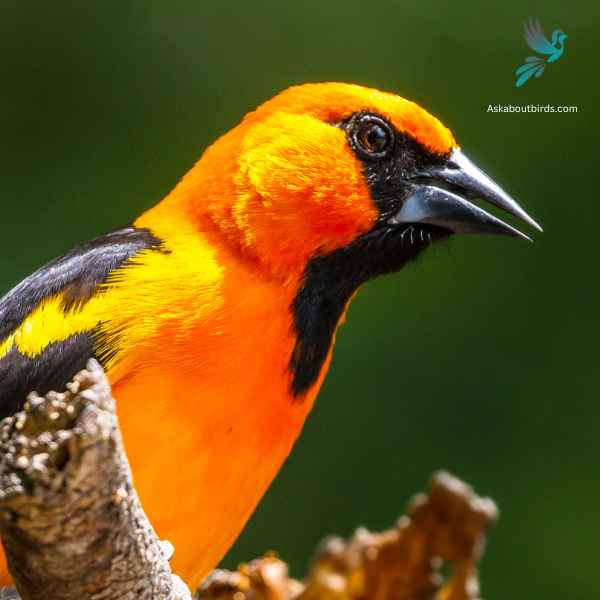
Bullock’s Oriole
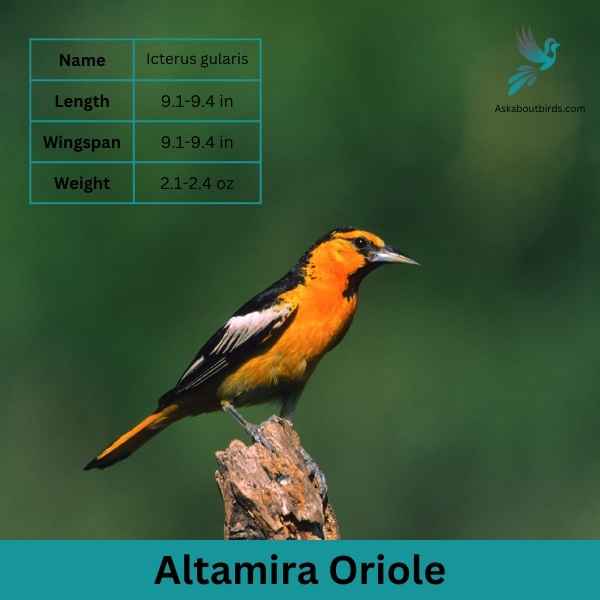

| Feature | Measurement (Imperial) |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus bullockii |
| Length | 7.5-8.5 inches |
| Wingspan | 11.8-12.6 inches |
| Weight | 0.9-1.2 oz |
The Bullock’s Oriole is a bright and lively songbird, known for its stunning contrasting colors and vibrant melodies, predominantly found across the western regions of North America.
Appearance: The male Bullock’s Oriole boasts a brilliant orange chest, belly, and face with a black crown, eye line, throat, and back. Its wings are black with a prominent white patch and white-edged coverts. Females are more muted in coloration, displaying a yellowish-orange hue with grayish-brown wings that still retain the white patches.
Diet: These orioles primarily feed on insects, especially caterpillars, beetles, and grasshoppers. Apart from insects, their diet also includes fruits, berries, and nectar. They’re adept foragers, often hanging upside-down on branches to find hidden prey.
Reproduction: Bullock’s Orioles are noted for their skill in crafting hanging, woven nests, often positioned on the tips of slender branches, ensuring they are difficult for predators to access. Both parents partake in feeding the young, who then fledge about two weeks after hatching.
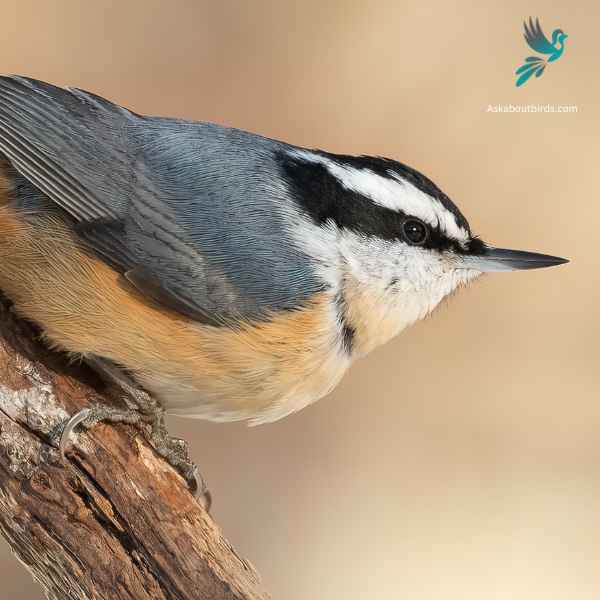
Red-breasted Nuthatch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sitta canadensis |
| Length | 4.3–4.7 in |
| Wingspan | 8.3 in |
| Weight | 0.3–0.5 oz |
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, agile songbird, known for its ability to move headfirst down tree trunks while searching for food.
Appearance: This bird boasts a slate-blue back and a pale rust-red underside. A prominent black stripe runs through the eye and is bordered above by a white eyebrow. Their sharp, pointed bill is characteristic of the species.
Diet: Red-breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds, especially those from coniferous trees. They have a fondness for large seeds, which they wedge into bark crevices to hack open with their bills.
Reproduction: These birds construct nests in natural tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker holes, often lining the entrance with resin. This is thought to deter predators or competitors from entering. The female typically lays a clutch of 5 to 6 eggs, and both parents partake in feeding the chicks once they hatch.
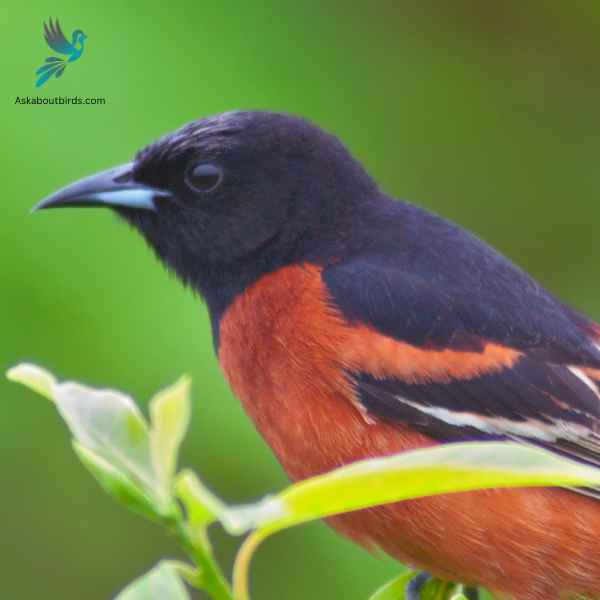
Orchard Oriole
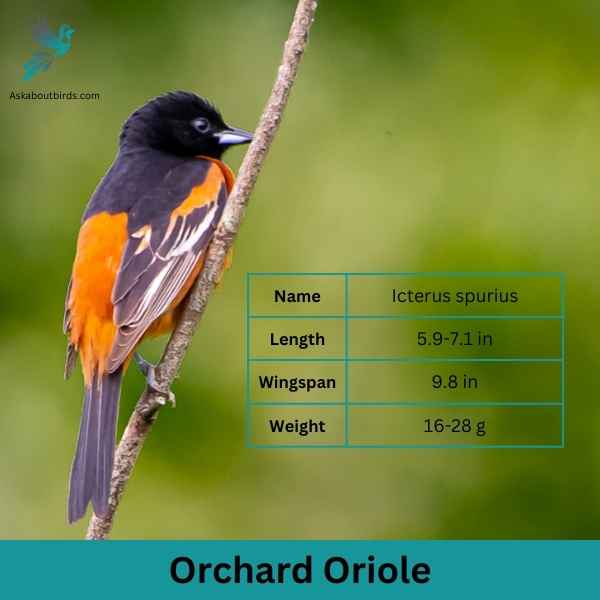

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus spurius |
| Length | 5.9-7.1 in |
| Wingspan | 9.8 in |
| Weight | 16-28 g |
The Orchard Oriole is a small songbird noted for its distinctive coloration and melodic song.
Appearance: Male Orchard Orioles are a striking sight with their dark chestnut body and black head and black and white wings, while females and immature males are olive-green and feature a yellowish underpart. The species is often recognized by its slender body and pointed bill.
Diet: The diet of the Orchard Oriole consists primarily of insects, fruits, and nectar. They are adept at catching insects mid-air and are also known to sip nectar from flowers, aiding in pollination. When fruits are in season, they make up a substantial portion of the bird’s diet.
Reproduction: Orchard Orioles often nest in open woodlands and orchards, hence their name. The female is responsible for building the nest, typically choosing a location in a tree or shrub. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs, which she incubates for about two weeks.
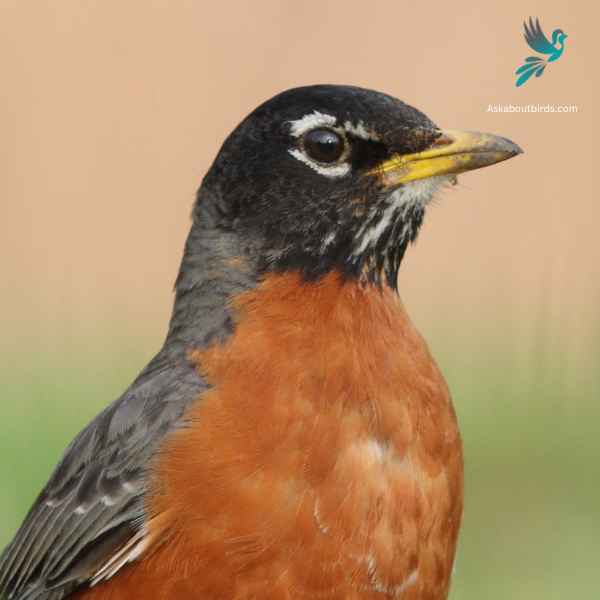
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
Barn Swallow
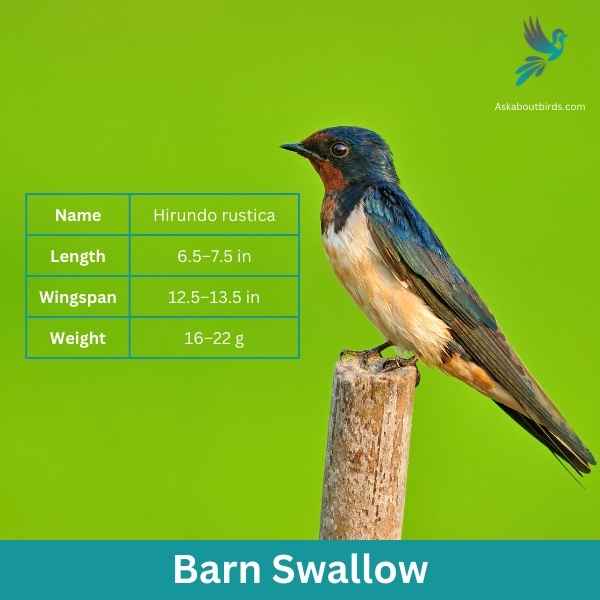

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hirundo rustica |
| Length | 6.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.5–13.5 in |
| Weight | 16–22 g |
The Barn Swallow is a sleek, agile bird renowned for its graceful flight patterns and iconic forked tail, often seen darting over fields and water bodies in search of flying insects.
Appearance: Barn Swallows have deep blue, almost iridescent, upperparts and a rufous to tawny underbelly. Their distinctively forked tail and long wings give them a streamlined look. Both males and females have a similar appearance, though males often exhibit slightly brighter colors and a deeper fork in the tail.
Diet: Barn Swallows feed primarily on flying insects, which they catch in mid-air during their agile and acrobatic flights. Their diet includes flies, beetles, moths, and other small flying insects.
Reproduction: Barn Swallows are known for building their mud nests on man-made structures, particularly barns, bridges, and eaves. The nest is cup-shaped and made from mud pellets, often lined with feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs.
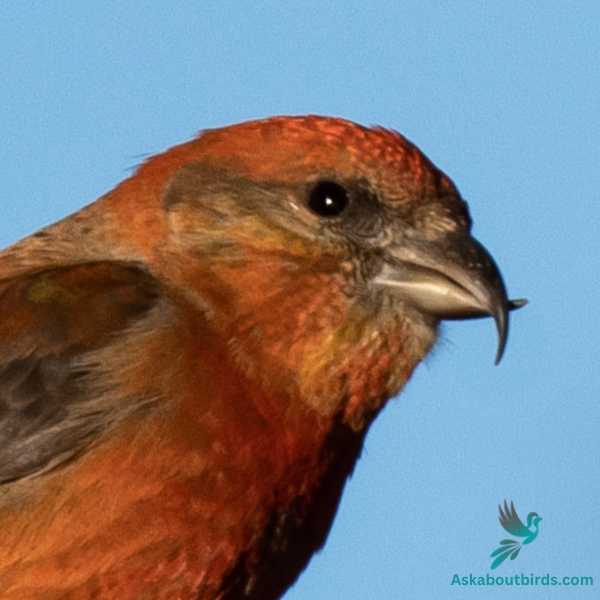
Red Crossbill


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Loxia curvirostra |
| Length | 20 cm |
| Wingspan | 27–29 cm |
| Weight | 40-53 g |
The Red Crossbill is a peculiar bird species, celebrated for its unique beak structure and vibrant coloration.
Appearance: Red Crossbills are named for their distinctive crossed mandibles, which are adapted to extracting seeds from conifer cones. Male Red Crossbills are usually bright red or orange, while females and juveniles are greenish-yellow. All have dark wings and notched tails.
Diet: The diet of the Red Crossbill is primarily composed of conifer seeds, their unique beak allowing them to access these seeds with ease. This diet includes seeds from pine, spruce, and other types of coniferous trees. They are also known to consume some insects.
Reproduction: Red Crossbills are known for their flexible breeding season, which can occur any time of the year when there is an abundance of food. They typically nest in conifers, where the female lays a clutch of 3 to 4 eggs.
House Finch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Haemorhous mexicanus |
| Length | 5–6 in |
| Wingspan | 8–10 in |
| Weight | 0.6–0.9 oz |
The House Finch is a small songbird widely distributed across North America and is commonly found in urban and suburban areas.
Appearance: Males of this species are brightly colored with crimson faces and throats, which can extend to the chest and back, while their flanks have streaks. The female is streaked brown and lacks the red coloring. Both have a square-tipped tail and a distinctively long, flat-topped bill.
Diet: House Finches primarily eat seeds, grains, and berries. They have a particular fondness for sunflower seeds and can be commonly seen at bird feeders. Occasionally, they will also consume insects, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction: House Finches are cavity-nesters and might choose ledges, vents, ledges, and other urban settings. They might also utilize trees or shrubs. Their nests can be made of a wide array of materials, from feathers to twigs.
Rufous Hummingbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Selasphorus rufus |
| Length | 3.1–3.9 in |
| Wingspan | 4.3 in |
| Weight | 0.1–0.2 oz |
The Rufous Hummingbird is a small, brilliantly colored bird known for its impressive migratory journeys and feisty behavior.
Appearance: The male Rufous Hummingbird boasts a gleaming orange-red body with a white chest and an iridescent red throat, called a gorget. The female has green upperparts with rufous-washed flanks and tail. Her throat may have some iridescent patches, but it’s generally whitish.
Diet: Like other hummingbirds, the Rufous Hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar from a variety of flowering plants. They also eat insects and spiders for protein, catching them in flight or plucking them from vegetation.
Reproduction: Rufous Hummingbirds nest in trees, shrubs, or even ferns. The female alone selects the site, builds the nest, and cares for the offspring.
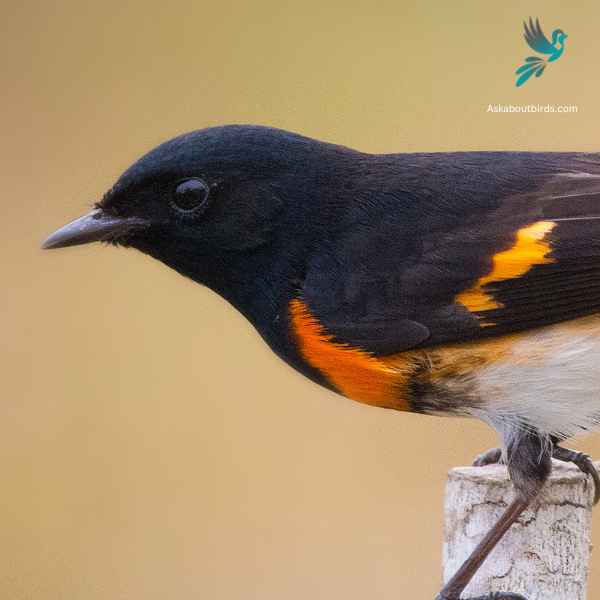
American Redstart
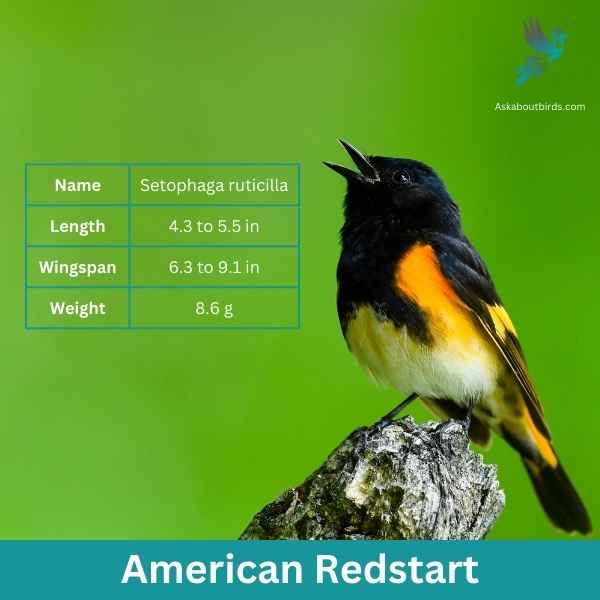

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
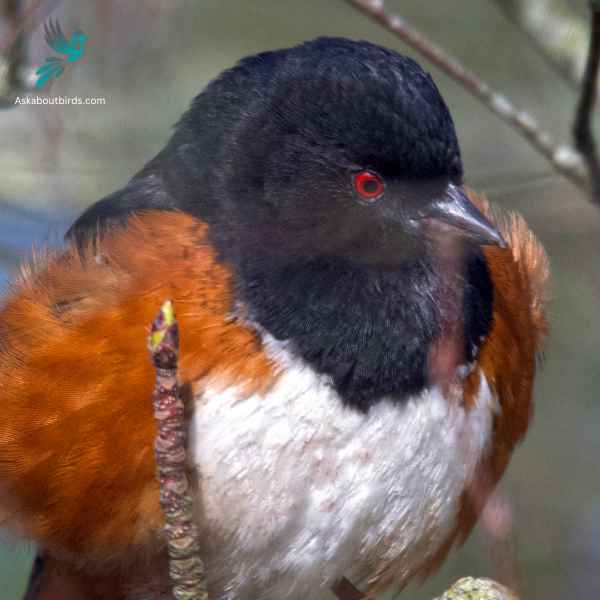
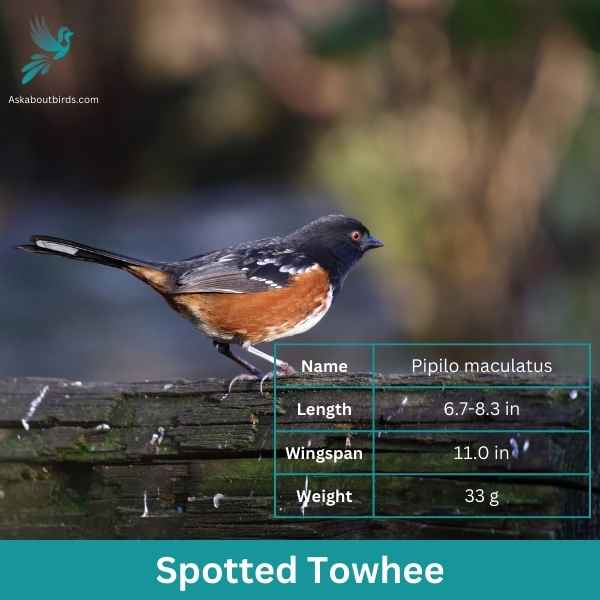
Spotted Towhee

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo maculatus |
| Length | 6.7-8.3 in |
| Wingspan | 11.0 in |
| Weight | 33 g |
The Spotted Towhee is a distinctive songbird commonly found in the shrubby undergrowth and thickets of the western parts of North America. Its song, a series of melodious chirps, often punctuates the early morning air.
Appearance: Male Spotted Towhees showcase a coal-black head, throat, and upper body contrasted with rufous sides and a white belly. Their wings and back are dark but adorned with white spots, hence their name. Females have a similar pattern but are more brownish than black.
Diet: Spotted Towhees primarily feed on a mixture of insects and seeds. They often forage on the ground, scratching through leaf litter to uncover beetles, ants, and other insects, as well as various seeds and berries.
Reproduction: Spotted Towhees usually nest on the ground, concealed by dense vegetation or sometimes in low shrubs. The female builds the nest and lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. She incubates the eggs, while the male stands guard and both parents partake in feeding the fledglings after hatching.
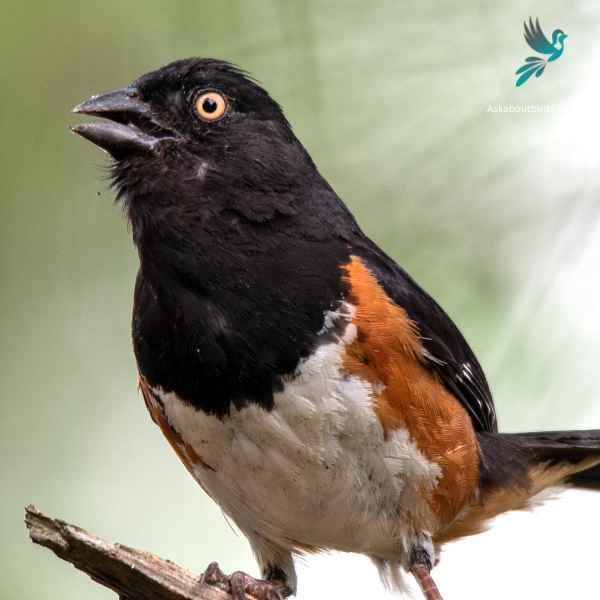
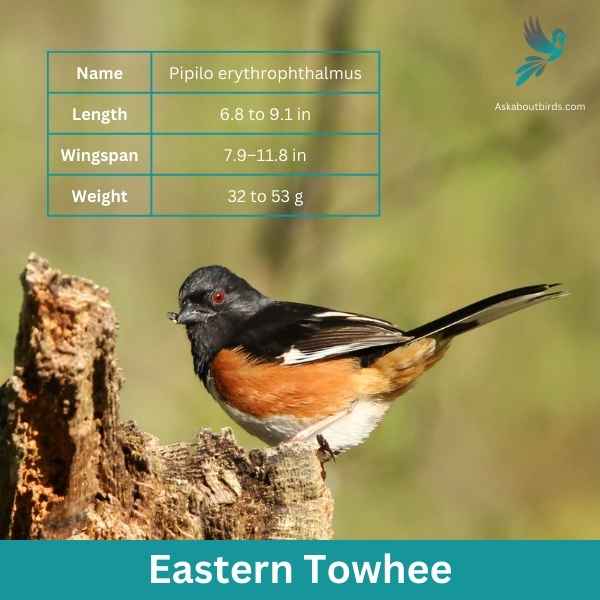
Eastern Towhee

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipilo erythrophthalmus |
| Length | 6.8 to 9.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9–11.8 in |
| Weight | 32 to 53 g |
The Eastern Towhee is a distinctive songbird known for its unique calls and eye-catching coloration.
Appearance: Male Eastern Towhees are characterized by a striking combination of a black head, back and tail, contrasting with a white belly and rufous flanks. Females sport similar patterns but instead of black, they have a rich brown color. Both genders have red eyes, lending a special charm to their overall appearance.
Diet: Eastern Towhees primarily feed on a variety of insects, seeds, and berries. Their diet is quite diverse, taking advantage of seasonal offerings, which includes beetles, caterpillars, spiders, acorns, grass seeds, and various fruits and berries.
Reproduction: Eastern Towhees build their nests on or near the ground, often in a shrub or a small tree. The female lays around 3-5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubating them over about 12-13 days.
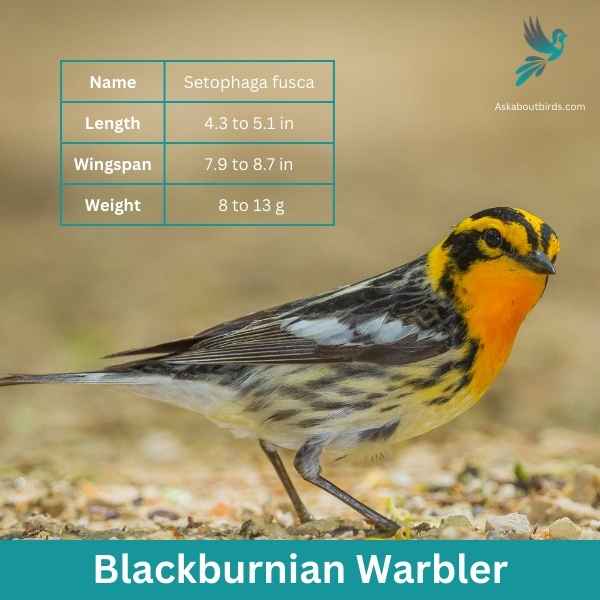
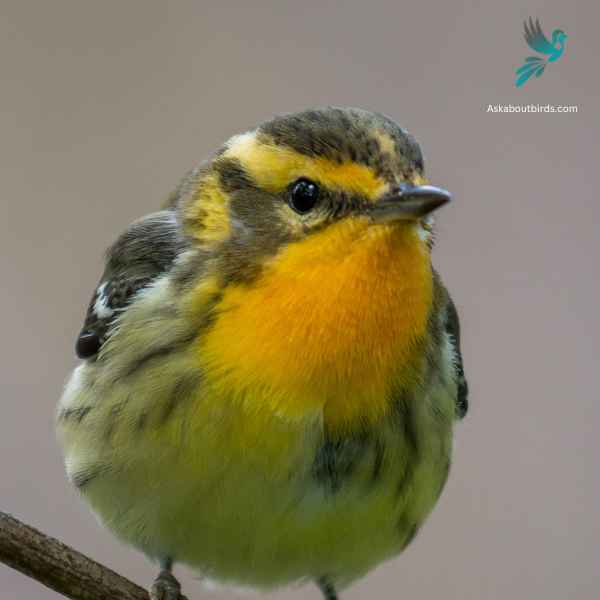
Blackburnian Warbler


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga fusca |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.1 in |
| Wingspan | 7.9 to 8.7 in |
| Weight | 8 to 13 g |
The Blackburnian Warbler is a strikingly colored songbird that captivates observers with its vivid plumage, especially during the breeding season. Often found flitting high in the treetops of North American forests, its melodious song is as enchanting as its appearance.
Appearance: Male Blackburnian Warblers are distinguished by their fiery-orange throats, contrasting sharply with a black face, crown, and streaked back. They also have white underparts with black streaks on the sides. Females have a more muted coloration, with a yellowish or pale orange throat and less pronounced streaking.
Diet: Blackburnian Warblers primarily feed on insects and spiders. They are adept at foraging in the canopy, where they glean insects from the surface of leaves and branches or catch them mid-air in quick, agile flights.
Reproduction: Blackburnian Warblers build their nests high up in coniferous trees, often on horizontal branches. The nest is a neat cup made of twigs, grass, and moss, lined with softer materials like hair or feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 5 eggs and takes the lead in incubation.
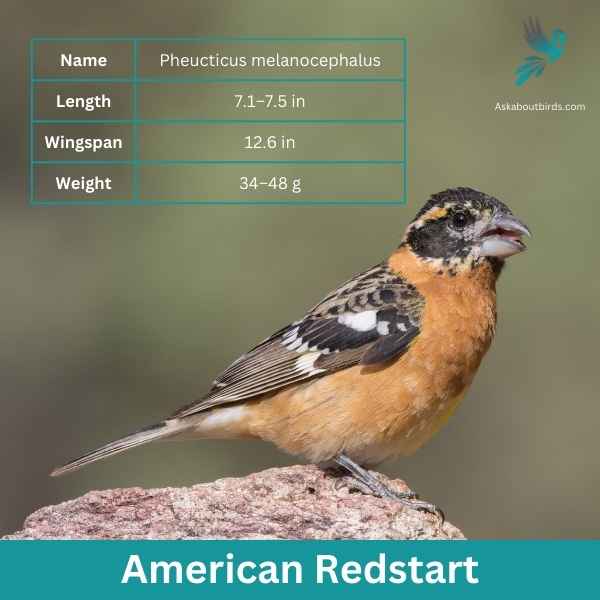
Black-headed Grosbeak

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pheucticus melanocephalus |
| Length | 7.1–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.6 in |
| Weight | 34–48 g |
The Black-headed Grosbeak is a vibrant songbird known for its melodious song, often confused with that of the American Robin but more rich and varied.
Appearance: Males are recognizable by their orange chest, black head, and black and white wings. Females, on the other hand, have a streaked brown appearance, resembling large sparrows but with hints of orange on their sides and flanks.
Diet: Black-headed Grosbeaks primarily feed on insects, seeds, and fruits. They are especially fond of beetles and caterpillars, and they’re one of the few birds that can eat monarch butterflies without suffering from the toxins.
Reproduction: They often nest in deciduous trees or shrubs. The nest is a loose, cup-like structure made from twigs and grasses. The female usually lays 3 to 4 eggs, which she incubates. Both parents share the responsibility of feeding the chicks.
Where to Spot Oklahoma’s Orange Birds
Oklahoma’s diverse habitats are a haven for bird enthusiasts, offering unique locations that are particularly remarkable for observing a plethora of orange-feathered avians.
- Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge: Located in southwestern Oklahoma, this refuge is home to free-ranging American bison, longhorn cattle, and white-tailed deer, creating a vibrant ecosystem that attracts various bird species, especially during migration seasons.
- Salt Plains National Wildlife Refuge: A crucial stopover for migratory birds, this location provides a stunning backdrop of crystal-like salt flats and is a prime location to spot a variety of orange birds amidst the shimmering plains.
- Oxley Nature Center: Situated in Tulsa, Oxley boasts diverse habitats from marshes to forests. The well-marked trails and boardwalks make it an accessible place to watch vibrant birdlife, including many orange-hued species.
- Sequoyah National Wildlife Refuge: Nestled where the Arkansas and Canadian rivers meet, this refuge is teeming with waterfowl and other bird species, offering watchers a chance to see diverse avian life amidst scenic landscapes.
- Red Slough Wildlife Management Area: Located in the southeastern corner of the state, this wetland habitat is Oklahoma’s birdwatching gem, drawing enthusiasts with its rich array of bird species, including many that sport vibrant orange plumages.
| State’s Orange Birds | Best Spots for Orange Birds |
|---|---|
| Texas’s Orange birds | 1. Big Bend National Park 2. Aransas National Wildlife Refuge 3. High Island |
| Arkansas’s Orange birds | 1. Hot Springs National Park 2. Buffalo National River 3. Holla Bend National Wildlife Refuge |
| Missouri’s Orange birds | 1. Mingo National Wildlife Refuge 2. Mark Twain National Forest 3. Swan Lake National Wildlife Refuge |
| Kansas’s Orange birds | 1. Quivira National Wildlife Refuge 2. Cheyenne Bottoms 3. Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve |
| Colorado’s Orange birds | 1. Rocky Mountain National Park 2. San Juan National Forest 3. Pawnee National Grassland |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in Oklahoma
What bird has an orange chest in Oklahoma?
In Oklahoma, the Western Tanager is a bird known for its striking orange chest. Male Western Tanagers display a brilliant combination of a bright red face and an orange-yellow chest, with black wings and back, making them stand out in the state’s diverse avian population.
What bird has a bright orange beak in Oklahoma?
The American White Pelican, commonly found in Oklahoma during its migratory periods, sports a bright orange beak. This large bird is distinctive not only because of its bill but also its size, white plumage, and black wingtips. While they mainly feed on fish, their vibrant beaks play an essential role in their scooping feeding method.
Oklahoma’s landscapes, dotted with tall trees, provide a haven for a variety of bird species, each adding its unique hue to the state’s natural palette. Among these, birds with bright orange plumage, like the Baltimore Oriole, stand out remarkably against the lush greenery. This striking bird, along with others like the Eastern Towhee, flaunts a rusty orange breast and rusty orange feathers, making them easy to spot for even the novice birdwatcher.
It’s not just the shades of orange that catch the eye; the state is also home to several birds with bright yellow feathers, such as the American Goldfinch. These yellow birds, juxtaposed with those of a rusty orange color, create a vibrant tapestry of life in Oklahoma’s woodlands and backyards. As the sun filters through the branches of the tall trees, it casts a shimmering light on these colorful inhabitants, making birdwatching in Oklahoma a truly enchanting experience.




