From the arid deserts to the rugged mountains, Nevada’s diverse landscapes are home to a colorful array of avian wonders. The Great Basin’s varying elevations and isolated water sources draw migratory routes, while the state’s ecological diversity supports both desert-adapted birds and mountain dwellers.
Dive into our guide on the 9 most captivating orange birds you can spot in the Silver State, complete with a complimentary photo guide to enhance your birdwatching experience.
Orange Birds Found In Nevada
Nevada’s unique blend of arid landscapes, alpine woodlands, and wetland oases creates diverse habitats that cater to a wide array of avian species. It’s this geographical juxtaposition that makes Nevada a birdwatcher’s paradise, with a rich tapestry of species awaiting discovery.
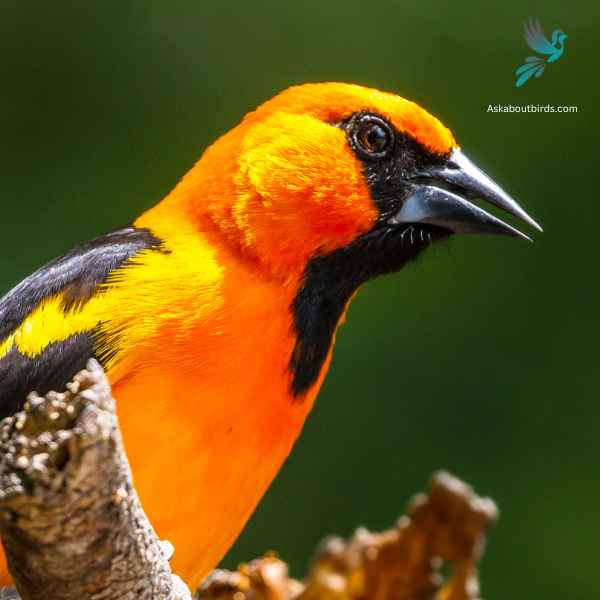
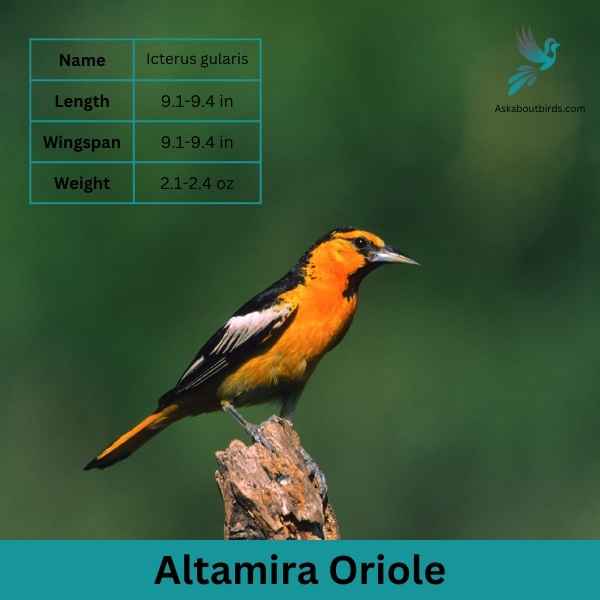
Bullock’s Oriole

| Feature | Measurement (Imperial) |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus bullockii |
| Length | 7.5-8.5 inches |
| Wingspan | 11.8-12.6 inches |
| Weight | 0.9-1.2 oz |
The Bullock’s Oriole is a bright and lively songbird, known for its stunning contrasting colors and vibrant melodies, predominantly found across the western regions of North America.
Appearance: The male Bullock’s Oriole boasts a brilliant orange chest, belly, and face with a black crown, eye line, throat, and back. Its wings are black with a prominent white patch and white-edged coverts. Females are more muted in coloration, displaying a yellowish-orange hue with grayish-brown wings that still retain the white patches.
Diet: These orioles primarily feed on insects, especially caterpillars, beetles, and grasshoppers. Apart from insects, their diet also includes fruits, berries, and nectar. They’re adept foragers, often hanging upside-down on branches to find hidden prey.
Reproduction: Bullock’s Orioles are noted for their skill in crafting hanging, woven nests, often positioned on the tips of slender branches, ensuring they are difficult for predators to access. Both parents partake in feeding the young, who then fledge about two weeks after hatching.
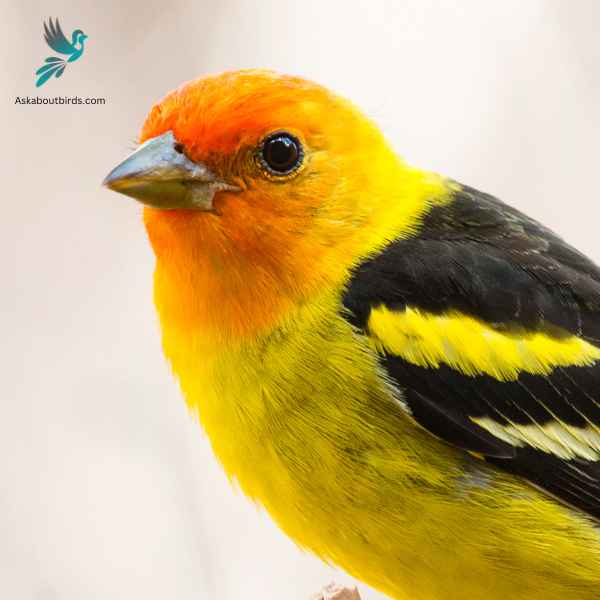
Western Tanager


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga ludoviciana |
| Length | 6.3-7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 11.5 in |
| Weight | 24-36 g |
The Western Tanager is a vibrant songbird that graces the forests and woodlands of the western regions of North America, enchanting observers with its colorful plumage and melodious song.
Appearance: The male Western Tanager is renowned for its bright yellow body contrasted with a striking red head and black wings and tail. The females are more subdued in hue, primarily being yellow with grayish wings and back, and lacking the brilliant red head of the males.
Diet: Western Tanagers primarily feed on insects, especially when breeding, but they also incorporate a significant amount of fruits and berries into their diet, especially during migration and winter.
Reproduction: Western Tanagers build their nests high in coniferous trees, often well concealed from potential predators. The female usually lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs and takes the primary role in incubation, while both parents are involved in feeding the chicks after they hatch.
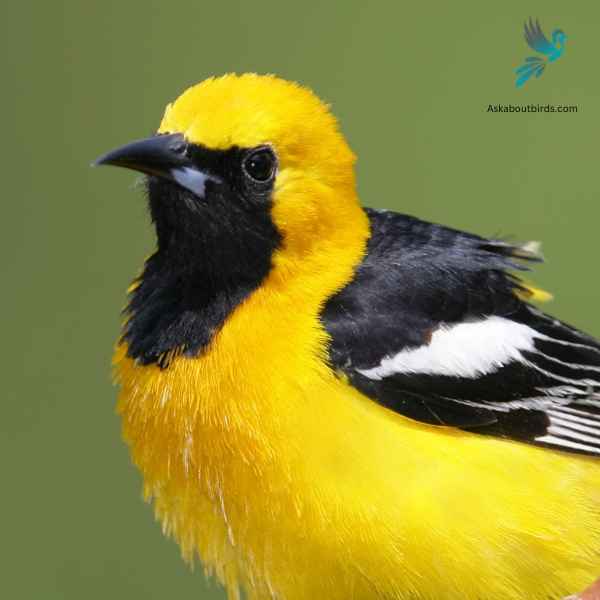
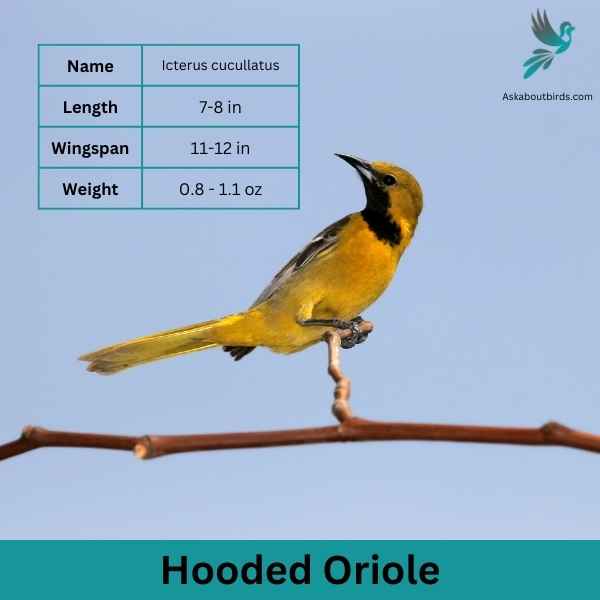
Hooded Oriole

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Icterus cucullatus |
| Length | 7-8 in |
| Wingspan | 11-12 in |
| Weight | 0.8 – 1.1 oz |
The Hooded Oriole is a brightly colored bird commonly found in the southwestern United States and Mexico, recognized for its vibrant orange-yellow plumage and melodic songs.
Appearance: Males boast a deep orange body contrasted with a black bib, face, and throat, while the wings and tail are predominantly black with white wing bars. Females have a paler, yellow-green appearance, lacking the distinctive hood found in males. Both sexes have long tail feathers and a slightly curved bill.
Diet: The Hooded Oriole’s diet mainly consists of insects, nectar, and fruit. They are especially fond of the nectar from flowers and hummingbird feeders, often competing with hummingbirds for access.
Reproduction: These birds are known to use palm trees for nesting, weaving their nests to the underside of large palm fronds. The nest is a deep pouch, which offers protection to the 3-5 eggs that are typically laid. Both parents share in feeding the young after they hatch.
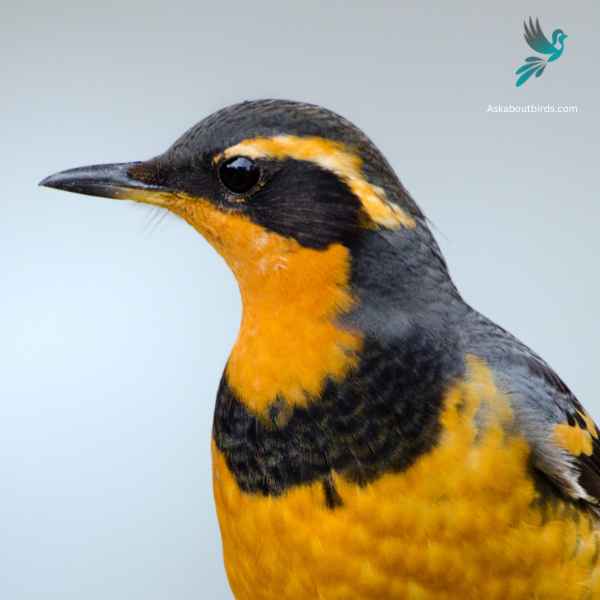
Varied Thrush


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ixoreus naevius |
| Length | 7.9 to 10.2 in |
| Wingspan | 13 to 17 in |
| Weight | 65 to 100 g |
The Varied Thrush is a songbird known for its striking appearance and melodious, haunting song that echoes through the dense forests of the Pacific Northwest.
Appearance: The Varied Thrush has a bold pattern. Males display a blue-gray upper body, contrasted with an orange throat and breast, and a black band that extends from the eyes to the neck. The wings have two orange bands and the belly is usually lighter. Females have a similar pattern but are generally more muted in color.
Diet: Varied Thrushes primarily consume insects, berries, and seeds. Their diet can shift seasonally, with insects being more prevalent in the warmer months and berries and seeds making up the bulk of their diet in colder months.
Reproduction: Varied Thrushes nest in trees, often close to the trunk and concealed by dense branches or foliage. The female typically lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates.
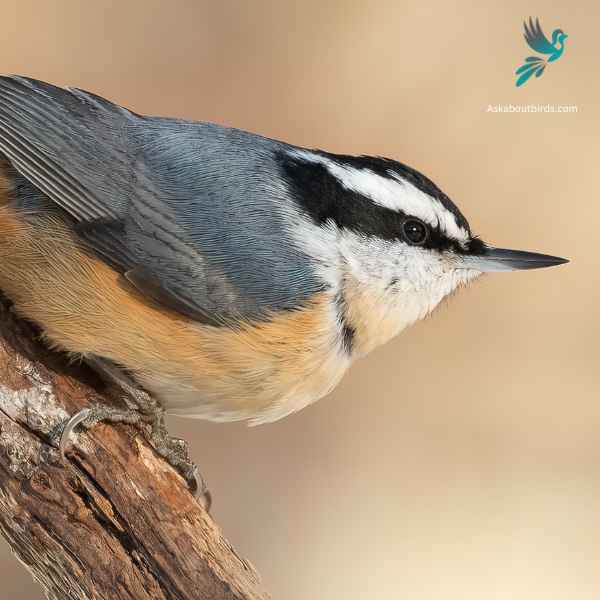
Red-breasted Nuthatch


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sitta canadensis |
| Length | 4.3–4.7 in |
| Wingspan | 8.3 in |
| Weight | 0.3–0.5 oz |
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, agile songbird, known for its ability to move headfirst down tree trunks while searching for food.
Appearance: This bird boasts a slate-blue back and a pale rust-red underside. A prominent black stripe runs through the eye and is bordered above by a white eyebrow. Their sharp, pointed bill is characteristic of the species.
Diet: Red-breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds, especially those from coniferous trees. They have a fondness for large seeds, which they wedge into bark crevices to hack open with their bills.
Reproduction: These birds construct nests in natural tree cavities or abandoned woodpecker holes, often lining the entrance with resin. This is thought to deter predators or competitors from entering. The female typically lays a clutch of 5 to 6 eggs, and both parents partake in feeding the chicks once they hatch.
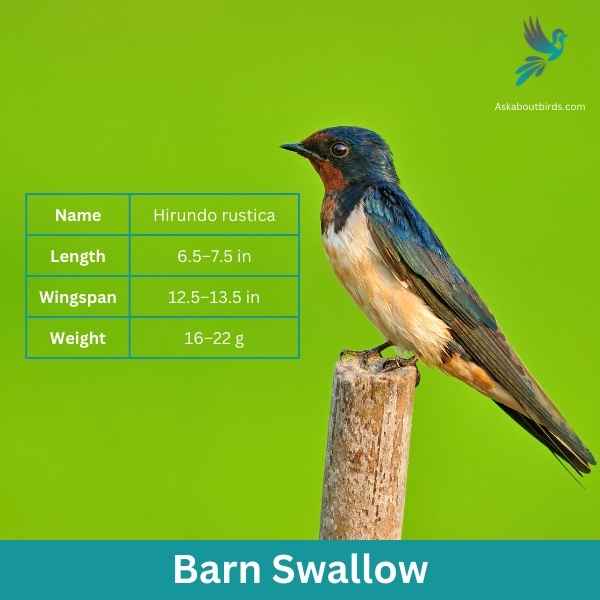
Barn Swallow

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hirundo rustica |
| Length | 6.5–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.5–13.5 in |
| Weight | 16–22 g |
The Barn Swallow is a sleek, agile bird renowned for its graceful flight patterns and iconic forked tail, often seen darting over fields and water bodies in search of flying insects.
Appearance: Barn Swallows have deep blue, almost iridescent, upperparts and a rufous to tawny underbelly. Their distinctively forked tail and long wings give them a streamlined look. Both males and females have a similar appearance, though males often exhibit slightly brighter colors and a deeper fork in the tail.
Diet: Barn Swallows feed primarily on flying insects, which they catch in mid-air during their agile and acrobatic flights. Their diet includes flies, beetles, moths, and other small flying insects.
Reproduction: Barn Swallows are known for building their mud nests on man-made structures, particularly barns, bridges, and eaves. The nest is cup-shaped and made from mud pellets, often lined with feathers. The female lays a clutch of 4 to 6 eggs.
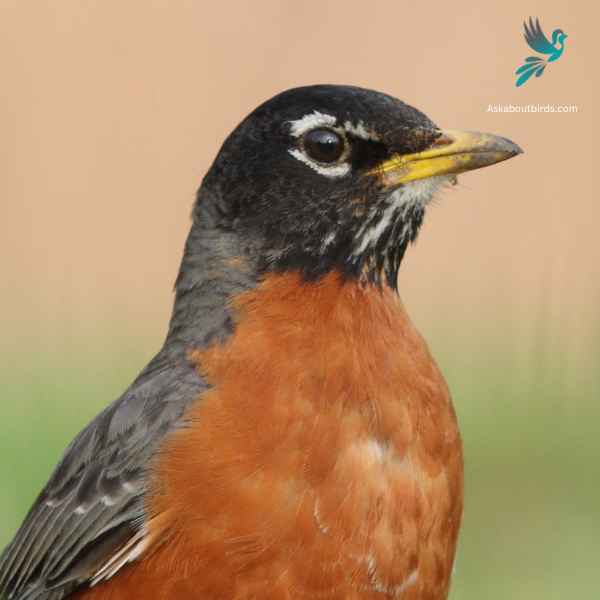
American Robins


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptotila plumbeicep |
| Length | 10.6-11.8 in |
| Wingspan | — |
| Weight | 160-200 g |
The American Robin is a widely recognized bird species known for its melodious song and early bird tendencies.
Appearance: American Robins are medium-sized birds with a distinctive appearance. Both males and females sport a gray to brown back and a warm red to orange breast and belly and gray wings. They also have a characteristic white eye-ring and a black head, but males are usually darker than females.
Diet: American Robins have a diverse diet that changes depending on the season. In summer, they feed heavily on earthworms, beetles, and other invertebrates, which they catch on the ground. During winter, they mostly eat fruits and berries.
Reproduction: American Robins usually build their nests in trees or shrubs, but they are also known to nest on human-made structures. The female lays a clutch of about 3 to 5 eggs, which she incubates for about 12 to 14 days.
Rufous Hummingbird


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Selasphorus rufus |
| Length | 3.1–3.9 in |
| Wingspan | 4.3 in |
| Weight | 0.1–0.2 oz |
The Rufous Hummingbird is a small, brilliantly colored bird known for its impressive migratory journeys and feisty behavior.
Appearance: The male Rufous Hummingbird boasts a gleaming orange-red body with a white chest and an iridescent red throat, called a gorget. The female has green upperparts with rufous-washed flanks and tail. Her throat may have some iridescent patches, but it’s generally whitish.
Diet: Like other hummingbirds, the Rufous Hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar from a variety of flowering plants. They also eat insects and spiders for protein, catching them in flight or plucking them from vegetation.
Reproduction: Rufous Hummingbirds nest in trees, shrubs, or even ferns. The female alone selects the site, builds the nest, and cares for the offspring.
Northern Flicker


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Colaptes auratus |
| Length | 11–12 in |
| Wingspan | 17–20 in |
| Weight | 3.9–5.6 oz |
The Northern Flicker is a medium-sized woodpecker, recognized by its unique patterns and coloring, often found drumming on trees or foraging on the ground across North America.
Appearance: The Northern Flicker stands out with its grayish brown body, black-scalloped plumage, and a black bib. Males sport a distinctive black or red mustache stripe. Depending on the subspecies, the underwing and undertail feathers can be bright yellow or red, flashing vividly during flight.
Diet: While most woodpeckers are tree-bark foragers, the Northern Flicker prefers hunting on the ground. Its primary diet consists of ants and beetles, supplemented occasionally by fruits, berries, seeds, and other small insects.
Reproduction: Northern Flickers are cavity nesters, preferring to excavate their nesting hole in dead or diseased tree trunks. The interior of the nest is lined with wood chips.
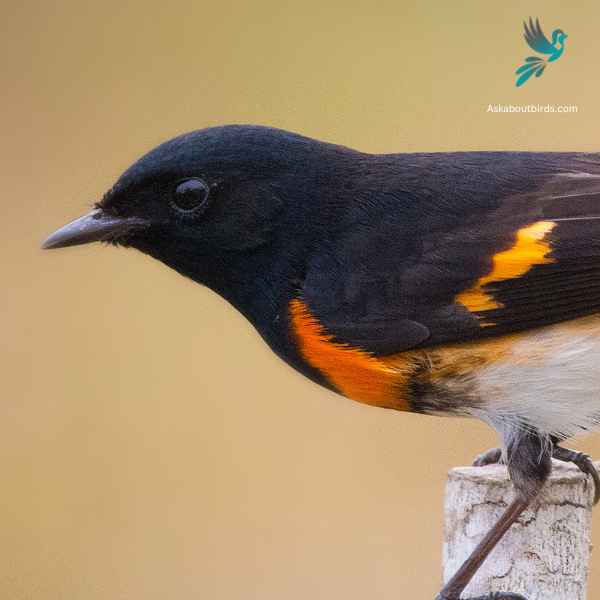
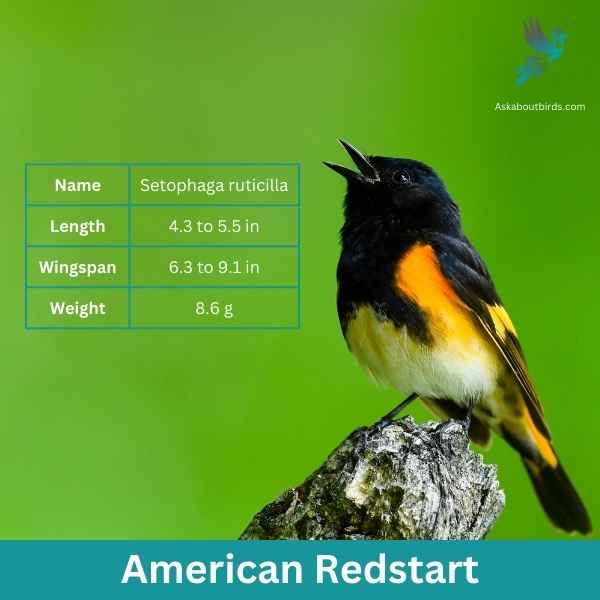
American Redstart

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Setophaga ruticilla |
| Length | 4.3 to 5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 6.3 to 9.1 in |
| Weight | 8.6 g |
The American Redstart is a lively warbler known for its vivid colors and active hunting style, often seen flitting about, fanning its tail to startle and catch insects.
Appearance: Adult male American Redstarts boast striking black plumage with bright orange patches on the sides, wings, and tail. Females and immature males have grayish-olive upperparts with yellow patches in the same areas where the males display orange.
Diet: American Redstarts are primarily insectivores. They actively forage for flying insects, as well as caterpillars and spiders, often using their colorful tails to startle prey and make them easier to catch.
Reproduction: The female American Redstart builds a cup-shaped nest in the fork of a tree branch. Typically, she lays a clutch of 3 to 5 eggs. The female takes on the primary responsibility of incubating the eggs, while both parents participate in feeding the fledglings after they hatch.
Black-headed Grosbeak
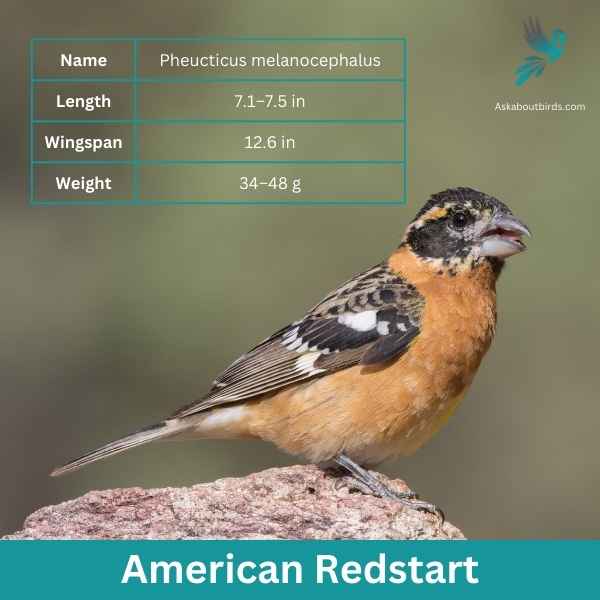

| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pheucticus melanocephalus |
| Length | 7.1–7.5 in |
| Wingspan | 12.6 in |
| Weight | 34–48 g |
The Black-headed Grosbeak is a vibrant songbird known for its melodious song, often confused with that of the American Robin but more rich and varied.
Appearance: Males are recognizable by their orange chest, black head, and black and white wings. Females, on the other hand, have a streaked brown appearance, resembling large sparrows but with hints of orange on their sides and flanks.
Diet: Black-headed Grosbeaks primarily feed on insects, seeds, and fruits. They are especially fond of beetles and caterpillars, and they’re one of the few birds that can eat monarch butterflies without suffering from the toxins.
Reproduction: They often nest in deciduous trees or shrubs. The nest is a loose, cup-like structure made from twigs and grasses. The female usually lays 3 to 4 eggs, which she incubates. Both parents share the responsibility of feeding the chicks.
Summer Tanager


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Piranga rubra |
| Length | 6.7 in |
| Wingspan | 28 to 30 cm |
| Weight | 29 g |
The Summer Tanager is a medium-sized songbird admired for its radiant plumage and melodious song.
Appearance: Male Summer Tanagers are an impressive bright red, while females and juveniles present a softer, yellow-orange color. Both genders have a large, slightly hooked bill and relatively short tail.
Diet: Summer Tanagers primarily feed on insects, including bees and wasps, which they catch in flight or pick off vegetation. They are also known to eat fruits and berries, making them helpful in controlling pest populations and seed dispersal.
Reproduction: The female Summer Tanager builds a loose, shallow cup-shaped nest out of twigs and grass, usually hidden in the foliage of trees. The female typically lays 3-5 eggs, which she will incubate for about two weeks.
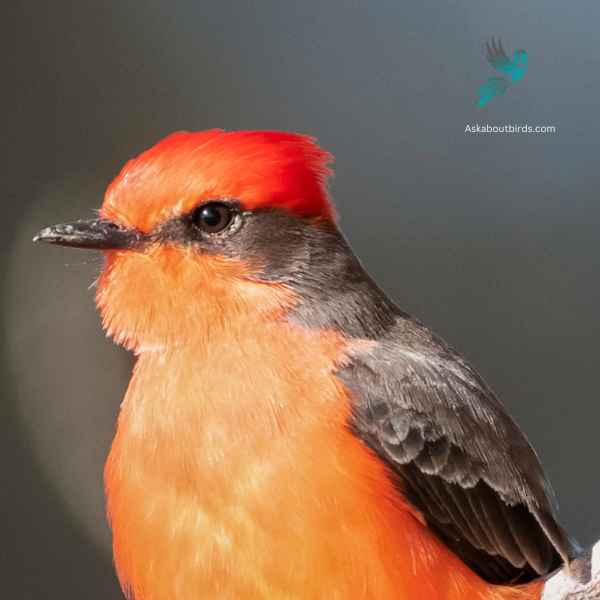
Vermilion Flycatcher


| Feature | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pyrocephalus obscurus |
| Length | 5.1–5.5 in |
| Wingspan | 9.4 to 9.8 in |
| Weight | 11 to 14 g |
The Vermilion Flycatcher is a small and colorful bird native to the Americas. The male Vermilion Flycatcher is a striking sight, displaying a vibrant red plumage on its head, breast, and underparts, contrasting with its brown wings and black tail below. Females, on the other hand, have more muted colors, featuring a pale yellowish belly and grayish-brown upperparts.
Vermilion Flycatchers are known for their lively and acrobatic flight displays, which they perform during courtship or to defend their territories. They often sing a series of soft, whistled notes while engaged in these aerial displays. They construct cup-shaped nests, usually in shrubs or low trees, where females lay their eggs and raise their young.
Where to Spot Nevada’s Orange Birds
Nevada’s sweeping terrains, from its sun-baked deserts to hidden wetland treasures, house an impressive array of birdlife. Here are the top locales every birdwatcher should have on their Nevada bucket list:”
- Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge: A shimmering oasis in the Mojave Desert, this refuge boasts the highest concentration of endemic species in the U.S. Its freshwater springs and marshes attract a wide variety of birds, including vibrant orange avians.
- Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge: Situated in the Lahontan Valley, this refuge is a critical stopover for migratory birds on the Pacific Flyway. Its diverse habitats, from wetlands to sand dunes, ensure a myriad of bird sightings.
- Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area: Beyond its dramatic red rock formations, this area provides habitats for numerous desert birds. During spring and fall, it becomes a hotspot for migratory species, adding to its avian diversity.
- Ruby Lake National Wildlife Refuge: Nestled at the base of the Ruby Mountains, this high-desert marsh is a haven for waterfowl and marsh birds. Its varied ecosystem also supports raptors, songbirds, and of course, some striking orange feathered visitors.
- Henderson Bird Viewing Preserve: Just outside of Las Vegas, this preserve is a delightful surprise for birders. With nine ponds and a desert landscape, it draws a fascinating mix of waterbirds and desert-adapted species.
| State‘s Orange Birds | Top Spots for Orange Birds |
|---|---|
| California’s Orange Birds | Point Reyes National Seashore, Bolsa Chica Ecological Reserve, San Joaquin Wildlife Sanctuary |
| Oregon’s Orange Birds | Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, Mount Hood National Forest, Dean Creek Elk Viewing Area |
| Idaho’s Orange Birds | Camas National Wildlife Refuge, Bear Lake National Wildlife Refuge, Coeur d’Alene River Wildlife Management Area |
| Utah’s Orange Birds | Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge, Zion National Park, Antelope Island State Park |
| Arizona’s Orange Birds | Chiricahua Mountains, Saguaro National Park, Gilbert Riparian Preserve |
FAQs on Orange Bird Species Found in Nevada
What bird has an orange chest in Nevada?
In Nevada, the Western Tanager is a bird known for its vibrant orange chest. Male Western Tanagers, in particular, display a brilliant combination of a bright red face and an orange-yellow chest, while their back, wings, and tail are black with prominent white wing bars. These colorful birds are often found in coniferous forests during the breeding season and are a treat for birdwatchers and enthusiasts in the state.
In the diverse habitats of Nevada, bird enthusiasts are often treated to sightings of various species, some of which exhibit vibrant colorations, many coming from South America or Central America. The Scott’s Oriole, for instance, is one such bird that graces the state with its presence. Adult males are adorned with bright yellow bodies contrasted by black on their head, back, and black throat. The Bullock’s Oriole, another beauty, sports brilliant orange plumage complemented by darker wings. Both these orioles, like many birds, are partial to sunflower seeds, making bird feeders stocked with these seeds a hotspot for avian activity.




